|
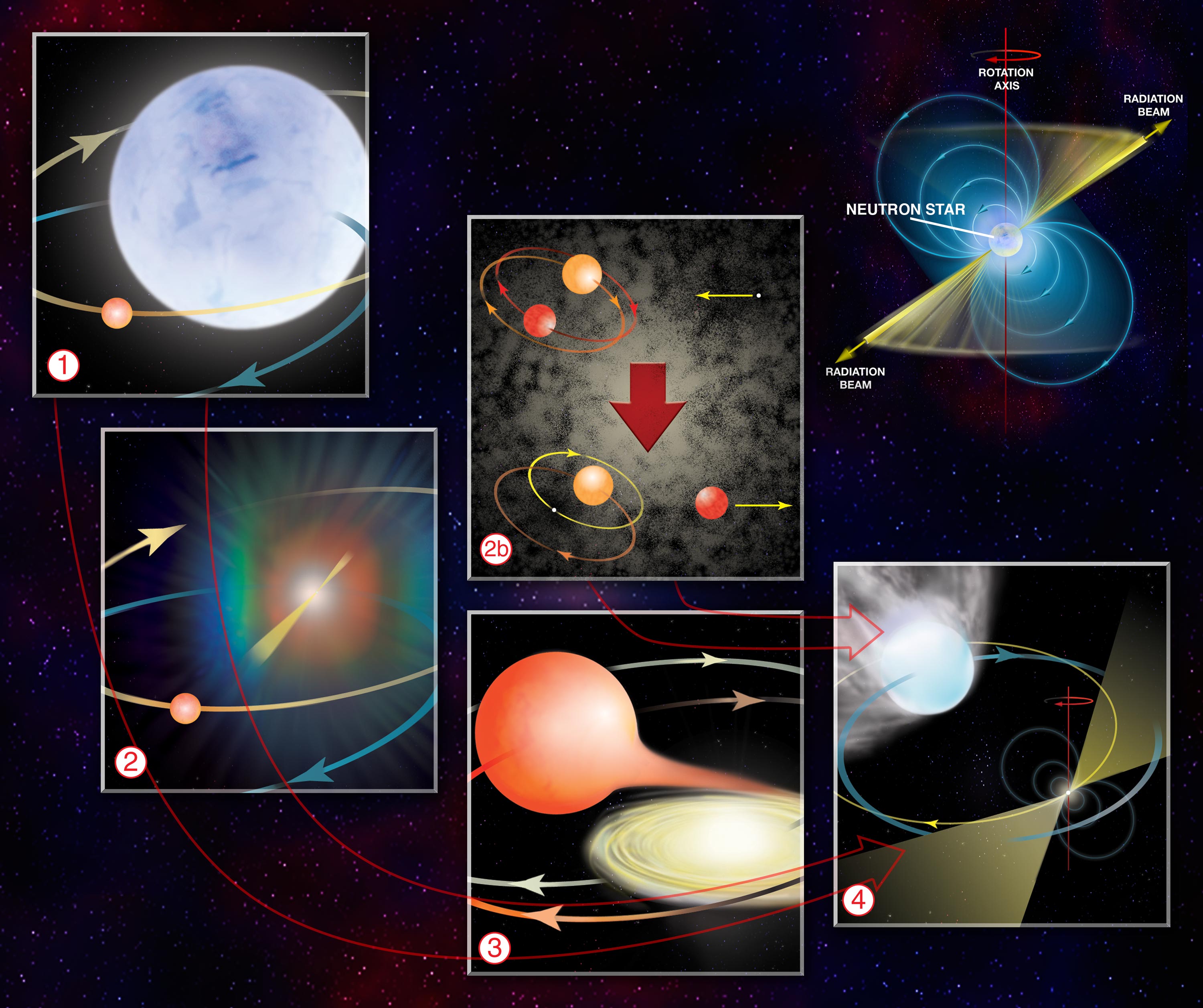
Neutron Star Spin-up
Neutron star spin up is the name given to the increase in rotational speed over time first noted in Cen X-3 and Her X-1 but now observed in other X-ray pulsars. In the case of Cen X-3, the pulse period is decreasing over a timescale of 3400 years (defined as P/\dot, where P is the rotation period and \dot is the rate of change in the rotation period). Ever since the detection of the first millisecond pulsar (MSP), it has been theorized that MSPs are neutron stars that have been spun up by accretion in a close binary system. The change in rotational period of the neutron star comes from the transition region between the magnetosphere and the plasma flow from the companion star. In this context the magnetosphere is defined as the region of space surrounding the neutron star, in which the magnetic field determines the motion of the plasma. Inside the magnetic field, the plasma will eventually co-rotate with the neutron star while in the transition region, angular momentum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cen X-3
Centaurus X-3 (4U 1118-60) is an X-ray pulsar with a period of 4.84 seconds. It was the first X-ray pulsar to be discovered, and the third X-ray source to be discovered in the constellation Centaurus. The system consists of a neutron star orbiting a massive, O-type supergiant star dubbed Krzeminski's star after its discoverer, Wojciech Krzemiński. Matter is being accreted from the star onto the neutron star, resulting in X-ray emission. History Centaurus X-3 was first observed during experiments of cosmic X-ray sources made on May 18, 1967. These initial X-ray spectrum and location measurements were performed using a sounding rocket. In 1971, further observations were performed with the Uhuru satellite, in the form of twenty-seven 100-second duration sightings. These sightings were found to pulsate with an average period of 4.84 seconds, with a variation in the period of 0.02 seconds. Later, it became clear that the period variations followed a 2.09 day sinusoidal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Her X-1
Hercules X-1 (Her X-1), also known as 4U1656+35, is a moderately strong X-ray binary source first studied by the Uhuru satellite. It is composed of a neutron star accreting matter from a normal star (HZ Her) probably due to Roche lobe overflow. Intermediate-mass X-ray binary (IMXB) Her X-1 is the prototype for the massive X-ray binaries although it falls on the borderline, , between high- and low-mass X-ray binaries. An intermediate-mass X-ray binary (IMXB) is a binary star system where one of the components is a neutron star or a black hole. The other component is an intermediate mass star. Intensity The source exhibits complex time variability, pulsing with a period of 1.24 s due to the rotation of the neutron star, eclipsing every 1.70 days with the period of the binary orbit, and also varying with a 35-day period believed associated with the precession of the accretion disk. From observations, a twisted accretion disk, in retrograde precession, modulates the X-rays illum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Pulsar
X-ray pulsars or accretion-powered pulsars are a class of astronomical objects that are X-ray sources displaying strict periodic variations in X-ray intensity. The X-ray periods range from as little as a fraction of a second to as much as several minutes. Characteristics An X-ray pulsar consists of a magnetized neutron star in orbit with a normal stellar companion and is a type of binary star system. The magnetic-field strength at the surface of the neutron star is typically about 108 Tesla, over a trillion times stronger than the strength of the magnetic field measured at the surface of the Earth (60 μT). Gas is accreted from the stellar companion and is channeled by the neutron star's magnetic field on to the magnetic poles producing two or more localized X-ray hot spots, similar to the two auroral zones on Earth, but far hotter. At these hotspots the infalling gas can reach half the speed of light before it impacts the neutron star surface. So much gravitational potentia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millisecond Pulsar
A millisecond pulsar (MSP) is a pulsar with a rotational period less than about 10 milliseconds. Millisecond pulsars have been detected in radio, X-ray, and gamma ray portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. The leading theory for the origin of millisecond pulsars is that they are old, rapidly rotating neutron stars that have been spun up or "recycled" through accretion of matter from a companion star in a close binary system. For this reason, millisecond pulsars are sometimes called recycled pulsars. Millisecond pulsars are thought to be related to low-mass X-ray binary systems. It is thought that the X-rays in these systems are emitted by the accretion disk of a neutron star produced by the outer layers of a companion star that has overflowed its Roche lobe. The transfer of angular momentum from this accretion event can theoretically increase the rotation rate of the pulsar to hundreds of times per second, as is observed in millisecond pulsars. There has been recent evidence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron Star
A neutron star is the collapsed core of a massive supergiant star, which had a total mass of between 10 and 25 solar masses, possibly more if the star was especially metal-rich. Except for black holes and some hypothetical objects (e.g. white holes, quark stars, and strange stars), neutron stars are the smallest and densest currently known class of stellar objects. Neutron stars have a radius on the order of and a mass of about 1.4 solar masses. They result from the supernova explosion of a massive star, combined with gravitational collapse, that compresses the core past white dwarf star density to that of atomic nuclei. Once formed, they no longer actively generate heat, and cool over time; however, they may still evolve further through collision or accretion. Most of the basic models for these objects imply that neutron stars are composed almost entirely of neutrons (subatomic particles with no net electrical charge and with slightly larger mass than protons); the electro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accretion (astrophysics)
In astrophysics, accretion is the accumulation of particles into a massive object by gravitationally attracting more matter, typically gaseous matter, in an accretion disk. Most astronomical objects, such as galaxies, stars, and planets, are formed by accretion processes. Overview The accretion model that Earth and the other terrestrial planets formed from meteoric material was proposed in 1944 by Otto Schmidt, followed by the ''protoplanet theory'' of William McCrea (1960) and finally the ''capture theory'' of Michael Woolfson. For details of Kant's position, see In 1978, Andrew Prentice resurrected the initial Laplacian ideas about planet formation and developed the ''modern Laplacian theory''. None of these models proved completely successful, and many of the proposed theories were descriptive. The 1944 accretion model by Otto Schmidt was further developed in a quantitative way in 1969 by Viktor Safronov. He calculated, in detail, the different stages of terrestrial plane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Star
A binary star is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separate stars, in which case they are called ''visual binaries''. Many visual binaries have long orbital periods of several centuries or millennia and therefore have orbits which are uncertain or poorly known. They may also be detected by indirect techniques, such as spectroscopy (''spectroscopic binaries'') or astrometry (''astrometric binaries''). If a binary star happens to orbit in a plane along our line of sight, its components will eclipse and transit each other; these pairs are called ''eclipsing binaries'', or, together with other binaries that change brightness as they orbit, ''photometric binaries''. If components in binary star systems are close enough they can gravitationally distort their mutual outer stellar atmospheres. In some cases, thes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma (physics)
Plasma () 1, where \nu_ is the electron gyrofrequency and \nu_ is the electron collision rate. It is often the case that the electrons are magnetized while the ions are not. Magnetized plasmas are ''anisotropic'', meaning that their properties in the direction parallel to the magnetic field are different from those perpendicular to it. While electric fields in plasmas are usually small due to the plasma high conductivity, the electric field associated with a plasma moving with velocity \mathbf in the magnetic field \mathbf is given by the usual Lorentz force, Lorentz formula \mathbf = -\mathbf\times\mathbf, and is not affected by Debye shielding. Mathematical descriptions To completely describe the state of a plasma, all of the particle locations and velocities that describe the electromagnetic field in the plasma region would need to be written down. However, it is generally not practical or necessary to keep track of all the particles in a plasma. Therefore, plasma physicist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Companion Star
A binary star is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separate stars, in which case they are called ''visual binaries''. Many visual binaries have long orbital periods of several centuries or millennia and therefore have orbits which are uncertain or poorly known. They may also be detected by indirect techniques, such as spectroscopy (''spectroscopic binaries'') or astrometry (''astrometric binaries''). If a binary star happens to orbit in a plane along our line of sight, its components will eclipse and transit each other; these pairs are called ''eclipsing binaries'', or, together with other binaries that change brightness as they orbit, ''photometric binaries''. If components in binary star systems are close enough they can gravitationally distort their mutual outer stellar atmospheres. In some cases, thes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field. A permanent magnet's magnetic field pulls on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets. In addition, a nonuniform magnetic field exerts minuscule forces on "nonmagnetic" materials by three other magnetic effects: paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, although these forces are usually so small they can only be detected by laboratory equipment. Magnetic fields surround magnetized materials, and are created by electric currents such as those used in electromagnets, and by electric fields varying in time. Since both strength and direction of a magnetic field may vary with location, it is described mathematically by a function assigning a vector to each point of space, cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Momentum
In physics, angular momentum (rarely, moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a conserved quantity—the total angular momentum of a closed system remains constant. Angular momentum has both a direction and a magnitude, and both are conserved. Bicycles and motorcycles, frisbees, rifled bullets, and gyroscopes owe their useful properties to conservation of angular momentum. Conservation of angular momentum is also why hurricanes form spirals and neutron stars have high rotational rates. In general, conservation limits the possible motion of a system, but it does not uniquely determine it. The three-dimensional angular momentum for a point particle is classically represented as a pseudovector , the cross product of the particle's position vector (relative to some origin) and its momentum vector; the latter is in Newtonian mechanics. Unlike linear momentum, angular m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accretion Disk
An accretion disk is a structure (often a circumstellar disk) formed by diffuse material in orbital motion around a massive central body. The central body is typically a star. Friction, uneven irradiance, magnetohydrodynamic effects, and other forces induce instabilities causing orbiting material in the disk to spiral inward towards the central body. Gravitational and frictional forces compress and raise the temperature of the material, causing the emission of electromagnetic radiation. The frequency range of that radiation depends on the central object's mass. Accretion disks of young stars and protostars radiate in the infrared; those around neutron stars and black holes in the X-ray part of the spectrum. The study of oscillation modes in accretion disks is referred to as diskoseismology. Manifestations Accretion disks are a ubiquitous phenomenon in astrophysics; active galactic nuclei, protoplanetary disks, and gamma ray bursts all involve accretion disks. These disks very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |