|
Null Fill
Null fill in radio engineering is used in radio antenna systems which are located on mountains or tall towers, to prevent too much of the signal from overshooting the nearest part of intended coverage area. Phasing is used between antenna elements to take power away from the main lobe and electrically direct more of it at a more downward angle in the vertical plane. This requires a phased array. Changing the relative power supplied to each element also changes the radiation pattern in this manner, and often both methods are used in combination. References * "Analysis of Antenna Null-fill and Broadcast Coverage." Myron D. Fanton. ''ERI Technical Series'', vol. 6, April 200* "The Tide is Turning." Charles Rhodes* "A Study on Null-Fill Array Antenna for Service Coverage Expansion in PCS Band" Youngseok Ko See also *Null (radio) In radio electronics, a null is a direction in an antenna's radiation pattern where the antenna radiates almost no radio waves, so the far field signal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Engineering
Broadcast engineering is the field of electrical engineering, and now to some extent computer engineering and information technology, which deals with radio and television broadcasting. Audio engineering and RF engineering are also essential parts of broadcast engineering, being their own subsets of electrical engineering. Broadcast engineering involves both the studio and transmitter aspects (the entire airchain), as well as remote broadcasts. Every station has a broadcast engineer, though one may now serve an entire station group in a city. In small media markets the engineer may work on a contract basis for one or more stations as needed. Duties Modern duties of a broadcast engineer include maintaining broadcast automation systems for the studio and automatic transmission systems for the transmitter plant. There are also important duties regarding radio towers, which must be maintained with proper lighting and painting. Occasionally a station's engineer must deal with c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connected to an antenna which radiates the waves, and received by another antenna connected to a radio receiver. Radio is very widely used in modern technology, in radio communication, radar, radio navigation, remote control, remote sensing, and other applications. In radio communication, used in radio and television broadcasting, cell phones, two-way radios, wireless networking, and satellite communication, among numerous other uses, radio waves are used to carry information across space from a transmitter to a receiver, by modulating the radio signal (impressing an information signal on the radio wave by varying some aspect of the wave) in the transmitter. In radar, used to locate and track objects like aircraft, ships, spacecraf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antenna (radio)
In radio engineering, an antenna or aerial is the interface between radio waves propagating through space and electric currents moving in metal conductors, used with a transmitter or receiver. In transmission, a radio transmitter supplies an electric current to the antenna's terminals, and the antenna radiates the energy from the current as electromagnetic wave In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of waves of the electromagnetic (EM) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visib ...s (radio waves). In Receiver (radio), reception, an antenna intercepts some of the power of a radio wave in order to produce an electric current at its terminals, that is applied to a receiver to be Amplifier, amplified. Antennas are essential components of all radio equipment. An antenna is an array of conductor (material), conductors (Driven element, elements), elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited Summit (topography), summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are Monadnock, isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountain formation, Mountains are formed through Tectonic plate, tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through Slump (geology), slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce Alpine climate, colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the Montane ecosystems, ecosys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tower
A tower is a tall Nonbuilding structure, structure, taller than it is wide, often by a significant factor. Towers are distinguished from guyed mast, masts by their lack of guy-wires and are therefore, along with tall buildings, self-supporting structures. Towers are specifically distinguished from buildings in that they are built not to be habitable but to serve other functions using the height of the tower. For example, the height of a clock tower improves the visibility of the clock, and the height of a tower in a fortified building such as a castle increases the visibility of the surroundings for defensive purposes. Towers may also be built for observation tower, observation, leisure, or telecommunication purposes. A tower can stand alone or be supported by adjacent buildings, or it may be a feature on top of a larger structure or building. Etymology Old English ''torr'' is from Latin ''turris'' via Old French ''tor''. The Latin term together with Greek language, Greek τύ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signalling (telecommunications)
In telecommunication, signaling is the use of signals for controlling communications. This may constitute an information exchange concerning the establishment and control of a telecommunication circuit and the management of the network. Classification Signaling systems may be classified based on several principal characteristics. In-band and out-of-band signaling In the public switched telephone network (PSTN), in-band signaling is the exchange of call control information within the same physical channel, or within the same frequency band, that the telephone call itself is using. An example is dual-tone multi-frequency signaling (DTMF), which is used on most telephone lines to customer premises. Out-of-band signaling is telecommunication signaling on a dedicated channel separate from that used for the telephone call. Out-of-band signaling has been used since Signaling System No. 6 (SS6) was introduced in the 1970s, and also in Signalling System No. 7 (SS7) in 1980 which became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Shifting
In physics and mathematics, the phase of a periodic function F of some real variable t (such as time) is an angle-like quantity representing the fraction of the cycle covered up to t. It is denoted \phi(t) and expressed in such a scale that it varies by one full turn as the variable t goes through each period (and F(t) goes through each complete cycle). It may be measured in any angular unit such as degrees or radians, thus increasing by 360° or 2\pi as the variable t completes a full period. This convention is especially appropriate for a sinusoidal function, since its value at any argument t then can be expressed as \phi(t), the sine of the phase, multiplied by some factor (the amplitude of the sinusoid). (The cosine may be used instead of sine, depending on where one considers each period to start.) Usually, whole turns are ignored when expressing the phase; so that \phi(t) is also a periodic function, with the same period as F, that repeatedly scans the same range of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Power
Electric power is the rate at which electrical energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt, one joule per second. Standard prefixes apply to watts as with other SI units: thousands, millions and billions of watts are called kilowatts, megawatts and gigawatts respectively. A common misconception is that electric power is bought and sold, but actually electrical energy is bought and sold. For example, electricity is sold to consumers in kilowatt-hours (kilowatts multiplied by hours), because energy is power multiplied by time. Electric power is usually produced by electric generators, but can also be supplied by sources such as electric batteries. It is usually supplied to businesses and homes (as domestic mains electricity) by the electric power industry through an electrical grid. Electric power can be delivered over long distances by transmission lines and used for applications such as motion, light or heat with high efficiency. Def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main Lobe
In a radio antenna's radiation pattern, the main lobe, or main beam, is the lobe containing the higher power. This is the lobe that exhibits the greater field strength. The radiation pattern of most antennas shows a pattern of "''lobes''" at various angles, directions where the radiated signal strength reaches a maximum, separated by "''nulls''", angles at which the radiation falls to zero. In a directional antenna in which the objective is to emit the radio waves in one direction, the lobe in that direction is designed to have higher field strength than the others, so on a graph of the radiation pattern it appears biggest; this is the main lobe. The other lobes are called "''sidelobes''", and usually represent unwanted radiation in undesired directions. The sidelobe in the opposite direction from the main lobe is called the "''backlobe''". The radiation pattern referred to above is usually the horizontal radiation pattern, which is plotted as a function of azimuth about th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertical Plane
In astronomy, geography, and related sciences and contexts, a '' direction'' or ''plane'' passing by a given point is said to be vertical if it contains the local gravity direction at that point. Conversely, a direction or plane is said to be horizontal if it is perpendicular to the vertical direction. In general, something that is vertical can be drawn from up to down (or down to up), such as the y-axis in the Cartesian coordinate system. Historical definition The word ''horizontal'' is derived from the Latin , which derives from the Greek , meaning 'separating' or 'marking a boundary'. The word ''vertical'' is derived from the late Latin ', which is from the same root as ''vertex'', meaning 'highest point' or more literally the 'turning point' such as in a whirlpool. Girard Desargues defined the vertical to be perpendicular to the horizon in his 1636 book ''Perspective''. Geophysical definition The plumb line and spirit level In physics, engineering and construction, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
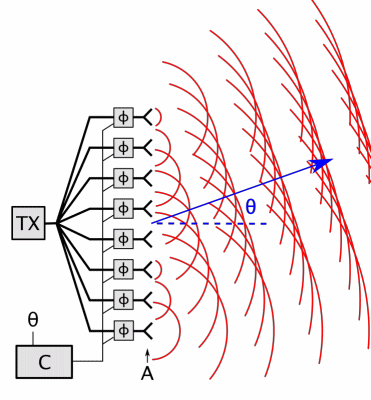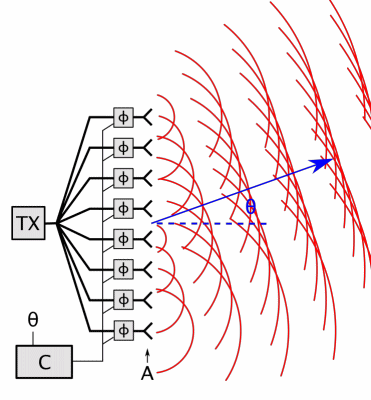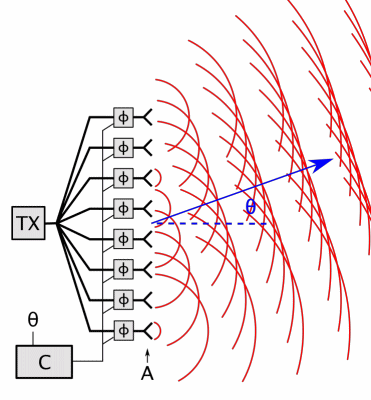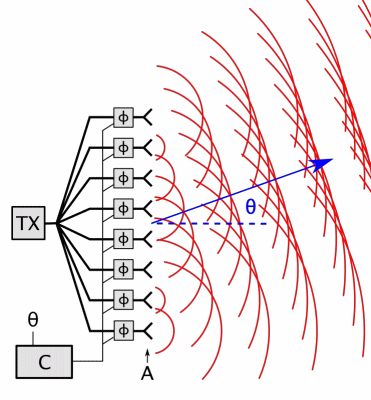
Phased Array
In antenna theory, a phased array usually means an electronically scanned array, a computer-controlled array of antennas which creates a beam of radio waves that can be electronically steered to point in different directions without moving the antennas. In a simple array antenna, the radio frequency current from the transmitter is fed to multiple individual antenna elements with the proper phase relationship so that the radio waves from the separate elements combine ( superpose) to form beams, to increase power radiated in desired directions and suppress radiation in undesired directions. In a phased array, the power from the transmitter is fed to the radiating elements through devices called ''phase shifters'', controlled by a computer system, which can alter the phase or signal delay electronically, thus steering the beam of radio waves to a different direction. Since the size of an antenna array must extend many wavelengths to achieve the high gain needed for narrow bea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation Pattern
In the field of antenna design the term radiation pattern (or antenna pattern or far-field pattern) refers to the ''directional'' (angular) dependence of the strength of the radio waves from the antenna or other source.Constantine A. Balanis: “Antenna Theory, Analysis and Design”, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2nd ed. 1982 David K Cheng: “Field and Wave Electromagnetics”, Addison-Wesley Publishing Company Inc., Edition 2, 1998. Edward C. Jordan & Keith G. Balmain; “Electromagnetic Waves and Radiating Systems” (2nd ed. 1968) Prentice-Hall. Particularly in the fields of fiber optics, lasers, and integrated optics, the term radiation pattern may also be used as a synonym for the near-field pattern or Fresnel pattern.Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, “The IEEE standard dictionary of electrical and electronics terms”; 6th ed. New York, N.Y., Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, c1997. IEEE Std 100-1996. d. Standards Coordinating Committee 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |