|
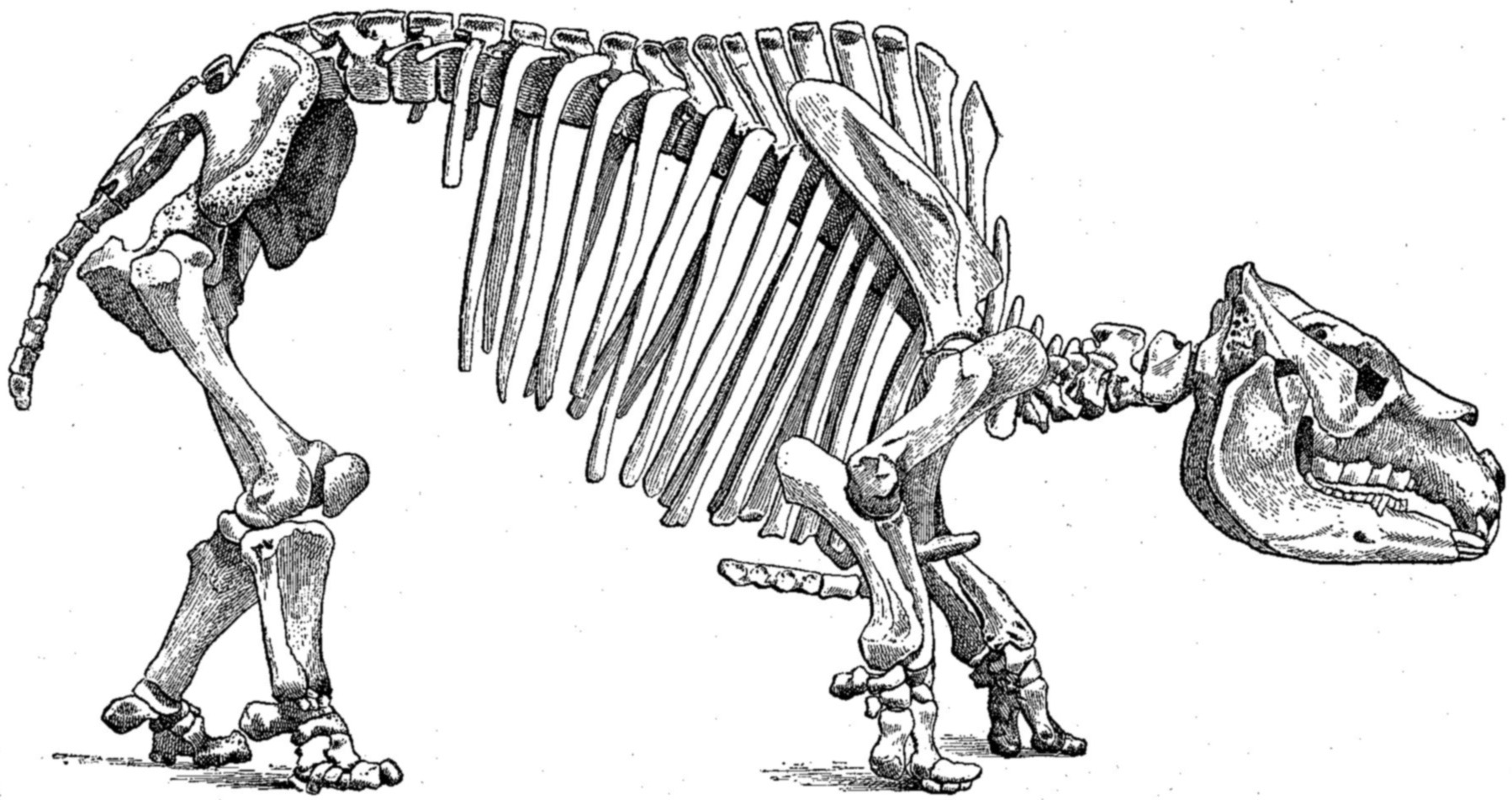
Notoungulate
Notoungulata is an extinct order of mammalian ungulates that inhabited South America from the early Paleocene to the Holocene, living from approximately 61 million to 11,000 years ago. Notoungulates were morphologically diverse, with forms resembling animals as disparate as rabbits and rhinoceroses. Notoungulata are the largest group of South American native ungulates, with over 150 genera in 14 families having been described, divided into two major subgroupings, Typotheria and Toxodontia. Notoungulates first diversified during the Eocene. Their diversity declined during the Late Neogene, with only the large toxodontids persisting until the end of the Pleistocene. Collagen analysis suggests that notoungulates are closely related to litopterns, another group of South American ungulates, and their closest living relatives being perissodactyls (odd-toed ungulates), including rhinoceroses, tapirs and equines. but their relationships to other South American ungulates are uncertain. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South American Native Ungulates
South American native ungulates, commonly abbreviated as SANUs, are extinct ungulate-like mammals of controversial affinities that were indigenous to South America prior to the Great American Biotic Interchange. They comprise five major groups conventionally ranked as orders— Astrapotheria, Litopterna, Notoungulata, Pyrotheria, and Xenungulata—as well as some other taxa, such as Didolodontidae and Kollpaniidae. It has been proposed that some or all of the members of this group form a clade, named Meridiungulata, though the relationships of South American ungulates remain largely unresolved. The two largest groups of South American ungulates, the notoungulates and the litopterns, were the only groups to persist beyond the mid Miocene. Only a few of the largest species of notoungulates and litopterns survived until the end-Pleistocene extinctions. Though most SANUs lived in South America, astrapotheres and litopterns are known from Eocene aged deposits in the Antarctic Peni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henricosborniidae
Henricosborniidae is a family of extinct notoungulate mammals known from the Late Paleocene to Middle Eocene of Argentina, Bolivia and Brazil. The name honors U.S. paleontologist Henry Fairfield Osborn. Description Henricosborniidae is a group of primitive notoungulates assigned to the suborder Notioprogonia together with Notostylopidae, not because these two families share any derived features, but because they do not clearly belong to any other clade. The henricosborniids are only known from the late Paleocene and early Eocene (Itaboraian-Casamayoran SALMA, ), making them slightly older and more primitive than the notostylopids. The henricosborniid dentition is the most generalized and primitive of all notoungulates, and they are believed to be near the source of all notoungulates. They have low teeth crowns and the dental formula . George Gaylord Simpson noted that many of the mammals that Ameghino had, and Simpson himself did, describe from the Río Chico Formation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Litopterna
Litopterna (from grc, λῑτή πτέρνα "smooth heel") is an extinct order of fossil hoofed mammals from the Cenozoic era. The order is one of the five great orders of South American ungulates that were endemic to the continent, until the Great American Biotic Interchange brought new ungulate species. Like other endemic South American mammals, their relationship to other mammal groups had long been unclear, but recent genetic and proteomic evidence indicates that their closest living relatives are Perissodactyls (odd-toed ungulates) including horses, rhinoceros, and tapirs, and that litopterns are closely related to notoungulates, another widespread group of South American ungulates. There were two major groups of litopterns: Proterotheriidae and Macraucheniidae. Proterotheriids were medium to large animals that evolved adaptations for fast running, and occupied a variety of niches that elsewhere were filled by animals such as goats and antelopes, mouse deer, and horses. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxodonta
Toxodontia. Retrieved April 2013. is a suborder of the meridiungulate order Notoungulata. Most of the members of the five included families, including the largest notoungulates, share several dental, auditory and tarsal specializations. The group is named after ''Toxodon'', the first example of the group to be discovered by science. Description Isotemnidae, the oldest and most primitive family of toxodonts, were generally large animals with larger canines than other early notoungulates. The family is probably paraphyletic or polyphyletic since only primitive dental features unite the 12 included genera, such as a complete dentition with unreduced canines and no diastemata in the earliest genera. Likewise, they are only weakly linked to other toxodonts by a few dental features, and their primitive cheek tooth pattern can be basal to all notoungulates except notioprogonians. The oldest of the 12 genera in this family is '' Isotemnus'' known from the Riochican-Casamayoran, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxodontidae
Toxodontidae is an extinct family of notoungulate mammals, known from the Oligocene to the Holocene (11,000 BP) of South America, with one genus, '' Mixotoxodon'', also known from the Pleistocene of Central America and southwestern North America (Texas).E. Lundelius, et al. 2013. The first occurrence of a toxodont (Mammalia, Notoungulata) in the United States. ''Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology'', Vol 33, No 1, pp. 229–23DOI:10.1080/02724634.2012.711405/ref> They somewhat resembled rhinoceroses, and had teeth with high crowns and open roots, suggesting that they often fed on tough pampas grass. However, isotopic analyses have led to the conclusion that the most recent forms were grazing and browsing generalists. Taxonomy The endemic notoungulate and litoptern ungulates of South America have been shown by studies of collagen and mitochondrial DNA sequences to be a sister group to the perissodactyl Odd-toed ungulates, mammals which constitute the taxonomic order Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pachyrukhos
''Pachyrukhos'' is an extinct genus of hegetotheriid notoungulate from the Early to Middle Miocene (Colhuehuapian-Friasian in the SALMA classification) of Argentina and Chile. Fossils of this genus have been found in the Collón Curá, Sarmiento and Santa Cruz Formations of Argentina and the Río Frías Formation of Chile.''Pachyrukhos'' at .org Description It was about long and closely resembled a , with a short tail and long hind feet. ''Pachyrukhos'' was probably also able to hop, and it had a rabbit-like |
Thomashuxleya
''Thomashuxleya'' is an extinct genus of notoungulate mammal, named after famous 19th-century biologist Thomas Huxley. Description ''Thomashuxleya'' was about in length and weighted an estimated , with a heavy body and strong limbs.D. Patterson, Bruce (€2012) ''Bones, Clones, and Biomes: The History and Geography of Recent Neotropical Mammals'' p.83 Its large skull had 44 teeth in its jaws, including large canines which may have been used to dig around in earth. It had four toes on each foot, and probably walked somewhat like a modern peccary. It was a relatively generalised animal, not specialised for any particular way of life. There's an almost complete skeleton of this animal in exhibition in the American Museum of Natural History. This skeleton was discovered during the Scarrit expedition to Patagonia, Argentina, that was led by the paleontologist George Gaylord Simpson. Fossils of ''Thomashuxleya'' have been found in the Sarmiento and Casamayor Formations of Argentin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxodon
''Toxodon'' (meaning "bow tooth" in reference to the curvature of the teeth) is an extinct genus of South American mammals from the Late Miocene to early Holocene epochs ( Mayoan to Lujanian in the SALMA classification) (about 11.6 million to 11,000 years ago). It is a member of Notoungulata, one of several now extinct orders of hoofed mammals indigenous to South America distinct from living perissodactyls and artiodactyls. It was among the largest and last members of its order, and was probably the most common large hoofed mammal in South America of its time. Taxonomy ''Toxodon'' was one of the last members of Notoungulata, a group of ungulates that had been part of the fauna of South America since the Paleocene. ''Toxodon'' was a member of Toxodontidae a large bodied group including similar, vaguely rhinoceros like forms. Charles Darwin was one of the first to collect ''Toxodon'' fossils, after paying 18 pence for a ''T. platensis'' skull from a farmer in Urug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosotherium
''Prosotherium'' is an extinct genus of hegetotheriid notoungulate. It lived during the Late Oligocene (between ~29-24 Ma), and its fossilized remains were found in South America. Description This animal was similar to rabbits, in aspect and in size. Its hind legs were particularly long. Crania Its crania was light and thin, notably in the posterior part. The tympanic part of the temporal bone was particularly developed, even more than its relative ''Pachyrukhos'', and it is probable that its auricle was quite large, similar to the ears of a hare. The maxilla and the mandible were high and deep ; the mandible had a subtle coronoid process. The teeth were characterized by incisors pointing inward, molars and premolars covered by a thin layer of dental cementum, generally on the outside part of the upper teeth and on the inside part of the lower teeth. Postcranial skeleton The humerus was large and thin, like the ulna and radius. Metacarpals and phalanges indicates that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hegetotheriidae
Hegetotheriidae is an extinct family of notoungulate mammals known from the Oligocene through the Pliocene of South America South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the souther .... References Typotheres Oligocene mammals Miocene mammals of South America Pliocene mammals Pliocene extinctions Pliocene notoungulates Prehistoric mammal families {{paleo-mammal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ungulate
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Ungulata which primarily consists of large mammals with hooves. These include odd-toed ungulates such as horses, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and even-toed ungulates such as cattle, pigs, giraffes, camels, sheep, deer, and hippopotamuses. Cetaceans such as whales, dolphins, and porpoises are also classified as even-toed ungulates, although they do not have hooves. Most terrestrial ungulates use the hoofed tips of their toes to support their body weight while standing or moving. The term means, roughly, "being hoofed" or "hoofed animal". As a descriptive term, "ungulate" normally excludes cetaceans as they do not possess most of the typical morphological characteristics of other ungulates, but recent discoveries indicate that they were also descended from early artiodactyls. Ungulates are typically herbivorous and many employ specialized gut bacteria to allow them to digest cellulose. Some modern species, such as pigs, are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |