|
Noncommutative Standard Model
In theoretical particle physics, the non-commutative Standard Model (best known as Spectral Standard Model ), is a model based on noncommutative geometry that unifies a modified form of general relativity with the Standard Model (extended with right-handed neutrinos). The model postulates that space-time is the product of a 4-dimensional compact spin manifold \mathcal by a finite space \mathcal. The full Lagrangian (in Euclidean signature) of the Standard model minimally coupled to gravity is obtained as pure gravity over that product space. It is therefore close in spirit to Kaluza–Klein theory but without the problem of massive tower of states. The parameters of the model live at unification scale and physical predictions are obtained by running the parameters down through renormalization. It is worth stressing that it is more than a simple reformation of the Standard Model. For example, the scalar sector and the fermions representations are more constrained than in effec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Physics
Particle physics or high energy physics is the study of fundamental particles and forces that constitute matter and radiation. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) and bosons (force-carrying particles). There are three generations of fermions, but ordinary matter is made only from the first fermion generation. The first generation consists of up and down quarks which form protons and neutrons, and electrons and electron neutrinos. The three fundamental interactions known to be mediated by bosons are electromagnetism, the weak interaction, and the strong interaction. Quarks cannot exist on their own but form hadrons. Hadrons that contain an odd number of quarks are called baryons and those that contain an even number are called mesons. Two baryons, the proton and the neutron, make up most of the mass of ordinary matter. Mesons are unstable and the longest-lived last for only a few hundredths of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
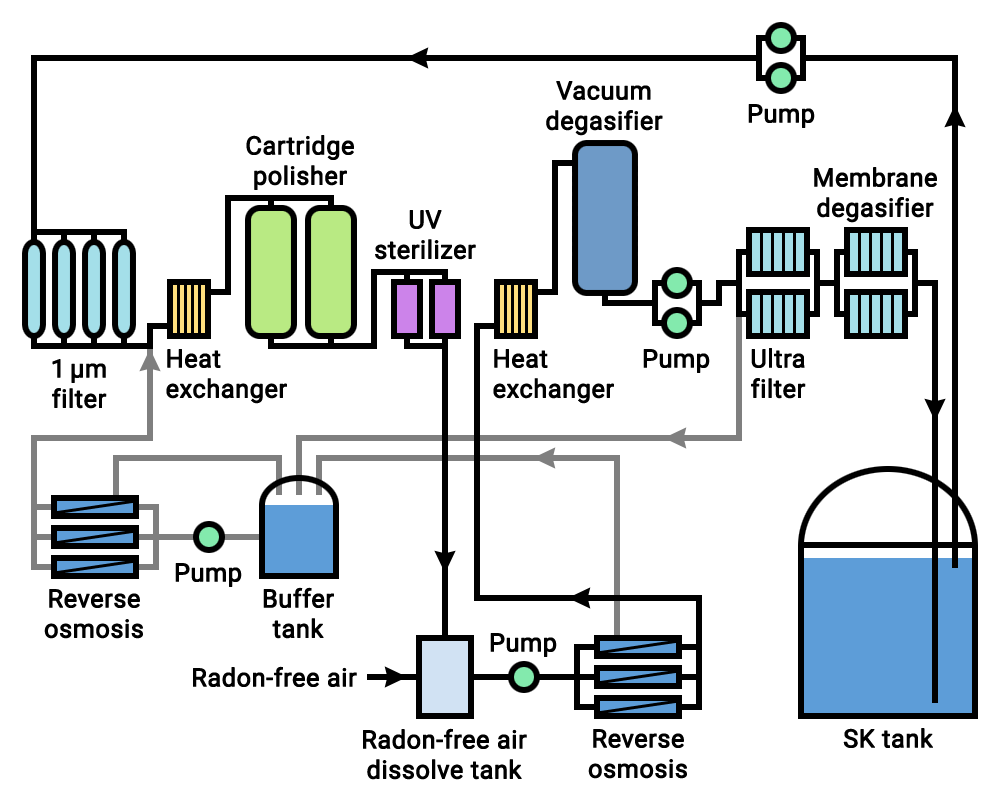
Super-Kamiokande
Super-Kamiokande (abbreviation of Super-Kamioka Neutrino Detection Experiment, also abbreviated to Super-K or SK; ja, スーパーカミオカンデ) is a neutrino observatory located under Mount Ikeno near the city of Hida, Gifu Prefecture, Japan. It is located underground in the Mozumi Mine in Hida's Kamioka area. The observatory was designed to detect high-energy neutrinos, to search for proton decay, study solar and atmospheric neutrinos, and keep watch for supernovae in the Milky Way Galaxy. It consists of a cylindrical stainless steel tank about in height and diameter holding 50,000 metric tons (55,000 US tons) of ultrapure water. Mounted on an inside superstructure are about 13,000 photomultiplier tubes that detect light from Cherenkov radiation. A neutrino interaction with the electrons or nuclei of water can produce an electron or positron that moves faster than the speed of light in water, which is slower than the speed of light in a vacuum. This creates a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timeline Of Atomic And Subatomic Physics
A timeline of atomic physics, atomic and subatomic particle, subatomic physics. Early beginnings *In 6th century BCE, Acharya Kaṇāda (philosopher), Kanada proposed that all matter must consist of indivisible particles and called them "anu". He proposes examples like ripening of fruit as the change in the number and types of atoms to create newer units. *430 BCE Democritus speculates about fundamental indivisible particles—calls them "atoms" The beginning of chemistry * 1766 Henry Cavendish discovers and studies hydrogen * 1778 Carl Scheele and Antoine Lavoisier discover that Earth's atmosphere, air is composed mostly of nitrogen and oxygen * 1781 Joseph Priestley creates water by igniting hydrogen and oxygen * 1800 William Nicholson (chemist), William Nicholson and Anthony Carlisle use electrolysis to separate water into hydrogen and oxygen * 1803 John Dalton introduces atomic theory, atomic ideas into chemistry and states that matter is composed of atomic weight, atoms of di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noncommutative Quantum Field Theory
In mathematical physics, noncommutative quantum field theory (or quantum field theory on noncommutative spacetime) is an application of noncommutative mathematics to the spacetime of quantum field theory that is an outgrowth of noncommutative geometry and index theory in which the coordinate functions are noncommutative. One commonly studied version of such theories has the "canonical" commutation relation: : [x^, x^]=i \theta^ \,\! which means that (with any given set of axes), it is impossible to accurately measure the position of a particle with respect to more than one axis. In fact, this leads to an uncertainty relation for the coordinates analogous to the Heisenberg uncertainty principle. Various lower limits have been claimed for the noncommutative scale, (i.e. how accurately positions can be measured) but there is currently no experimental evidence in favour of such a theory or grounds for ruling them out. One of the novel features of noncommutative field theories is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noncommutative Algebraic Geometry
Noncommutative algebraic geometry is a branch of mathematics, and more specifically a direction in noncommutative geometry, that studies the geometric properties of formal duals of non-commutative algebraic objects such as rings as well as geometric objects derived from them (e.g. by gluing along localizations or taking noncommutative stack quotients). For example, noncommutative algebraic geometry is supposed to extend a notion of an algebraic scheme by suitable gluing of spectra of noncommutative rings; depending on how literally and how generally this aim (and a notion of spectrum) is understood in noncommutative setting, this has been achieved in various level of success. The noncommutative ring generalizes here a commutative ring of regular functions on a commutative scheme. Functions on usual spaces in the traditional (commutative) algebraic geometry have a product defined by pointwise multiplication; as the values of these functions commute, the functions also commute: '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noncommutative Geometry
Noncommutative geometry (NCG) is a branch of mathematics concerned with a geometric approach to noncommutative algebras, and with the construction of ''spaces'' that are locally presented by noncommutative algebras of functions (possibly in some generalized sense). A noncommutative algebra is an associative algebra in which the multiplication is not commutative, that is, for which xy does not always equal yx; or more generally an algebraic structure in which one of the principal binary operations is not commutative; one also allows additional structures, e.g. topology or norm, to be possibly carried by the noncommutative algebra of functions. An approach giving deep insight about noncommutative spaces is through operator algebras (i.e. algebras of bounded linear operators on a Hilbert space). Perhaps one of the typical examples of a noncommutative space is the " noncommutative tori", which played a key role in the early development of this field in 1980s and lead to noncommutativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matilde Marcolli
Matilde Marcolli is an Italian and American mathematical physicist. She has conducted research work in areas of mathematics and theoretical physics; obtained the Heinz Maier-Leibnitz-Preis of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, and the Sofia Kovalevskaya Award of the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation. Marcolli has authored and edited numerous books in the field. She is currently the Robert F. Christy Professor of Mathematics and Computing and Mathematical Sciences at the California Institute of Technology. Career Marcolli obtained her Laurea in Physics in 1993 ''summa cum laude'' from the University of Milan under the supervision of Renzo Piccinini, with a thesis on ''Classes of self equivalences of fibre bundles''. She moved to the USA in 1994, where she obtained a master's degree (1994) and a PhD (1997) in Mathematics from the University of Chicago, under the supervision of Melvin Rothenberg, with a thesis on ''Three dimensional aspects of Seiberg-Witten Gauge Theory''. Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tevatron
The Tevatron was a circular particle accelerator (active until 2011) in the United States, at the Fermilab, Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (also known as ''Fermilab''), east of Batavia, Illinois, and is the second highest energy particle collider ever built, after the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) of the CERN, European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) near Geneva, Switzerland. The Tevatron was a synchrotron that accelerated protons and antiprotons in a ring to energies of up to 1 TeV, hence its name. The Tevatron was completed in 1983 at a cost of $120 million and significant upgrade investments were made during its active years of 1983–2011. The main achievement of the Tevatron was the discovery in 1995 of the top quark—the last Elementary particle#Fundamental fermions, fundamental fermion predicted by the Standard Model of particle physics. On July 2, 2012, scientists of the Collider Detector at Fermilab, CDF and D0 experiment, DØ collider experiment teams ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Top Quark
The top quark, sometimes also referred to as the truth quark, (symbol: t) is the most massive of all observed elementary particles. It derives its mass from its coupling to the Higgs Boson. This coupling y_ is very close to unity; in the Standard Model of particle physics, it is the largest (strongest) coupling at the scale of the weak interactions and above. The top quark was discovered in 1995 by the CDF and DØ experiments at Fermilab. Like all other quarks, the top quark is a fermion with spin and participates in all four fundamental interactions: gravitation, electromagnetism, weak interactions, and strong interactions. It has an electric charge of + ''e''. It has a mass of , which is close to the rhenium atom mass. The antiparticle of the top quark is the top antiquark (symbol: , sometimes called ''antitop quark'' or simply ''antitop''), which differs from it only in that some of its properties have equal magnitude but opposite sign. The top quark interacts with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Higgs Boson
The Higgs boson, sometimes called the Higgs particle, is an elementary particle in the Standard Model of particle physics produced by the quantum excitation of the Higgs field, one of the fields in particle physics theory. In the Standard Model, the Higgs particle is a massive scalar boson with zero spin, even (positive) parity, no electric charge, and no colour charge, that couples to (interacts with) mass. It is also very unstable, decaying into other particles almost immediately. The Higgs field is a scalar field, with two neutral and two electrically charged components that form a complex doublet of the weak isospin SU(2) symmetry. Its " Mexican hat-shaped" potential leads it to take a nonzero value ''everywhere'' (including otherwise empty space), which breaks the weak isospin symmetry of the electroweak interaction, and via the Higgs mechanism gives mass to many particles. Both the field and the boson are named after physicist Peter Higgs, who in 1964, along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John W
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died c. AD 30), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (lived c. AD 30), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudbury Neutrino Observatory
The Sudbury Neutrino Observatory (SNO) was a neutrino observatory located 2100 m underground in Vale's Creighton Mine in Sudbury, Ontario, Canada. The detector was designed to detect solar neutrinos through their interactions with a large tank of heavy water. The detector was turned on in May 1999, and was turned off on 28 November 2006. The SNO collaboration was active for several years after that analyzing the data taken. The director of the experiment, Art McDonald, was co-awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2015 for the experiment's contribution to the discovery of neutrino oscillation. The underground laboratory has been enlarged into a permanent facility and now operates multiple experiments as SNOLAB. The SNO equipment itself was being refurbished for use in the SNO+ experiment. Experimental motivation The first measurements of the number of solar neutrinos reaching the Earth were taken in the 1960s, and all experiments prior to SNO observed a third to a ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |