|
Operational Amplifier Applications
This article illustrates some typical operational amplifier applications. Operational amplifiers are optimised for use with negative feedback, and this article discusses only negative-feedback applications. When positive feedback is required, a comparator is usually more appropriate. See Comparator applications for further information. Practical considerations In this article, a simplified schematic notation is used that ignores details such as device selection and power supply connections. Non-ideal properties (such as those shown in Fig. 1) are ignored. Operational amplifiers parameter requirements In order for a particular device to be used in an application, it must satisfy certain requirements. The operational amplifier must * have large open-loop signal gain (voltage gain of 200,000 is obtained in early integrated circuit exemplars), and * have input impedance large with respect to values present in the feedback network. With these requirements satisfied, one ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Negative Feedback
Negative feedback (or balancing feedback) occurs when some function (Mathematics), function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is feedback, fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused by changes in the input or by other disturbances. Whereas positive feedback tends to instability via exponential growth, oscillation or chaos theory, chaotic behavior, negative feedback generally promotes stability. Negative feedback tends to promote a settling to List of types of equilibrium, equilibrium, and reduces the effects of perturbations. Negative feedback loops in which just the right amount of correction is applied with optimum timing, can be very stable, accurate, and responsive. Negative feedback is widely used in Mechanical engineering, mechanical and electronic engineering, and it is observed in many other fields including biology, chemistry and economics. General negative feedback systems are studied in Control engin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Inverting Differentiator
Inversion therapy, or simply inversion, is the process of seeking therapeutic benefits from hanging by the legs, ankles, or feet in an inverted angle or entirely upside down. It is a form of spinal traction.Spinal Traction can be useful for effects of decreasing muscle spasm, stretching muscles/ligaments of the back, increasing the space between vertebral bodies and thus rehydrating the intervertebral discs, decreasing disc bulging and decreasing pressure on nerve roots and the spinal cord. In turn, these effects can help for the reduction of pain and increasing tissue repair. Gravity boots are ankle supports designed for inversion therapy. Some people use gravity boots to add an extra challenge to workouts, doing inverted crunches or squats. People who have heart disease, high blood pressure, eye diseases (such as glaucoma), or are pregnant are at higher risk for the dangers related to inversion therapy and should consult their doctors about it first. The first time anyone t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Buffer Amplifier
In electronics, a buffer amplifier is a unity gain amplifier that copies a signal from one circuit to another while transforming its electrical impedance to provide a more ideal source (with a ''lower'' output impedance for a voltage buffer or a ''higher'' output impedance for a current buffer). This "buffers" the signal source in the first circuit against being affected by currents from the electrical load of the second circuit and may simply be called a buffer or follower when context is clear. Voltage buffer A voltage buffer amplifier is used to transform a voltage signal with high output impedance from a first circuit into an identical voltage with low impedance for a second circuit. The interposed buffer amplifier prevents the second circuit from loading the first circuit unacceptably and interfering with its desired operation, since without the voltage buffer, the voltage of the second circuit is influenced by output impedance of the first circuit (as it is larger than th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Op-Amp Unity-Gain Buffer
An operational amplifier (often op amp or opamp) is a DC-coupled electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input, a (usually) single-ended output, and an extremely high gain. Its name comes from its original use of performing mathematical operations in analog computers. By using negative feedback, an op amp circuit's characteristics (e.g. its gain, input and output impedance, bandwidth, and functionality) can be determined by external components and have little dependence on temperature coefficients or engineering tolerance in the op amp itself. This flexibility has made the op amp a popular building block in analog circuits. Today, op amps are used widely in consumer, industrial, and scientific electronics. Many standard integrated circuit op amps cost only a few cents; however, some integrated or hybrid operational amplifiers with special performance specifications may cost over . Op amps may be packaged as components or used as elements of more complex integrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Negative-feedback Amplifier
A negative-feedback amplifier (or feedback amplifier) is an electronic amplifier that subtracts a fraction of its output from its input, so that negative feedback opposes the original signal. The applied negative feedback can improve its performance (gain stability, linearity, frequency response, step response) and reduces sensitivity to parameter variations due to manufacturing or environment. Because of these advantages, many amplifiers and control systems use negative feedback. An idealized negative-feedback amplifier as shown in the diagram is a system of three elements (see Figure 1): * an ''amplifier'' with gain ''A''OL, * a ''feedback network'' ''β'', which senses the output signal and possibly transforms it in some way (for example by attenuating or filtering it), * a summing circuit that acts as a ''subtractor'' (the circle in the figure), which combines the input and the transformed output. Overview Fundamentally, all electronic devices that provide power ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
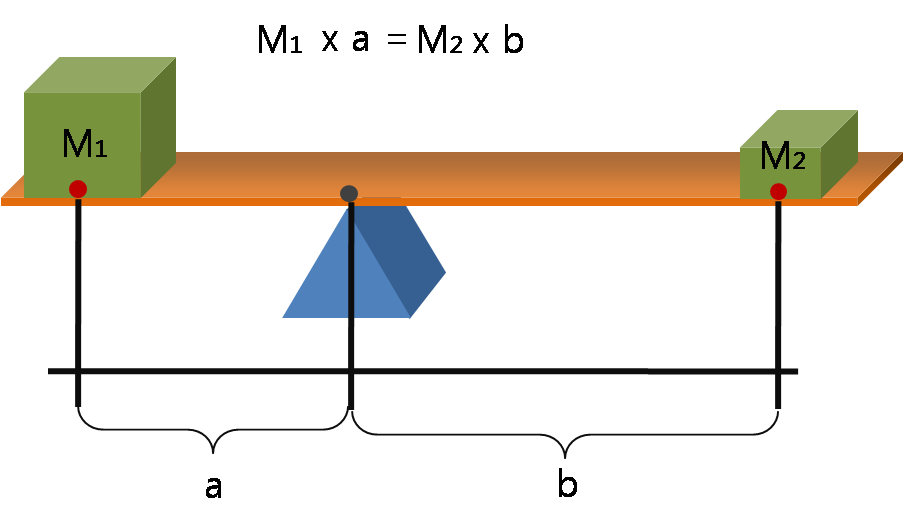
Lever
A lever is a simple machine consisting of a beam (structure), beam or rigid rod pivoted at a fixed hinge, or '':wikt:fulcrum, fulcrum''. A lever is a rigid body capable of rotating on a point on itself. On the basis of the locations of fulcrum, load, and effort, the lever is divided into Lever#Types of levers, three types. It is one of the six simple machines identified by Renaissance scientists. A lever amplifies an input force to provide a greater output force, which is said to provide leverage, which is mechanical advantage gained in the system, equal to the ratio of the output force to the input force. As such, the lever is a mechanical advantage device, trading off force against movement. Etymology The word "lever" entered English language, English around 1300 from . This sprang from the stem of the verb ''lever'', meaning "to raise". The verb, in turn, goes back to , itself from the adjective ''levis'', meaning "light" (as in "not heavy"). The word's primary origin is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Op-Amp Non-Inverting Amplifier
An operational amplifier (often op amp or opamp) is a DC-coupled electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input, a (usually) single-ended output, and an extremely high gain. Its name comes from its original use of performing mathematical operations in analog computers. By using negative feedback, an op amp circuit's characteristics (e.g. its gain, input and output impedance, bandwidth, and functionality) can be determined by external components and have little dependence on temperature coefficients or engineering tolerance in the op amp itself. This flexibility has made the op amp a popular building block in analog circuits. Today, op amps are used widely in consumer, industrial, and scientific electronics. Many standard integrated circuit op amps cost only a few cents; however, some integrated or hybrid operational amplifiers with special performance specifications may cost over . Op amps may be packaged as components or used as elements of more complex integrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Differential Amplifier
A differential amplifier is a type of electronic amplifier that amplifies the difference between two input voltages but suppresses any voltage common to the two inputs. It is an analog circuit with two inputs V_\text^- and V_\text^+ and one output V_\text, in which the output is ideally Proportionality (mathematics), proportional to the difference between the two voltages: : V_\text = A(V_\text^+ - V_\text^-), where A is the Gain (electronics), gain of the amplifier. Single amplifiers are usually implemented by either adding the appropriate feedback resistors to a standard Operational amplifier, op-amp, or with a dedicated integrated circuit containing internal feedback resistors. It is also a common sub-component of larger integrated circuits handling analog signals. Mathematics of the amplifier : V_\text = A_\text(V_\text^+ - V_\text^-), where V_\text^+ and V_\text^- are the input voltages, and A_\text is the differential gain. In practice, however, the gain is not quite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Op-Amp Inverting Amplifier
An operational amplifier (often op amp or opamp) is a DC-coupled electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input, a (usually) single-ended output, and an extremely high gain. Its name comes from its original use of performing mathematical operations in analog computers. By using negative feedback, an op amp circuit's characteristics (e.g. its gain, input and output impedance, bandwidth, and functionality) can be determined by external components and have little dependence on temperature coefficients or engineering tolerance in the op amp itself. This flexibility has made the op amp a popular building block in analog circuits. Today, op amps are used widely in consumer, industrial, and scientific electronics. Many standard integrated circuit op amps cost only a few cents; however, some integrated or hybrid operational amplifiers with special performance specifications may cost over . Op amps may be packaged as components or used as elements of more complex integrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Common-mode Rejection Ratio
In electronics, the common mode rejection ratio (CMRR) of a differential amplifier (or other device) is a metric used to quantify the ability of the device to reject common-mode signals, i.e. those that appear simultaneously and in-phase on both inputs. An ideal differential amplifier would have infinite CMRR, however this is not achievable in practice. A high CMRR is required when a differential signal must be amplified in the presence of a possibly large common-mode input, such as strong electromagnetic interference (EMI). An example is audio transmission over balanced line in sound reinforcement or recording. CMRR of an amplifier Ideally, a differential amplifier takes the voltages, V_+ and V_- on its two inputs and produces an output voltage V_\mathrm=A_\mathrm(V_+ - V_-), where A_\mathrm is the differential gain. However, the output of a real differential amplifier is better described as : :V_ = A_\mathrm (V_+ - V_-) + \tfrac A_\mathrm (V_+ + V_-) where A_\mathrm is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Subtraction
Subtraction (which is signified by the minus sign, –) is one of the four Arithmetic#Arithmetic operations, arithmetic operations along with addition, multiplication and Division (mathematics), division. Subtraction is an operation that represents removal of objects from a collection. For example, in the adjacent picture, there are peaches—meaning 5 peaches with 2 taken away, resulting in a total of 3 peaches. Therefore, the ''difference'' of 5 and 2 is 3; that is, . While primarily associated with natural numbers in arithmetic, subtraction can also represent removing or decreasing physical and abstract quantities using different kinds of objects including negative numbers, Fraction (mathematics), fractions, irrational numbers, Euclidean vector, vectors, decimals, functions, and matrices. In a sense, subtraction is the inverse of addition. That is, if and only if . In words: the difference of two numbers is the number that gives the first one when added to the second one. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Input Impedance
In electrical engineering, the input impedance of an electrical network is the measure of the opposition to current ( impedance), both static ( resistance) and dynamic ( reactance), into a load network or circuit that is ''external'' to the electrical source network. The input admittance (the reciprocal of impedance) is a measure of the load network's propensity to draw current. The source network is the portion of the network that transmits power, and the load network is the portion of the network that consumes power. For an electrical property measurement instrument like an oscilloscope, the instrument is a load circuit to an electrical circuit (source circuit) to be measured, so the input impedance is the impedance of the instrument seen by the circuit to be measured. Input impedance If the load network were replaced by a device with an output impedance equal to the input impedance of the load network (equivalent circuit), the characteristics of the source-load network w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |