|
Nutrient Canal
All bones possess larger or smaller foramina (openings) for the entrance of blood-vessels; these are known as the nutrient foramina, and are particularly large in the shafts of the larger long bones, where they lead into a nutrient canal, which extends into the medullary cavity. The nutrient canal(foramen)is directed away from the growing end of bone. The growing ends of bones in upper limb are upper end of humerus and lower ends of radius and ulna. In lower limb, the lower end of femur and upper end of tibia are the growing ends. The nutrient arteries along with veins pass through this canal. A nutrient canal is found in long bones, in the mandible, and in dental alveoli Dental alveoli (singular ''alveolus'') are sockets in the jaws in which the roots of teeth are held in the alveolar process with the periodontal ligament. The lay term for dental alveoli is tooth sockets. A joint that connects the roots of the t .... In long bones the nutrient canal is found in the shaft. Ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foramen
In anatomy and osteology, a foramen (; in Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary '. plural foramina, or foramens ) is an open hole that is present in extant or extinct s. Foramina inside the of typically allow , |
Blood-vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from the tissues. Blood vessels are needed to sustain life, because all of the body's tissues rely on their functionality. There are five types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the arterioles; the capillaries, where the exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and the tissues occurs; the venules; and the veins, which carry blood from the capillaries back towards the heart. The word ''vascular'', meaning relating to the blood vessels, is derived from the Latin ''vas'', meaning vessel. Some structures – such as cartilage, the epithelium, and the lens and cornea of the eye – do not contain blood vessels and are labeled ''avascular''. Etymology * artery: late Middle English; from Latin ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphysis
The diaphysis is the main or midsection (shaft) of a long bone. It is made up of cortical bone and usually contains bone marrow and adipose tissue (fat). It is a middle tubular part composed of compact bone which surrounds a central marrow cavity which contains red or yellow marrow. In diaphysis, primary ossification occurs. Ewing sarcoma tends to occur at the diaphysis.Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Board Review, Cuccurullo Additional images Illu long bone.jpg File:EpiMetaDiaphyse.jpg, Long bone See also *Epiphysis *Metaphysis The metaphysis is the neck portion of a long bone between the epiphysis and the diaphysis. It contains the growth plate, the part of the bone that grows during childhood, and as it grows it ossifies near the diaphysis and the epiphyses. The metap ... References Skeletal system Long bones {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Bone
The long bones are those that are longer than they are wide. They are one of five types of bones: long, Short bone, short, Flat bone, flat, Irregular bone, irregular and Sesamoid bone, sesamoid. Long bones, especially the femur and tibia, are subjected to most of the load during daily activities and they are crucial for skeletal mobility. They grow primarily by elongation of the diaphysis, with an epiphysis at each end of the growing bone. The ends of epiphyses are covered with hyaline cartilage ("articular cartilage"). The longitudinal growth of long bones is a result of endochondral ossification at the epiphyseal plate. Bone growth in length is stimulated by the production of growth hormone (GH), a secretion of the Anterior pituitary, anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. The long bone category includes the femora, tibiae, and fibulae of the legs; the humerus, humeri, Radius (bone), radii, and ulnae of the arms; metacarpals and metatarsals of the hands and feet, the Phalanx bone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medullary Cavity
The medullary cavity (''medulla'', innermost part) is the central cavity of bone shafts where red bone marrow and/or yellow bone marrow (adipose tissue) is stored; hence, the medullary cavity is also known as the marrow cavity. Located in the main shaft of a long bone (diaphysis) (consisting mostly of compact bone), the medullary cavity has walls composed of spongy bone (cancellous bone) and is lined with a thin, vascular membrane (endosteum). However, the medullary cavity is the area inside any bone (long, flat, etc.) that holds the bone marrow. This area is involved in the formation of red blood cells and white blood cells, and the calcium supply for bird eggshells. The area has been detected in fossil bones despite the fossilization process. Intramedullary is a medical term meaning the inside of a bone. Examples include intramedullary rods used to treat bone fractures in orthopedic surgery and intramedullary tumors occurring in some forms of cancer or benign tumors such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nutrient Artery
The nutrient artery (arteria nutricia, or medullary), usually accompanied by one or two veins, enters the bone through the nutrient foramen, runs obliquely through the cortex, sends branches upward and downward to the bone marrow, which ramify in the endosteum–the vascular membrane lining the medullary cavity–and give twigs to the adjoining canals. Nutrient arteries are the most apparent blood vessels of the bones. All bones possess larger or smaller foramina for the entrance of the nourishing blood-vessels; these are known as the nutrient foramina, and are particularly large in the shafts of the larger long bones, where they lead into a nutrient canal All bones possess larger or smaller foramina (openings) for the entrance of blood-vessels; these are known as the nutrient foramina, and are particularly large in the shafts of the larger long bones, where they lead into a nutrient canal, which e ..., which extends into the medullary cavity (bone marrow cavity). References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower tooth, teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone of the skull (discounting the ossicles of the middle ear). It is connected to the temporal bones by the temporomandibular joints. The bone is formed prenatal development, in the fetus from a fusion of the left and right mandibular prominences, and the point where these sides join, the mandibular symphysis, is still visible as a faint ridge in the midline. Like other symphyses in the body, this is a midline articulation where the bones are joined by fibrocartilage, but this articulation fuses together in early childhood.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, p. 59 The word "mandible" derives from the Latin word ''mandibula'', "jawbone" (literally "one used for chewing"), from ''wikt:mandere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
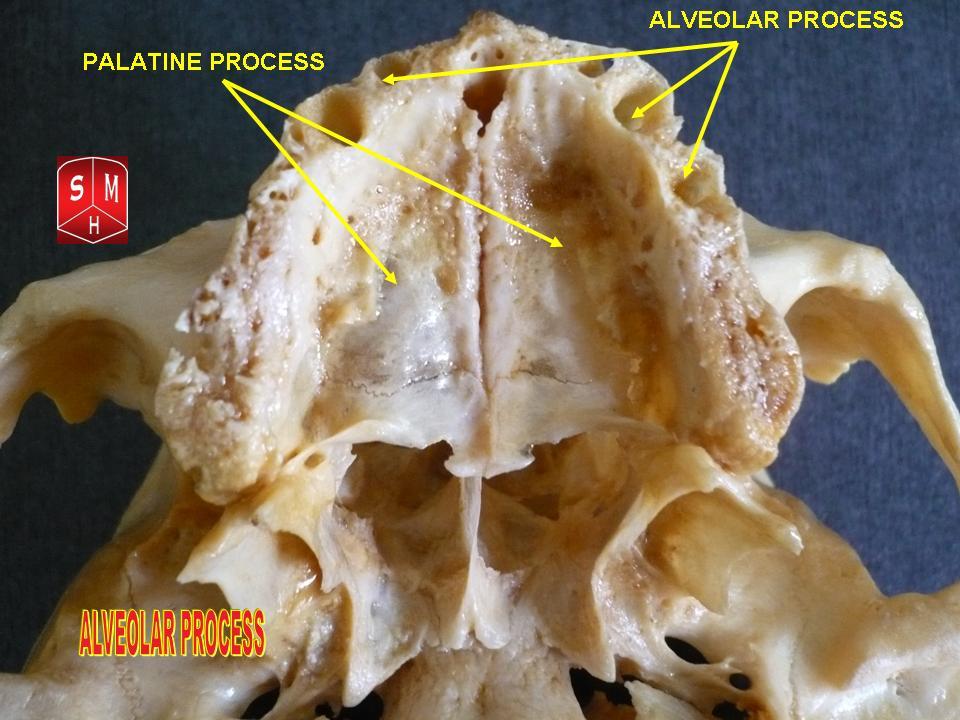
Dental Alveolus
Dental alveoli (singular ''alveolus'') are sockets in the jaws in which the roots of teeth are held in the alveolar process with the periodontal ligament. The lay term for dental alveoli is tooth sockets. A joint that connects the roots of the teeth and the alveolus is called ''gomphosis'' (plural ''gomphoses''). Alveolar bone is the bone that surrounds the roots of the teeth forming bone sockets. In mammals, tooth sockets are found in the maxilla, the premaxilla, and the mandible. Etymology 1706, "a hollow," especially "the socket of a tooth," from Latin alveolus "a tray, trough, basin; bed of a small river; small hollow or cavity," diminutive of alvus "belly, stomach, paunch, bowels; hold of a ship," from PIE root *aulo- "hole, cavity" (source also of Greek aulos "flute, tube, pipe;" Serbo-Croatian, Polish, Russian ulica "street," originally "narrow opening;" Old Church Slavonic uliji, Lithuanian aulys "beehive" (hollow trunk), Armenian yli "pregnant"). The word was extended in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |