|
Odontoblast Processes
An odontoblast process (also called Tomes's fibers or Tomes fibers, or by a dated term Tomes's fibrils) is an extension of a cell called an odontoblast, which forms dentin in a tooth. The odontoblast process is located in dentinal tubules. It forms during dentinogenesis and results from a part of the odontoblast staying in its location as the main body of the odontoblast moves toward the center of the tooth's pulp. The odontoblast process causes the secretion of hydroxyapatite crystals and mineralization of the matrix secreted by the odontoblasts. References * See also *Tomes's process *John Tomes Sir John Tomes (21 March 1815 – 29 July 1895) was an English dental surgeon. Life The eldest son of John Tomes and Sarah, his wife, daughter of William Baylies of Welford-on-Avon, then in Gloucestershire, he was born at Weston-on-Avon in G ... Tooth development {{dentistry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites.Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell '' fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos. It is also common to describe small molecules such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
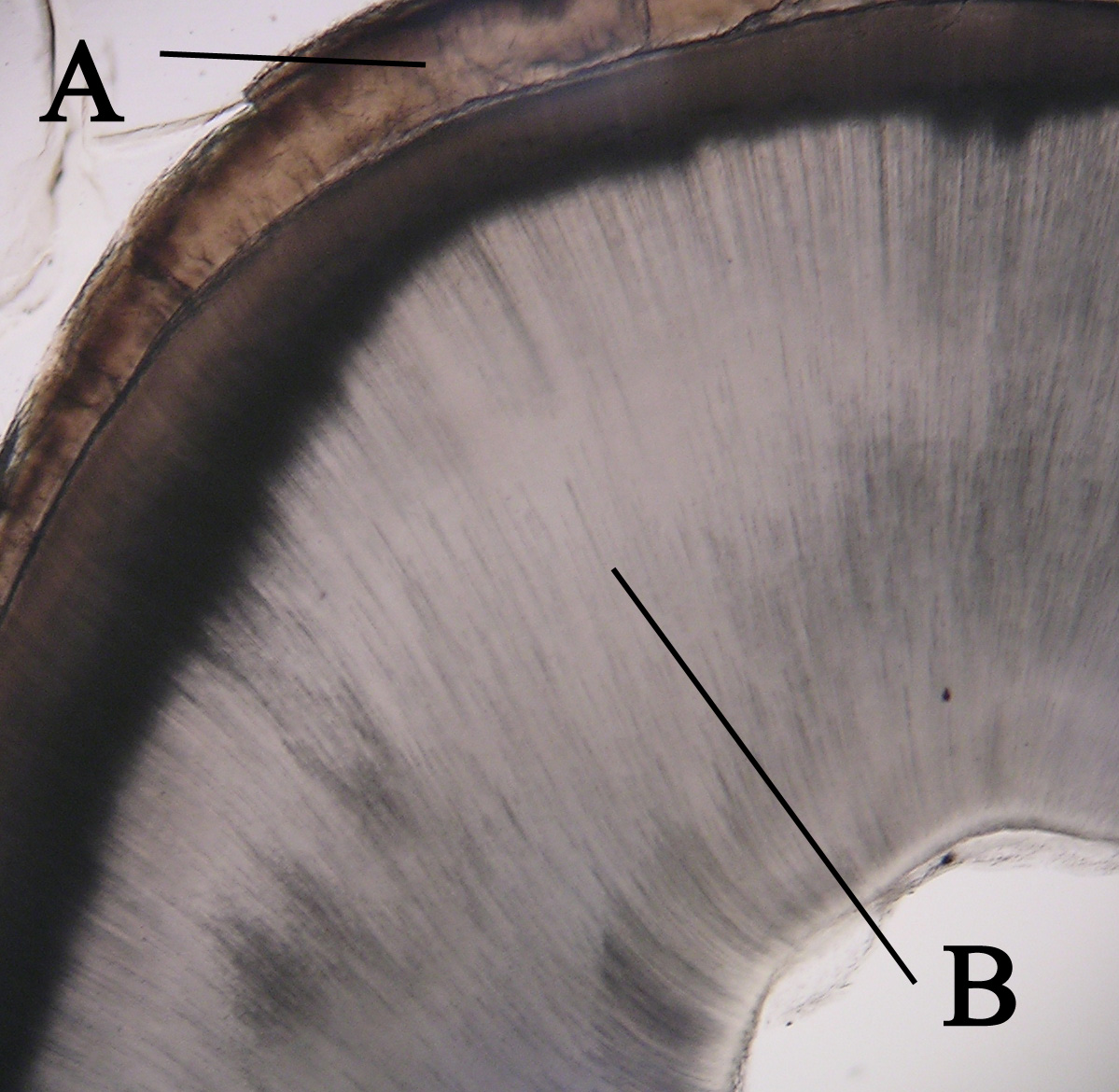
Odontoblast
In vertebrates, an odontoblast is a cell of neural crest origin that is part of the outer surface of the dental pulp, and whose biological function is dentinogenesis, which is the formation of dentin, the substance beneath the tooth enamel on the crown and the cementum on the root. Structure Odontoblasts are large columnar cells, whose cell bodies are arranged along the interface between dentin and pulp, from the crown to cervix to the root apex in a mature tooth. The cell is rich in endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi complex, especially during primary dentin formation, which allows it to have a high secretory capacity; it first forms the collagenous matrix to form predentin, then mineral levels to form the mature dentin. Odontoblasts form approximately 4 μm of predentin daily during tooth development.Ten Cate's Oral Histology, Nanci, Elsevier, 2013, page 170 During secretion after differentiation from the outer cells of the dental papilla, it is noted that it is polarized so its nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentin
Dentin () (American English) or dentine ( or ) (British English) ( la, substantia eburnea) is a calcified tissue of the body and, along with enamel, cementum, and pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by enamel on the crown and cementum on the root and surrounds the entire pulp. By volume, 45% of dentin consists of the mineral hydroxyapatite, 33% is organic material, and 22% is water. Yellow in appearance, it greatly affects the color of a tooth due to the translucency of enamel. Dentin, which is less mineralized and less brittle than enamel, is necessary for the support of enamel. Dentin rates approximately 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness. There are two main characteristics which distinguish dentin from enamel: firstly, dentin forms throughout life; secondly, dentin is sensitive and can become hypersensitive to changes in temperature due to the sensory function of odontoblasts, especially when enamel recedes and dentin channels becom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tearing food, for defensive purposes, to intimidate other animals often including their own, or to carry prey or their young. The roots of teeth are covered by gums. Teeth are not made of bone, but rather of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness that originate from the embryonic germ layer, the ectoderm. The general structure of teeth is similar across the vertebrates, although there is considerable variation in their form and position. The teeth of mammals have deep roots, and this pattern is also found in some fish, and in crocodilians. In most teleost fish, however, the teeth are attached to the outer surface of the bone, while in lizards they are attached to the inner surface of the jaw by one side. In cartilaginous fish, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentinogenesis
{{Refimprove, date=September 2014 Dentinogenesis is the formation of dentin, a substance that forms the majority of teeth. Dentinogenesis is performed by odontoblasts, which are a special type of biological cell on the outer wall of dental pulps, and it begins at the late bell stage of a tooth development. The different stages of dentin formation after differentiation of the cell result in different types of dentin: mantle dentin, primary dentin, secondary dentin, and tertiary dentin. Odontoblast differentiation Odontoblasts differentiate from cells of the dental papilla. This is an expression of signaling molecules and growth factors of the inner enamel epithelium (IEE). Formation of mantle dentin They begin secreting an organic matrix around the area directly adjacent to the IEE, closest to the area of the future cusp of a tooth. The organic matrix contains collagen fibers with large diameters (0.1-0.2 μm in diameter). The odontoblasts begin to move toward the center of the to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulp (tooth)
The pulp is the connective tissue, nerves, blood vessels, and odontoblasts that comprise the innermost layer of a tooth. The pulp's activity and signalling processes regulate its behaviour. Anatomy The pulp is the neurovascular bundle central to each tooth, permanent or primary. It is composed of a central pulp chamber, pulp horns, and radicular canals. The large mass of the pulp is contained within the pulp chamber, which is contained in and mimics the overall shape of the crown of the tooth.Illustrated Dental Embryology, Histology, and Anatomy, Bath-Balogh and Fehrenbach, Elsevier, 2011, page 164. Because of the continuous deposition of the dentine, the pulp chamber becomes smaller with the age. This is not uniform throughout the coronal pulp but progresses faster on the floor than on the roof or sidewalls. Radicular pulp canals extend down from the cervical region of the crown to the root apex. They are not always straight but vary in shape, size, and number. They are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxyapatite
Hydroxyapatite, also called hydroxylapatite (HA), is a naturally occurring mineral form of calcium apatite with the formula Ca5(PO4)3(OH), but it is usually written Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 to denote that the crystal unit cell comprises two entities. Hydroxyapatite is the hydroxyl endmember of the complex apatite group. The OH− ion can be replaced by fluoride, chloride or carbonate, producing fluorapatite or chlorapatite. It crystallizes in the hexagonal crystal system. Pure hydroxyapatite powder is white. Naturally occurring apatites can, however, also have brown, yellow, or green colorations, comparable to the discolorations of dental fluorosis. Up to 50% by volume and 70% by weight of human bone is a modified form of hydroxyapatite, known as bone mineral. Carbonated calcium-deficient hydroxyapatite is the main mineral of which dental enamel and dentin are composed. Hydroxyapatite crystals are also found in pathological calcifications such as those found in breast tumors, as w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystals
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macroscopic single crystals are usually identifiable by their geometrical shape, consisting of flat faces with specific, characteristic orientations. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography. The process of crystal formation via mechanisms of crystal growth is called crystallization or solidification. The word ''crystal'' derives from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning both "ice" and "rock crystal", from (), "icy cold, frost". Examples of large crystals include snowflakes, diamonds, and table salt. Most inorganic solids are not crystals but polycrystals, i.e. many microscopic crystals fused together into a single solid. Polycrystals include most metals, rocks, ceramics, and ice. A third category of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix (biology)
In biology, matrix (plural: matrices) is the material (or tissue) in between a eukaryotic organism's cells. The structure of connective tissues is an extracellular matrix. Fingernails and toenails grow from matrices. It is found in various connective tissues. It is generally used as a jelly-like structure instead of cytoplasm in connective tissue. Tissue matrices Extracellular matrix (ECM) The main ingredients of the extracellular matrix are glycoproteins secreted by the cells. The most abundant glycoprotein in the ECM of most animal cells is collagen, which forms strong fibers outside the cells. In fact, collagen accounts for about 40% of the total protein in the human body. The collagen fibers are embedded in a network woven from proteoglycans. A proteoglycan molecule consists of a small core protein with many carbohydrate chains covalently attached, so that it may be up to 95% carbohydrate. Large proteoglycan complexes can form when hundreds of proteoglycans become noncoval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harcourt Asia
Harcourt may refer to: People *Harcourt (surname) * Harcourt (given name) Places Canada *Harcourt Parish, New Brunswick *Harcourt, New Brunswick, an unincorporated community * Harcourt, Ontario, a village *Harcourt, Newfoundland and Labrador, a former village France *Harcourt, Eure, a ''commune'' ** Arboretum d'Harcourt, one of the oldest arboretums in the country Hong Kong *Harcourt Garden, Hong Kong, a small urban park * Harcourt House (Hong Kong), a commercial building * Harcourt Road, Hong Kong South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands * Harcourt Island **Cape Harcourt United Kingdom * Harcourt, Cornwall, a coastal settlement * Harcourt Hill, a hill and community in Oxfordshire *Harcourt Arboretum, owned and run by the University of Oxford *Kibworth Harcourt, Leicestershire *Newton Harcourt, Leicestershire *Stanton Harcourt, Oxfordshire *Wigston Harcourt, a suburb of Wigston, Leicestershire Elsewhere *Harcourt, Victoria, Australia, a town *Harcourt, Iowa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomes's Process
Tomes's processes (also called Tomes processes) are a histology, histologic landmark identified on an ameloblast, cells involved in the production of tooth enamel. During the synthesis of enamel, the ameloblast moves away from the Tooth enamel, enamel, forming a projection surrounded by the developing enamel. Tomes's processes are those projections and give the ameloblast a "picket-fence" appearance under a microscope. They are located on the secretory, basal, end of the ameloblast. Terminal bar apparatuses connect the Tomes's processes. Tonofilaments separate the developing enamel from the enamel organ. Gap junctions synchronize cell activation. The body of the cell between the processes first deposits enamel, which will become the periphery of the enamel prisms, then the Tomes's process will infill the main body of the enamel prism. More than one ameloblast contributes to a single prism. Tomes's processes are distinctly different from Tomes's fibers, which are odontoblastic pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Tomes
Sir John Tomes (21 March 1815 – 29 July 1895) was an English dental surgeon. Life The eldest son of John Tomes and Sarah, his wife, daughter of William Baylies of Welford-on-Avon, then in Gloucestershire, he was born at Weston-on-Avon in Gloucestershire on 21 March 1815. He was articled in 1831 to Thomas Furley Smith, a medical practitioner in Evesham, and in 1836 he entered the medical schools of King's College, London and the Middlesex Hospital, at that time united. He was house surgeon to the Middlesex Hospital during 1839–40. Research with Madder on histology of bone and teeth brought Tomes to the notice of Sir Thomas Watson and James Moncrieff Arnott, who advised him to concentrate on dental surgery. He was admitted a member of the College of Surgeons of England on 21 March 1839, and in 1840 he went into practice at 41 Mortimer Street (now Cavendish Place). He was also preoccupied with the question of general anæsthesia, shortly after the introduction of ether ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |