|
Notional Principal Contract
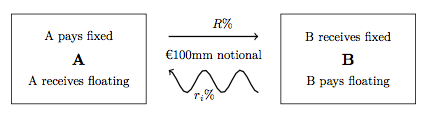
The term notional principal contract (NPC) is a term of art used by U.S. federal income tax professionals for contracts based on an underlying notional amount (other financial services professionals refer to such NPCs under the more general heading " swaps," although not all swaps are NPCs). The reason the underlying amount is "notional" is that neither party to the NPC is required to actually hold the property comprising the underlying amount. NPCs involve two parties who agree contractually to pay each other amounts at specified times, based on the underlying notional amount. The simplest example of an NPC is a so-called interest rate swap, in which one party (Party A) pays the other party (Party B) an amount each quarter determined by multiplying a floating, market-determined interest rate (e.g., LIBOR) by the notional amount; and Party B pays Party A on the same date an amount determined by multiplying a fixed interest rate by the notional amount. Definition Provided in Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Federal Income Tax
Income taxes in the United States are imposed by the federal government, and most states. The income taxes are determined by applying a tax rate, which may increase as income increases, to taxable income, which is the total income less allowable deductions. Income is broadly defined. Individuals and corporations are directly taxable, and estates and trusts may be taxable on undistributed income. Partnerships are not taxed (with some exceptions in the case of Federal income taxation), but their partners are taxed on their shares of partnership income. Residents and citizens are taxed on worldwide income, while nonresidents are taxed only on income within the jurisdiction. Several types of credits reduce tax, and some types of credits may exceed tax before credits. An alternative tax applies at the federal and some state levels. In the United States, the term "payroll tax" usually refers to FICA taxes that are paid to fund Social Security and Medicare, while "income tax" ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contract
A contract is a legally enforceable agreement between two or more parties that creates, defines, and governs mutual rights and obligations between them. A contract typically involves the transfer of goods, services, money, or a promise to transfer any of those at a future date. In the event of a breach of contract, the injured party may seek judicial remedies such as damages or rescission. Contract law, the field of the law of obligations concerned with contracts, is based on the principle that agreements must be honoured. Contract law, like other areas of private law, varies between jurisdictions. The various systems of contract law can broadly be split between common law jurisdictions, civil law jurisdictions, and mixed law jurisdictions which combine elements of both common and civil law. Common law jurisdictions typically require contracts to include consideration in order to be valid, whereas civil and most mixed law jurisdictions solely require a meeting of the mind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Notional Amount
The notional amount (or notional principal amount or notional value) on a financial instrument is the nominal or face amount that is used to calculate payments made on that instrument. This amount generally does not change and is thus referred to as ''notional.'' Explanation Contrast a bond with an interest rate swap: * In a bond, the buyer pays the principal amount at issue (start), then receives coupons (computed off this principal) over the life of the bond, then receives the principal back at maturity (end). * In a swap, no principal changes hands at inception (start) or expiry (end), and in the meantime, interest payments are computed based on a notional amount, which acts ''as if'' it were the principal amount of a bond, hence the term ''notional principal amount'', abbreviated to ''notional''. In simple terms, the notional principal amount is essentially how much of an asset or bonds a person owns. For example, if a premium bond were bought for £1, then the notional princip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swap (finance)
In finance, a swap is an agreement between two counterparties to exchange financial instruments, cashflows, or payments for a certain time. The instruments can be almost anything but most swaps involve cash based on a notional principal amount.Financial Industry Business Ontology Version 2 Annex D: Derivatives, EDM Council, Inc., Object Management Group, Inc., 2019 The general swap can also be seen as a series of forward contracts through which two parties exchange financial instruments, resulting in a common series of exchange dates and two streams of instruments, the ''legs'' of the swap. The legs can be almost anything but usually one leg involves cash flows based on a |
Libor
The London Inter-Bank Offered Rate is an interest-rate average calculated from estimates submitted by the leading banks in London. Each bank estimates what it would be charged were it to borrow from other banks. The resulting average rate is usually abbreviated to Libor () or LIBOR, or more officially to ICE LIBOR (for Intercontinental Exchange LIBOR). It was formerly known as BBA Libor (for British Bankers' Association Libor or the trademark bba libor) before the responsibility for the administration was transferred to Intercontinental Exchange. It is the primary benchmark, along with the Euribor, for short-term interest rates around the world. Libor was phased out at the end of 2021, and market participants are being encouraged to transition to risk-free interest rates. As of late 2022, parts of it have been discontinued, and the rest is scheduled to end within 2023; the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR) is its replacement. Libor rates are calculated for five currenci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treasury Regulation
Treasury Regulations are the tax regulations issued by the United States Internal Revenue Service (IRS), a bureau of the United States Department of the Treasury. These regulations are the Treasury Department's official interpretations of the Internal Revenue Code and are one source of U.S. federal income tax law. Authority and citations Section 7805 of the Internal Revenue Code gives the United States Secretary of the Treasury the power to create the necessary rules and regulations for enforcing the Internal Revenue Code. These regulations, including but not limited to the "Income Tax Regulations," are located in Title 26 of the Code of Federal Regulations, or "C.F.R." Each regulation is generally organized to correspond to the Internal Revenue Code section interpreted by that regulation. Citations to the Treasury Regulations may appear in different formats. For instance, the definition of gross income in the regulations may be cited to as "26 C.F.R. 1.61-1" or as "Treas. Reg. 1.6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Instrument
Financial instruments are monetary contracts between parties. They can be created, traded, modified and settled. They can be cash (currency), evidence of an ownership interest in an entity or a contractual right to receive or deliver in the form of currency (forex); debt ( bonds, loans); equity ( shares); or derivatives ( options, futures, forwards). International Accounting Standards IAS 32 and 39 define a financial instrument as "any contract that gives rise to a financial asset of one entity and a financial liability or equity instrument of another entity". Financial instruments may be categorized by "asset class" depending on whether they are equity-based (reflecting ownership of the issuing entity) or debt-based (reflecting a loan the investor has made to the issuing entity). If the instrument is debt it can be further categorized into short-term (less than one year) or long-term. Foreign exchange instruments and transactions are neither debt- nor equity-based and bel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Revenue Code
The Internal Revenue Code (IRC), formally the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, is the domestic portion of federal statutory tax law in the United States, published in various volumes of the United States Statutes at Large, and separately as Title 26 of the United States Code (USC). It is organized topically, into subtitles and sections, covering income tax in the United States, payroll taxes, estate taxes, gift taxes, and excise taxes; as well as procedure and administration. The Code's implementing federal agency is the Internal Revenue Service. Origins of tax codes in the United States Prior to 1874, U.S. statutes (whether in tax law or other subjects) were not codified. That is, the acts of Congress were not separately organized and published in separate volumes based on the subject matter (such as taxation, bankruptcy, etc.). Codifications of statutes, including tax statutes, undertaken in 1873 resulted in the Revised Statutes of the United States, approved June 22, 1874, eff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interest Rate Swaps
In finance, an interest rate swap (IRS) is an interest rate derivative (IRD). It involves exchange of interest rates between two parties. In particular it is a "linear" IRD and one of the most liquid, benchmark products. It has associations with forward rate agreements (FRAs), and with zero coupon swaps (ZCSs). In its December 2014 statistics release, the Bank for International Settlements reported that interest rate swaps were the largest component of the global OTC derivative market, representing 60%, with the notional amount outstanding in OTC interest rate swaps of $381 trillion, and the gross market value of $14 trillion. Interest rate swaps can be traded as an index through the FTSE MTIRS Index. Interest rate swaps General description An interest rate swap's (IRS's) effective description is a derivative contract, agreed between two counterparties, which specifies the nature of an exchange of payments benchmarked against an interest rate index. The most common IRS is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Currency Swap
In finance, a currency swap (more typically termed a cross-currency swap, XCS) is an interest rate derivative (IRD). In particular it is a linear IRD, and one of the most liquid benchmark products spanning multiple currencies simultaneously. It has pricing associations with interest rate swaps (IRSs), foreign exchange (FX) rates, and FX swaps (FXSs). General description A cross-currency swap's (XCS's) effective description is a derivative contract, agreed between two counterparties, which specifies the nature of an exchange of payments benchmarked against two interest rate indexes denominated in two different currencies. It also specifies an initial exchange of notional currency in each different currency and the terms of that repayment of notional currency over the life of the swap. The most common XCS, and that traded in interbank markets, is a mark-to-market (MTM) XCS, whereby notional exchanges are regularly made throughout the life of the swap according to FX rate f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basis Swap
A basis swap is an interest rate swap which involves the exchange of two floating rate financial instruments. A basis swap functions as a floating-floating interest rate swap under which the floating rate payments are referenced to different bases. The existence of a basis arises from demand and supply imbalances and where, for example, a basis is due for a borrower seeking dollars, this is indicative of a synthetic dollar interest rate in the FX market pricing higher than the direct dollar interest rate. The existence of the basis is a violation of the covered interest rate parity (CIP) condition. Usage of basis swaps for hedging Basis risk occurs for positions that have at least one paying and one receiving stream of cash flows that are driven by different factors and the correlation between those factors is less than one. Entering into a Basis Swap may offset the effect of gains or losses resulting from changes in the basis, thus reducing basis risk. # against exposure to curre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interest Rate Cap
An interest rate cap is a type of interest rate derivative in which the buyer receives payments at the end of each period in which the interest rate exceeds the agreed strike price. An example of a cap would be an agreement to receive a payment for each month the LIBOR rate exceeds 2.5%. Similarly an interest rate floor is a derivative contract in which the buyer receives payments at the end of each period in which the interest rate is below the agreed strike price. Caps and floors can be used to hedge against interest rate fluctuations. For example, a borrower who is paying the LIBOR rate on a loan can protect himself against a rise in rates by buying a cap at 2.5%. If the interest rate exceeds 2.5% in a given period the payment received from the derivative can be used to help make the interest payment for that period, thus the interest payments are effectively "capped" at 2.5% from the borrowers' point of view. Interest rate cap An interest rate cap is a derivative in which the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |