|
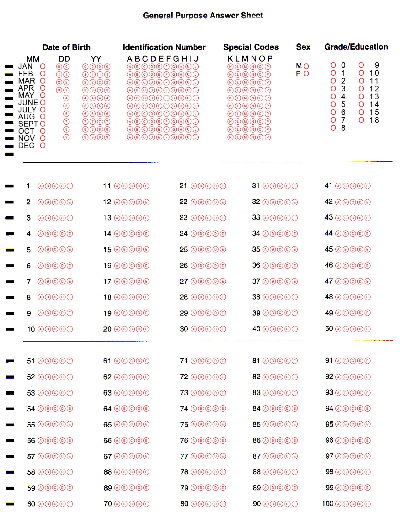
Optical Scan
An optical reader is a device found within most computer scanners that captures visual information and translates the image into digital information the computer is capable of understanding and displaying. An example of optical readers are marksense systems for elections where voters mark their choice by filling a rectangle, circle, or oval, or by completing an arrow. After the voting a tabulating device reads the votes using "dark mark logic", whereby the computer selects the darkest mark within a given set as the intended choice or vote. See also *Digital paper *Optical character recognition *Optical scan voting system *Optical mark recognition Optical mark recognition (also called optical mark reading and OMR) is the process of reading information that people mark on surveys, tests and other paper documents. OMR is used to read questionnaires, multiple choice examination papers in the ... References {{Optics-stub Optical devices ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Scan Voting System
An optical scan voting system is an electronic voting system and uses an optical scanner to read marked paper ballots and tally the results. History Marksense systems While mark sense technology dates back to the 1930s and optical mark recognition dates to the 1950s, these technologies were first explored in the context of standardized tests such as college entrance exams. The first suggestion to use mark sense technology to count ballots came in 1953, but practical optical scanners did not emerge until the 1960s. The Norden Electronic Vote Tallying System was the first to be deployed, but it required the use of special ink to mark the ballot. The Votronic, from 1965, was the first optical mark vote tabulator able to sense marks made with a graphite pencil. The oldest optical-scan voting systems scan ballots using optical mark recognition scanners. Voters mark their choice in a voting response location, usually filling a rectangle, circle or oval, or by completing an arrow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as Computer program, programs. These programs enable computers to perform a wide range of tasks. A computer system is a nominally complete computer that includes the Computer hardware, hardware, operating system (main software), and peripheral equipment needed and used for full operation. This term may also refer to a group of computers that are linked and function together, such as a computer network or computer cluster. A broad range of Programmable logic controller, industrial and Consumer electronics, consumer products use computers as control systems. Simple special-purpose devices like microwave ovens and remote controls are included, as are factory devices like industrial robots and computer-aided design, as well as general-purpose devi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Scanner
An image scanner—often abbreviated to just scanner—is a device that optically scans images, printed text, handwriting or an object and converts it to a digital image. Commonly used in offices are variations of the desktop ''flatbed scanner'' where the document is placed on a glass window for scanning. ''Hand-held scanners'', where the device is moved by hand, have evolved from text scanning "wands" to 3D scanners used for industrial design, reverse engineering, test and measurement, orthotics, gaming and other applications. Mechanically driven scanners that move the document are typically used for large-format documents, where a flatbed design would be impractical. Modern scanners typically use a charge-coupled device (CCD) or a contact image sensor (CIS) as the image sensor, whereas ''drum scanners'', developed earlier and still used for the highest possible image quality, use a photomultiplier tube (PMT) as the image sensor. A ''rotary scanner,'' used for high-speed documen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Data
Digital data, in information theory and information systems, is information represented as a string of discrete symbols each of which can take on one of only a finite number of values from some alphabet, such as letters or digits. An example is a text document, which consists of a string of alphanumeric characters . The most common form of digital data in modern information systems is ''binary data'', which is represented by a string of binary digits (bits) each of which can have one of two values, either 0 or 1. Digital data can be contrasted with ''analog data'', which is represented by a value from a continuous range of real numbers. Analog data is transmitted by an analog signal, which not only takes on continuous values, but can vary continuously with time, a continuous real-valued function of time. An example is the air pressure variation in a sound wave. The word ''digital'' comes from the same source as the words digit and ''digitus'' (the Latin word for ''finger'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark Sense
Electrographic is a term used for punched-card and page-scanning technology that allowed cards or pages marked with a pencil to be processed or converted into punched cards. The primary developer of electrographic systems was IBM, who used mark sense as a trade name for both the forms and processing system. The term has since come to be used generically for any technology allowing marks made using ordinary writing implements to be processed, encompassing both optical mark recognition and electrographic technology. The term "mark sense" is not generally used when referring to technology that distinguishes the shape of the mark; the general term optical character recognition is generally used when mark shapes are distinguished. Because the term mark-sense was originally a trade name, the Federal Government generally used the term electrographic. In the 1940s, 50s, and 60s, mark sense technology was widely used for applications like processing meter readings recordings on turnar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Election
An election is a formal group decision-making process by which a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold public office. Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative democracy has operated since the 17th century. Elections may fill offices in the legislature, sometimes in the executive and judiciary, and for regional and local government. This process is also used in many other private and business organisations, from clubs to voluntary associations and corporations. The global use of elections as a tool for selecting representatives in modern representative democracies is in contrast with the practice in the democratic archetype, ancient Athens, where the elections were considered an oligarchic institution and most political offices were filled using sortition, also known as allotment, by which officeholders were chosen by lot. Electoral reform describes the process of introducing fair electoral systems wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Paper
Digital paper, also known as interactive paper, is patterned paper used in conjunction with a digital pen to create handwritten digital documents. The printed dot pattern uniquely identifies the position coordinates on the paper. The digital pen uses this pattern to store handwriting and upload it to a computer. The paper The dot pattern is a two-dimensional barcode; the most common is the proprietary Anoto dot pattern. In the Anoto dot pattern, the paper is divided into a grid with a spacing of about 0.3 mm, a dot is printed near each intersection offset slightly in one of four directions, a camera in the pen typically records a 6 x 6 groups of dots. The full pattern is claimed to consist of 669,845,157,115,773,458,169 dots, and to encompass an area exceeding 4.6 million km² (this corresponds to 73 trillion unique sheets of letter-size paper). The complete pattern space is divided into various domains. These domains can be used to define paper types, or to indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Character Recognition
Optical character recognition or optical character reader (OCR) is the electronic or mechanical conversion of images of typed, handwritten or printed text into machine-encoded text, whether from a scanned document, a photo of a document, a scene-photo (for example the text on signs and billboards in a landscape photo) or from subtitle text superimposed on an image (for example: from a television broadcast). Widely used as a form of data entry from printed paper data records – whether passport documents, invoices, bank statements, computerized receipts, business cards, mail, printouts of static-data, or any suitable documentation – it is a common method of digitizing printed texts so that they can be electronically edited, searched, stored more compactly, displayed on-line, and used in machine processes such as cognitive computing, machine translation, (extracted) text-to-speech, key data and text mining. OCR is a field of research in pattern recognition, artificial intellig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Mark Recognition
Optical mark recognition (also called optical mark reading and OMR) is the process of reading information that people mark on surveys, tests and other paper documents. OMR is used to read questionnaires, multiple choice examination papers in the form of shaded areas. OMR background Many OMR devices have a scanner that shines a light onto a form. The device then looks at the contrasting reflectivity of the light at certain positions on the form. It will detect the black marks because they reflect less light than the blank areas on the form. Some OMR devices use forms that are printed on transoptic paper. The device can then measure the amount of light that passes through the paper. It will pick up any black marks on either side of the paper because they reduce the amount of light passing through. In contrast to the dedicated OMR device, desktop OMR software allows a user to create their own forms in a word processor or computer and print them on a laser laser printer. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |