|
Obligatory Baháʼí Prayers
Obligatory Baháʼí prayers are prayers which are to be said daily by Baháʼís according to a fixed form decreed by Baháʼu'lláh. Prayers in the Baháʼí Faith are reverent words which are addressed to God, and refers to two distinct concepts: ''obligatory prayer'' and ''devotional prayer'' (general prayer). The act of prayer is one of the most important Baháʼí laws for individual discipline. Along with fasting, obligatory prayer is one of the greatest obligations of a Baháʼí, and the purpose of the obligatory prayer is to foster the development of humility and devotion. The obligation of daily obligatory prayer was prescribed by Baháʼu'lláh, the founder of the Baháʼí Faith, in his book of laws, the '' Kitáb-i-Aqdas''. It is forbidden to perform the obligatory prayers in congregation, so the daily obligatory prayers are offered individually, though it is not required that they be said in private. History In the '' Bayán'' the Báb prescribed an obligato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prayer
File:Prayers-collage.png, 300px, alt=Collage of various religionists praying – Clickable Image, Collage of various religionists praying ''(Clickable image – use cursor to identify.)'' rect 0 0 1000 1000 Shinto festivalgoer praying in front of the Tagata fertility shrine rect 1000 0 2000 1000 Balinese Hindu bride praying during a traditional wedding ceremony rect 2000 0 3000 1000 Muslim pilgrim praying at the Masjid al-Haram rect 0 1000 1000 2000 Catholic Trappist monk praying before a crucifix rect 1000 1000 2000 2000 Ethiopian priest praying in Lalibela rect 2000 1000 3000 2000 Buddhists praying in Leh rect 0 2000 1000 3000 Sikh praying in Front of the Golden Temple in Amritsar rect 1000 2000 2000 3000 Members of the Mengjia Longshan Temple Association gather for a traditional Chinese prayer service rect 2000 2000 3000 3000 Jewish people praying at the Western Wall Prayer is an invocation or act that seeks to activate a rapport with an object of worship through d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mírzá Muhammad ʻAlí
Mírzá Muhammad ʻAlí ( 16 December 1853 – 10 December 1937) was the second surviving son of Baháʼu'lláh, the founder of the Baháʼí Faith, and the first from Baháʼu'lláh's second wife Fatimih. He is well-known for an attempted schism in which he claimed leadership over his half-brother ʻAbdu'l-Bahá, and was rejected by the overwhelming majority of Baháʼís, who regard him as a Covenant-breaker. The only result of his unsuccessful leadership attempt was to alienate most of the family of Baháʼu'lláh from ʻAbdu'l-Bahá. His schism was short lived and no longer exists; by the 1960s his descendants had largely melded into Muslim society and had no collective religious life. Muhammad ʻAlí was born in Baghdad among the group of Iranians exiled from Iran for their adherence to the Bábí Faith. He would follow the family into further exiles into Istanbul, Edirne, and `Akka. As a teenager in Edirne, he began transcribing the writings of Baháʼu'lláh, and att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salat
''Salah'' (, also spelled ''salat'') is the practice of formal ibadah, worship in Islam, consisting of a series of ritual prayers performed at prescribed times daily. These prayers, which consist of units known as rak'a, ''rak'ah'', include a specific set of physical postures, recitation from the Quran, and prayers from the Sunnah, and are performed while facing the direction towards the Kaaba in Mecca (''qibla''). The number of ''rak'ah'' varies depending on the specific prayer. Variations in practice are observed among adherents of different ''Madhhab, madhahib'' (schools of Islamic jurisprudence). The term ''salah'' may denote worship in general or specifically refer to the obligatory prayers performed by Muslims five times daily, or, in some traditions, three times daily.Jafarli, Durdana. "The historical conditions for the emergence of the Quranist movement in Egypt in the 19th-20th centuries." МОВА І КУЛЬТУРА (2017): 91. The obligatory prayers play an integ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universal House Of Justice
The Universal House of Justice is the nine-member supreme ruling body of the Baháʼí Faith. It was envisioned by Baháʼu'lláh, the founder of the Baháʼí Faith, as an institution that could legislate on issues not already addressed in the Baháʼí writings, providing flexibility for the Baháʼí Faith to adapt to changing conditions. It was first elected in 1963, and subsequently every five years, by delegates consisting of the members of Baháʼí National Spiritual Assemblies throughout the world. The Universal House of Justice, as the head of the religion, has provided direction to the worldwide Baháʼí community primarily through a series of multi-year plans, as well as through annual messages delivered during the Ridván festival. The messages have focused on increasing the number of Local Spiritual Assemblies, translating Baháʼí literature, establishing Baháʼí Centres, completing Baháʼí Houses of Worship, holding international conferences, and develop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baháʼí Symbols
There are several symbols used to express identification with the Baháʼí Faith: the Enneagram (geometry), nine-pointed star, a calligraphy known as the "Greatest Name", the Ringstone Symbol, or a five-pointed star. Nine-pointed star According to the abjad numerals, Abjad system of isopsephy, the word Baháʼ has a numerical equivalence of 9 (number), 9, and thus there is frequent use of the number 9 in Baháʼí symbols. The most commonly used symbol connected to the number 9 is the ''Enneagram (geometry), nine-pointed star'', ; there is no particular design of the nine-pointed star that is used more often than others. While the star is not a part of the teachings of the Baháʼí Faith, it is commonly used as an emblem representing "9", because of the association of number 9 with perfection, unity and Baháʼ. The number 9 also comes up several times in Baháʼí history and teachings. On the significance of the number 9, Shoghi Effendi wrote: Its use on gravestone markers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunrise
Sunrise (or sunup) is the moment when the upper rim of the Sun appears on the horizon in the morning, at the start of the Sun path. The term can also refer to the entire process of the solar disk crossing the horizon. Terminology Although the Sun appears to "rise" from the horizon, it is actually the ''Earth's'' motion that causes the Sun to appear. The illusion of a moving Sun results from Earth observers being in a rotating reference frame; this apparent motion caused many cultures to have mythologies and religions built around the geocentric model, which prevailed until astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus formulated his heliocentric model in the 16th century. Architect Buckminster Fuller proposed the terms "sunsight" and "sunclipse" to better represent the heliocentric model, though the terms have not entered into common language. Astronomically, sunrise occurs for only an instant, namely the moment at which the upper limb of the Sun appears tangent to the horizon. However, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
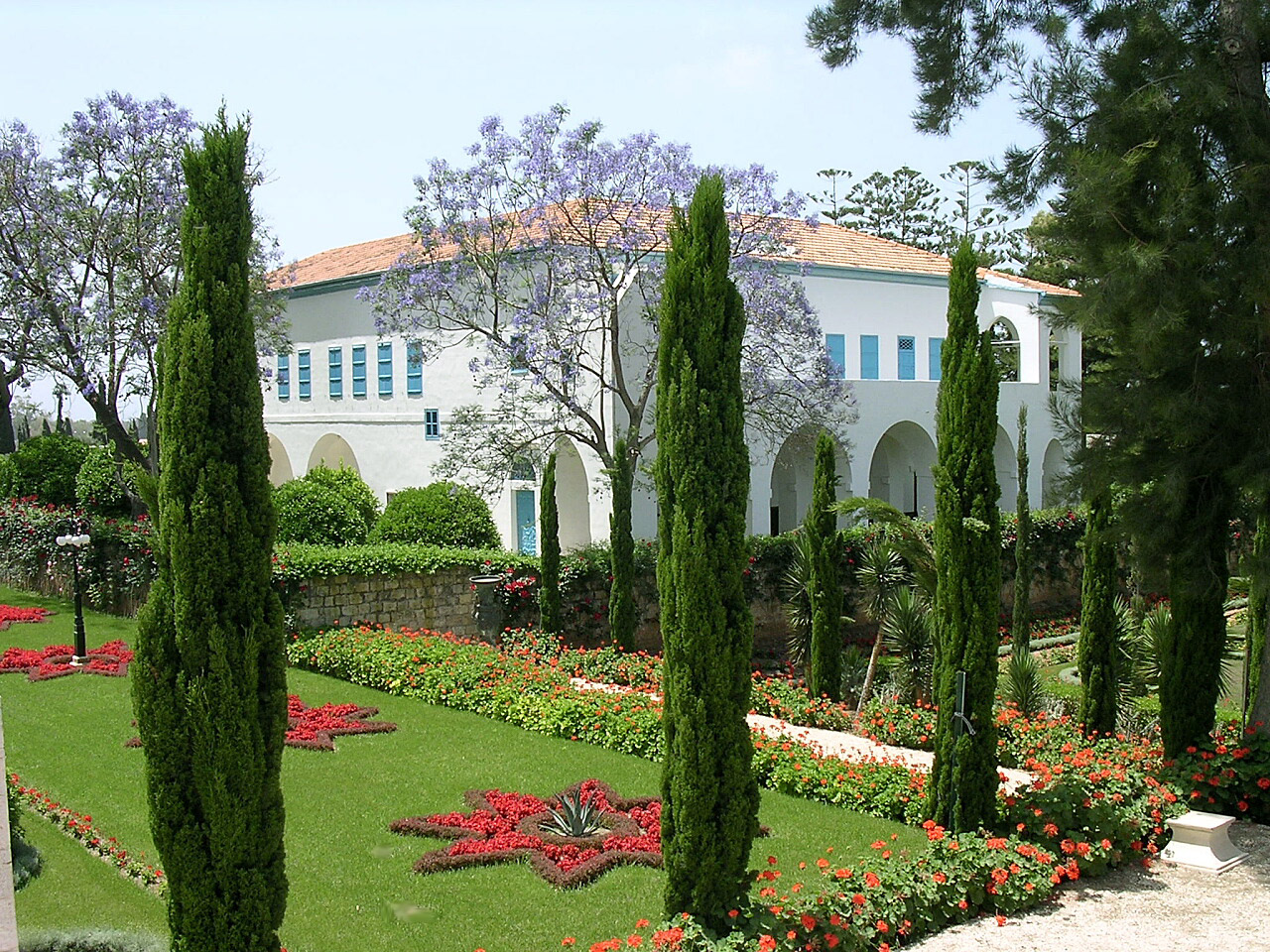
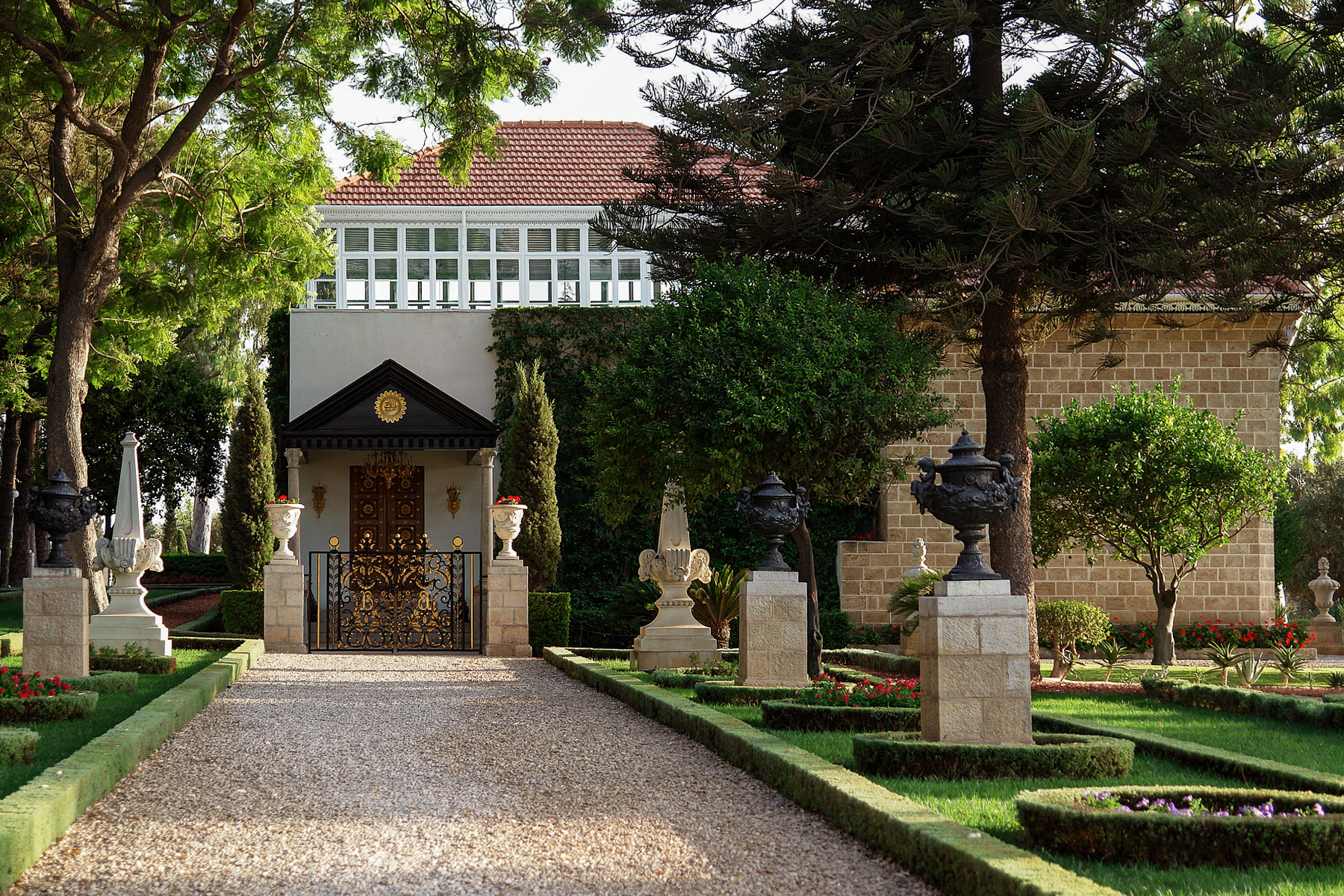
Shrine Of Baháʼu'lláh
The Mansion of Bahjí (, Qasr Bahjī, ''Mansion of Delight'') is a summer house in Acre, Israel where Baháʼu'lláh, the founder of the Baháʼí Faith, died in 1892. He was buried in an adjacent house, which became the Shrine of Baháʼu'lláh, a place of pilgrimage and the Baháʼí Qiblih. The whole area was called ''Al-Bahjá'' (''Place of Delight''). Mansion of Bahjí Baháʼu'lláh's son ʻAbdu'l-Bahá first rented, and then purchased, the mansion for his father and the Baháʼí holy family to live in, and Baháʼu'lláh moved from Mazra'ih to Bahji and resided in the building until his death. In 1890 the Cambridge orientalist Edward Granville Browne met Baháʼu'lláh in this house; after this meeting he wrote his famous Baháʼu'lláh#Final years, pen-portrait of Baháʼu'lláh. When Baháʼu'lláh died in 1892 he was interred in one of the surrounding buildings. The site has since been beautified with paradise gardens, which are termed ''Haram-i-Aqdas'' (the Most Holy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qiblih
__NOTOC__ In the Baháʼí Faith, the Qiblih (, "direction") is the location to which Baháʼís face when saying their daily obligatory prayers. The Qiblih is fixed at the Shrine of Baháʼu'lláh, near Acre, in present-day Israel; approximately at . In Bábism the Qiblih was originally identified by the Báb with " the One Whom God will make manifest", a messianic figure predicted by the Báb. Baháʼu'lláh, the Prophet-founder of the Baháʼí Faith claimed to be the figure predicted by the Báb. In the Kitáb-i-Aqdas, Baháʼu'lláh confirms the Báb's ordinance and further ordains his final resting-place as the Qiblih for his followers. ʻAbdu'l-Bahá describes that spot as the "luminous Shrine", "the place around which circumambulate the Concourse on High". The concept exists in other religions. Jews face Jerusalem, more specifically the site of the former Temple of Jerusalem. Muslims face the Kaaba in Mecca, which they also call the ''Qibla'' (another translitera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ritual Purification
Ritual purification is a ritual prescribed by a religion through which a person is considered to be freed of ''uncleanliness'', especially prior to the worship of a deity, and ritual purity is a state of ritual cleanliness. Ritual purification may also apply to objects and places. Ritual uncleanliness is not identical with ordinary physical impurity, such as dirt stains; nevertheless, body fluids are generally considered ritually unclean. Most of these rituals existed long before the germ theory of disease, and figure prominently from the earliest known Ancient Near Eastern religion, religious systems of the Ancient Near East. Some writers connect the rituals to taboos. Some have seen benefits of these practices as a point of health and preventing infections especially in areas where humans come in close contact with each other. While these practices came before the idea of the germ theory was public in areas that use daily cleaning, the destruction of infectious agents seems t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dawn
Dawn is the time that marks the beginning of twilight before sunrise. It is recognized by the diffuse sky radiation, appearance of indirect sunlight being Rayleigh scattering, scattered in Earth's atmosphere, when the centre of the Sun's disc has reached 18° below the observer's horizon. This morning twilight period will last until sunrise (when the Sun's upper limb breaks the horizon), when daylight, direct sunlight outshines the light scattering by particles, diffused light. Etymology "Dawn" derives from the Old English verb , "to become day". Types of dawn Dawn begins with the first sight of lightness in the morning, and continues until the Sun breaks the horizon. The morning twilight is divided in three phases, which are determined by the angular distance of the centre of the Sun (degree (angle), degrees below the horizon) in the morning. These are astronomical, nautical and civil twilight. Astronomical dawn Astronomical dawn begins when the center of the Sun is 18 d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunset
Sunset (or sundown) is the disappearance of the Sun at the end of the Sun path, below the horizon of the Earth (or any other astronomical object in the Solar System) due to its Earth's rotation, rotation. As viewed from everywhere on Earth, it is a phenomenon that happens approximately once every 24 hours, except in areas close to the Geographical pole, poles. The equinox Sun sets due west at the moment of both the spring and autumn equinoxes. As viewed from the Northern Hemisphere, the Sun sets to the northwest (or not at all) in the spring and summer, and to the southwest in the autumn and winter; these seasons are reversed for the Southern Hemisphere. The sunset is defined in astronomy the moment the upper limb of the Sun disappears below the horizon. Near the horizon, atmospheric refraction causes sunlight rays to be distorted to such an extent that geometrically the solar disk is already about one diameter below the horizon when a sunset is observed. Sunset is distinct from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |