|
Nuchal Lines
The nuchal lines are four curved lines on the external surface of the occipital bone: * The upper, often faintly marked, is named the highest nuchal line, but is sometimes referred to as the Mempin line or linea suprema, and it attaches to the epicranial aponeurosis. * Below the highest nuchal line is the superior nuchal line. To it is attached, the splenius capitis muscle, the trapezius muscle, and the occipitalis. * From the external occipital protuberance a ridge or crest, the external occipital crest also called the median nuchal line, often faintly marked, descends to the foramen magnum, and affords attachment to the nuchal ligament. * Running from the middle of this line is the inferior nuchal line. Attached are the obliquus capitis superior muscle, rectus capitis posterior major muscle, and rectus capitis posterior minor muscle The rectus capitis posterior minor (or rectus capitis posticus minor, both being Latin for ''lesser posterior straight muscle of the head'') arises ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occipital Bone
The occipital bone () is a neurocranium, cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull). It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. The occipital bone overlies the occipital lobes of the cerebrum. At the base of skull in the occipital bone, there is a large oval opening called the foramen magnum, which allows the passage of the spinal cord. Like the other cranial bones, it is classed as a flat bone. Due to its many attachments and features, the occipital bone is described in terms of separate parts. From its front to the back is the basilar part of occipital bone, basilar part, also called the basioccipital, at the sides of the foramen magnum are the lateral parts of occipital bone, lateral parts, also called the exoccipitals, and the back is named as the squamous part of occipital bone, squamous part. The basilar part is a thick, somewhat quadrilateral piece in front of the foramen magnum and directed towards the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occipital Bone
The occipital bone () is a neurocranium, cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull). It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. The occipital bone overlies the occipital lobes of the cerebrum. At the base of skull in the occipital bone, there is a large oval opening called the foramen magnum, which allows the passage of the spinal cord. Like the other cranial bones, it is classed as a flat bone. Due to its many attachments and features, the occipital bone is described in terms of separate parts. From its front to the back is the basilar part of occipital bone, basilar part, also called the basioccipital, at the sides of the foramen magnum are the lateral parts of occipital bone, lateral parts, also called the exoccipitals, and the back is named as the squamous part of occipital bone, squamous part. The basilar part is a thick, somewhat quadrilateral piece in front of the foramen magnum and directed towards the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epicranial Aponeurosis
The epicranial aponeurosis (aponeurosis epicranialis, galea aponeurotica) is an aponeurosis (a tough layer of dense fibrous tissue). It covers the upper part of the skull in humans and many other animals. Structure In humans, the epicranial aponeurosis originates from the external occipital protuberance and highest nuchal lines of the occipital bone. It merges with the occipitofrontalis muscle. In front, it forms a short and narrow prolongation between its union with the frontalis muscle (the frontal part of the occipitofrontalis muscle). On either side, the epicranial aponeurosis attaches to the anterior auricular muscles and the superior auricular muscles. Here it is less aponeurotic, and is continued over the temporal fascia to the zygomatic arch as a layer of laminated areolar tissue. It is closely connected to the integument by the firm, dense, fibro-fatty layer which forms the superficial fascia of the scalp. It is attached to the pericranium by loose cellular tiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splenius Capitis Muscle
The splenius capitis () () is a broad, straplike muscle in the back of the neck. It pulls on the base of the skull from the vertebrae in the neck and upper thorax. It is involved in movements such as shaking the head. Structure It arises from the lower half of the nuchal ligament, from the spinous process of the seventh cervical vertebra, and from the spinous processes of the upper three or four thoracic vertebrae. The fibers of the muscle are directed upward and laterally and are inserted, under cover of the sternocleidomastoideus, into the mastoid process of the temporal bone, and into the rough surface on the occipital bone just below the lateral third of the superior nuchal line. The splenius capitis is deep to sternocleidomastoideus at the mastoid process, and to the trapezius for its lower portion. It is one of the muscles that forms the floor of the posterior triangle of the neck. The splenius capitis muscle is innervated by the posterior ramus of spinal nerves C3 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
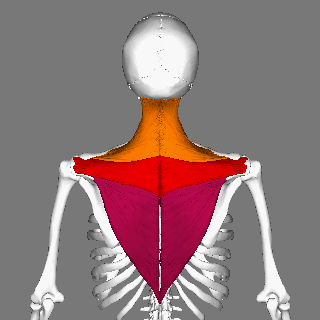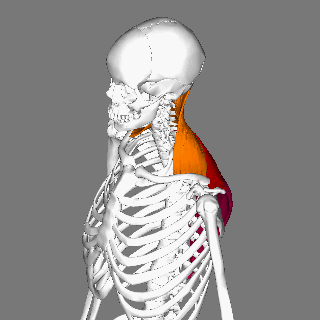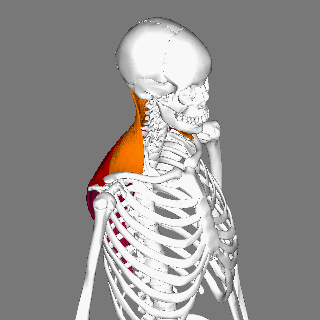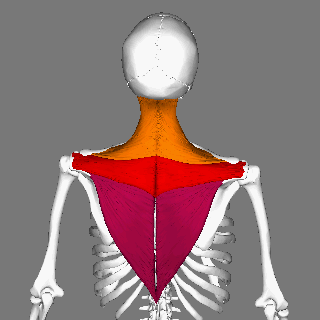
Trapezius Muscle
The trapezius is a large paired trapezoid-shaped surface muscle that extends longitudinally from the occipital bone to the lower thoracic vertebrae of the spine and laterally to the spine of the scapula. It moves the scapula and supports the arm. The trapezius has three functional parts: an upper (descending) part which supports the weight of the arm; a middle region (transverse), which retracts the scapula; and a lower (ascending) part which medially rotates and depresses the scapula. Name and history The trapezius muscle resembles a trapezium, also known as a trapezoid, or diamond-shaped quadrilateral. The word "spinotrapezius" refers to the human trapezius, although it is not commonly used in modern texts. In other mammals, it refers to a portion of the analogous muscle. Similarly, the term "tri-axle back plate" was historically used to describe the trapezius muscle. Structure The ''superior'' or ''upper'' (or descending) fibers of the trapezius originate from the sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occipitalis
The occipitalis muscle (occipital belly) is a muscle which covers parts of the skull. Some sources consider the occipital muscle to be a distinct muscle. However, Terminologia Anatomica currently classifies it as part of the occipitofrontalis muscle along with the frontalis muscle. The occipitalis muscle is thin and quadrilateral in form. It arises from tendinous fibers from the lateral two-thirds of the superior nuchal line of the occipital bone and from the mastoid process of the temporal and ends in the epicranial aponeurosis. The occipitalis muscle is innervated by the facial nerve and its function is to move the scalp back. The muscles receives blood from the occipital artery. Additional image File:Occipitalis muscle animation small.gif, Position of occipitalis muscle (shown in red). See also * Occipitofrontalis muscle The occipitofrontalis muscle (epicranius muscle) is a muscle which covers parts of the skull. It consists of two parts or bellies: the occipital belly, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
External Occipital Protuberance
Near the middle of the squamous part of occipital bone is the external occipital protuberance, the highest point of which is referred to as the inion. The inion is the most prominent projection of the protuberance which is located at the posterioinferior (rear lower) part of the human skull. The nuchal ligament and trapezius muscle attach to it. The inion (ἰνίον, iníon, Greek for the occipital bone) is used as a landmark in the 10-20 system in electroencephalography (EEG) recording. Extending laterally from it on either side is the superior nuchal line, and above it is the faintly marked highest nuchal line. A study of 16th-century Anatolian remains showed that the external occipital protuberance statistically tends to be less pronounced in female remains. Additional images See also * Internal occipital protuberance * Occipital bun The occipital bone () is a cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull). It is trapezoidal in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
External Occipital Crest
The external occipital crest is part of the external surface of the squamous part of occipital bone, squamous part of the occipital bone. It is a ridge along the midline, beginning at the external occipital protuberance and descending to the foramen magnum, that gives attachment to the nuchal ligament. It is also called the median nuchal line. References External links Bones of the head and neck {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foramen Magnum
The foramen magnum ( la, great hole) is a large, oval-shaped opening in the occipital bone of the skull. It is one of the several oval or circular openings (foramina) in the base of the skull. The spinal cord, an extension of the medulla oblongata, passes through the foramen magnum as it exits the cranial cavity. Apart from the transmission of the medulla oblongata and its membranes, the foramen magnum transmits the vertebral arteries, the anterior and posterior spinal arteries, the tectorial membranes and alar ligaments. It also transmits the accessory nerve into the skull. The foramen magnum is a very important feature in bipedal mammals. One of the attributes of a biped's foramen magnum is a forward shift of the anterior border of the cerebellar tentorium; this is caused by the shortening of the cranial base. Studies on the foramen magnum position have shown a connection to the functional influences of both posture and locomotion. The forward shift of the foramen magnum i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuchal Ligament
The nuchal ligament is a ligament at the back of the neck that is continuous with the supraspinous ligament. Structure The nuchal ligament extends from the external occipital protuberance on the skull and median nuchal line to the spinous process of the seventh cervical vertebra in the lower part of the neck. From the anterior border of the nuchal ligament, a fibrous lamina is given off. This is attached to the posterior tubercle of the atlas, and to the spinous processes of the cervical vertebrae, and forms a septum between the muscles on either side of the neck. The trapezius and splenius capitis muscle attach to the nuchal ligament. Function It is a tendon-like structure that has developed independently in humans and other animals well adapted for running. In some four-legged animals, particularly ungulates, the nuchal ligament serves to sustain the weight of the head. Clinical significance In Chiari malformation treatment, decompression and duraplasty with a harvested n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obliquus Capitis Superior Muscle
The obliquus capitis superior muscle () is a small muscle in the upper back part of the neck and is one of the suboccipital muscles and part of the suboccipital triangle. It arises from the lateral mass of the atlas bone. It passes superiorly and posteriorly to insert into the lateral half of the inferior nuchal line on the external surface of the occipital bone. The muscle is innervated by the suboccipital nerve, the dorsal ramus of the first spinal nerve. It acts at the atlanto-occipital joint to extend the head and flex the head to the ipsilateral side. Additional images File:Obliquus capitis superior muscle - animation04.gif, Position of obliquus capitis superior (shown in red). Animation. File:Obliquus capitis superior muscle05.png, Still image. Posterior view. File:Obliquus capitis superior.png, Deep muscles of the back (obliquus capitis superior labeled at upper left) File:Gray129.png, Occipital bone. Outer surface. Muscle attachments are shown as red circles. File ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectus Capitis Posterior Major Muscle
The rectus capitis posterior major (or rectus capitis posticus major, both being Latin for ''larger posterior straight muscle of the head'') arises by a pointed tendon from the spinous process of the axis, and, becoming broader as it ascends, is inserted into the lateral part of the inferior nuchal line of the occipital bone and the surface of the bone immediately below the line. A soft tissue connection bridging from the rectus capitis posterior major to the cervical dura mater was described in 2011. Various clinical manifestations may be linked to this anatomical relationship. It has also been postulated that this connection serves as a monitor of dural tension along with the rectus capitis posterior minor and the obliquus capitis inferior. As the muscles of the two sides pass upward and lateralward, they leave between them a triangular space, in which the rectus capitis posterior minor is seen. Its main actions are to extend and rotate the atlanto-occipital joint. See also * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |