|
Oleuropein
Oleuropein is a glycosylated seco-iridoid, a type of phenolic bitter compound found in green olive skin, flesh, seeds, and leaves. The term oleuropein is derived from the botanical name of the olive tree, ''Olea europaea''. Because of its bitter taste, oleuropein must be completely removed or decomposed to make olives edible. During processing of bitter and inedible green olives for consumption as table olives, oleuropein is removed from olives via a number of methods, including by immersion in lye. Chemical treatment Oleuropein is a derivative of elenolic acid linked to the orthodiphenol hydroxytyrosol by an ester bond and to a molecule of glucose by a glycosidic bond. When olives are immersed in a lye solution, the alkaline conditions lead to hydrolysis of the ester bond. The basic conditions also significantly increases the solubility of these derivatives, facilitating their release into the lye solution. The high pH accelerates the oxidation of the phenolics, leading to blac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxytyrosol
Hydroxytyrosol is an organic compound with the formula . Classified as a phenylethanoid, i.e. a relative of phenethyl alcohol, Its derivatives are found in a variety of natural sources, notably olive oils and wines. The compound is colorless solid. although commercial samples are often beige. It is a derivative, formally speaking, of catechol. It or its derivatives occurs in olives and in wines Occurrence Olives left, Oleuropein, a bitter component found in green olive skin, is an ester of hydroxytyrosol.">olive.html" ;"title="Oleuropein, a bitter component found in green olive">Oleuropein, a bitter component found in green olive skin, is an ester of hydroxytyrosol. The olives, leaves, and olive pulp contain large amounts of hydroxytyrosol derivative Oleuropein, more so than olive oil). Unprocessed, green (unripe) olives, contain between 4.3 and 116 mg of hydroxytyrosol per 100g of olives, while unprocessed, black (ripe) olives contain up to 413.3 mg per 100g. The r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxytyrosol
Hydroxytyrosol is an organic compound with the formula . Classified as a phenylethanoid, i.e. a relative of phenethyl alcohol, Its derivatives are found in a variety of natural sources, notably olive oils and wines. The compound is colorless solid. although commercial samples are often beige. It is a derivative, formally speaking, of catechol. It or its derivatives occurs in olives and in wines Occurrence Olives left, Oleuropein, a bitter component found in green olive skin, is an ester of hydroxytyrosol.">olive.html" ;"title="Oleuropein, a bitter component found in green olive">Oleuropein, a bitter component found in green olive skin, is an ester of hydroxytyrosol. The olives, leaves, and olive pulp contain large amounts of hydroxytyrosol derivative Oleuropein, more so than olive oil). Unprocessed, green (unripe) olives, contain between 4.3 and 116 mg of hydroxytyrosol per 100g of olives, while unprocessed, black (ripe) olives contain up to 413.3 mg per 100g. The r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olive Leaf
Olive leaf is the leaf of the olive tree (''Olea europaea''). Although olive oil is well known for its flavor and possible health benefits, the leaf and its extracts remain under preliminary research with unknown effects on human health. Leaf characteristics The silvery green leaves are oblong, measuring long and wide. When consumed, leaves have an astringent bitter taste. Chemical compounds Olive phenolics are much more concentrated in the leaves compared with olive fruit or olive oil: 1450 mg total phenolics/100 g fresh leaf vs. 110 mg/100 g fruit and 23 mg/100 ml extra virgin olive oil. Chemical compounds in unprocessed olive leaf are oleuropein and hydroxytyrosol, as well as polyphenols and flavonoids, including luteolin, rutin, caffeic acid, catechin and apigenin. Elenolic acid is a component of olive oil and olive leaf extract. It can be considered as a marker for maturation of olives. Oleuropein, together with other closely related compounds such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olives
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'', meaning 'European olive' in Latin, is a species of small tree or shrub in the family Oleaceae, found traditionally in the Mediterranean Basin. When in shrub form, it is known as ''Olea europaea'' 'Montra', dwarf olive, or little olive. The species is cultivated in all the countries of the Mediterranean, as well as in Australia, New Zealand, North and South America and South Africa. ''Olea europaea'' is the type species for the genus ''Olea''. The olive's fruit, also called an "olive", is of major agricultural importance in the Mediterranean region as the source of olive oil; it is one of the core ingredients in Mediterranean cuisine. The tree and its fruit give their name to the plant family, which also includes species such as lilac, jasmine, forsythia, and the true ash tree. Thousands of cultivars of the olive tree are known. Olive cultivars may be used primarily for oil, eating, or both. Olives cultivated for consumption are ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oleocanthal
Oleocanthal is a phenylethanoid, or a type of natural phenolic compound found in extra-virgin olive oil. It appears to be responsible for the burning sensation that occurs in the back of the throat when consuming such oil. Oleocanthal is a tyrosol ester and its chemical structure is related to oleuropein, also found in olive oil. Potential biological effects Anti-inflammatory Oleocanthal has been found to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties ''in vitro''. Similar to classical non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, it is a non-selective inhibitor of cyclooxygenase (COX). 50 g (more than three and a half tablespoons) of a typical extra virgin olive oil per day contains an amount of oleocanthal with similar ''in vitro'' anti-inflammatory effect as 1/10 of the adult ibuprofen dose. It is therefore suggested that long-term consumption of small quantities may be responsible in part for the low incidence of heart disease and Alzheimer's disease associated with a Mediter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPER Agonists
G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1 (GPER), also known as G protein-coupled receptor 30 (GPR30), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GPER'' gene. GPER binds to and is activated by the female sex hormone estradiol and is responsible for some of the rapid effects that estradiol has on cells. Discovery The classical estrogen receptors first characterized in 1958 are water-soluble proteins located in the interior of cells that are activated by estrogenenic hormones such as estradiol and several of its metabolites such as estrone or estriol. These proteins belong to the nuclear hormone receptor class of transcription factors that regulate gene transcription. Since it takes time for genes to be transcribed into RNA and translated into protein, the effects of estrogens binding to these classical estrogen receptors is delayed. However, estrogens are also known to have effects that are too fast to be caused by regulation of gene transcription. In 2005, it was discovered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elenolic Acid
Elenolic acid is a component of olive oil, olive infusion and olive leaf extract. It can be considered as a marker for maturation of olives. Oleuropein, a chemical compound found in olive leaf from the olive tree, together with other closely related compounds such as 10-hydroxyoleuropein, ligstroside and 10-hydroxyligstroside, are tyrosol ester In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides ar ...s of elenolic acid. References {{heterocyclic-stub Carboxylic acids Aldehydes Dihydropyrans Methyl esters Olive oil Olives Aldehydic acids Enones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olive
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'', meaning 'European olive' in Latin, is a species of small tree or shrub in the family Oleaceae, found traditionally in the Mediterranean Basin. When in shrub form, it is known as ''Olea europaea'' 'Montra', dwarf olive, or little olive. The species is cultivated in all the countries of the Mediterranean, as well as in Australia, New Zealand, North and South America and South Africa. ''Olea europaea'' is the type species for the genus ''Olea''. The olive's fruit, also called an "olive", is of major agricultural importance in the Mediterranean region as the source of olive oil; it is one of the core ingredients in Mediterranean cuisine. The tree and its fruit give their name to the plant family, which also includes species such as lilac, jasmine, forsythia, and the true ash tree. Thousands of cultivars of the olive tree are known. Olive cultivars may be used primarily for oil, eating, or both. Olives cultivated for consumption ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elenolic Acid
Elenolic acid is a component of olive oil, olive infusion and olive leaf extract. It can be considered as a marker for maturation of olives. Oleuropein, a chemical compound found in olive leaf from the olive tree, together with other closely related compounds such as 10-hydroxyoleuropein, ligstroside and 10-hydroxyligstroside, are tyrosol ester In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides ar ...s of elenolic acid. References {{heterocyclic-stub Carboxylic acids Aldehydes Dihydropyrans Methyl esters Olive oil Olives Aldehydic acids Enones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
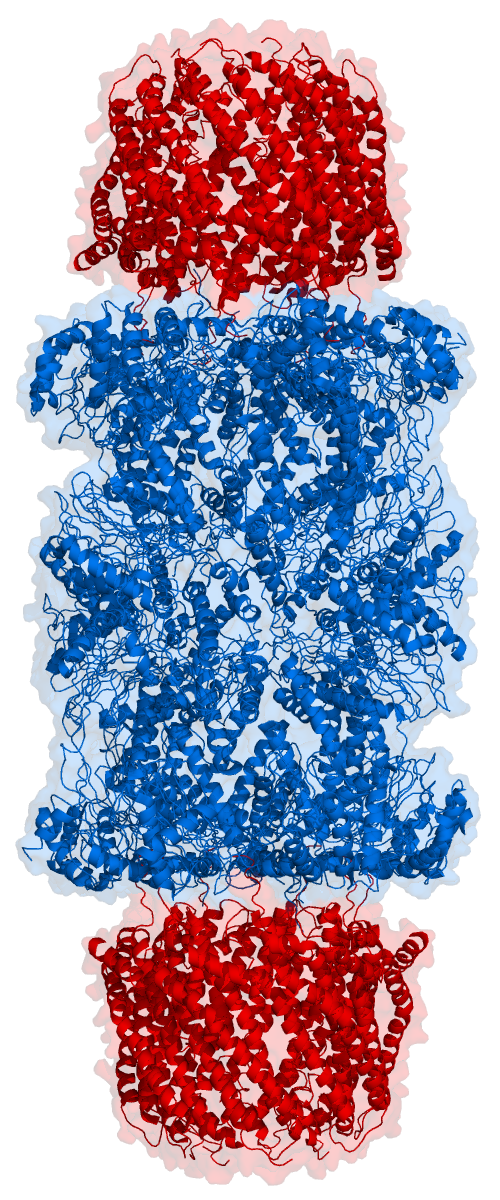
Proteasome
Proteasomes are protein complexes which degrade unneeded or damaged proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions are called proteases. Proteasomes are part of a major mechanism by which cells regulate the concentration of particular proteins and degrade misfolded proteins. Proteins are tagged for degradation with a small protein called ubiquitin. The tagging reaction is catalyzed by enzymes called ubiquitin ligases. Once a protein is tagged with a single ubiquitin molecule, this is a signal to other ligases to attach additional ubiquitin molecules. The result is a ''polyubiquitin chain'' that is bound by the proteasome, allowing it to degrade the tagged protein. The degradation process yields peptides of about seven to eight amino acids long, which can then be further degraded into shorter amino acid sequences and used in synthesizing new proteins. Proteasomes are found inside all eukaryotes and archaea, and in so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenol Antioxidants
Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns. Phenol was first extracted from coal tar, but today is produced on a large scale (about 7 billion kg/year) from petroleum-derived feedstocks. It is an important industrial commodity as a precursor to many materials and useful compounds. It is primarily used to synthesize plastics and related materials. Phenol and its chemical derivatives are essential for production of polycarbonates, epoxies, Bakelite, nylon, detergents, herbicides such as phenoxy herbicides, and numerous pharmaceutical drugs. Properties Phenol is an organic compound appreciably soluble in water, with about 84.2 g dissolving in 1000 mL (0.895 M). Homogeneous mixtures of phenol and water at phenol to wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenylethanoids
Phenylethanoids are a type of phenolic compounds characterized by a phenethyl alcohol structure. Tyrosol and hydroxytyrosol are examples of such compounds. Glycosides The red deadnettle (''Lamium purpureum'') contains phenylethanoid glycosides named lamiusides A, B, C, D and E. The aerial parts of '' Stachys officinalis'' contain phenylethanoid glycosides, ( betonyosides A, B, C, D, E and F). Chemical investigation of methanol extracts from '' Pithecoctenium crucigerum'' (Bignoniaceae) showed the presence of five phenylethanoid glycosides ( verbascoside, isoverbascoside, forsythoside B, jionoside D and leucosceptoside B), these all active against DPPH DPPH is a common abbreviation for the organic chemical compound 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl. It is a dark-colored crystalline powder composed of stable free radical molecules. DPPH has two major applications, both in laboratory research: one is .... Verbascoside and echinacoside are phenylethanoid and phenylpr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |