|
Nftables
nftables is a subsystem of the Linux kernel providing filtering and classification of network packets/datagrams/frames. It has been available since Linux kernel 3.13 released on 19 January 2014. nftables replaces the legacy iptables portions of Netfilter. Among the advantages of nftables over iptables is less code duplication and easier extension to new protocols. nftables is configured via the user-space utility ''nft'', while legacy tools are configured via the utilities '' iptables'', ''ip6tables'', '' arptables'' and ''ebtables'' frameworks. nftables utilizes the building blocks of the Netfilter infrastructure, such as the existing hooks into the networking stack, connection tracking system, userspace queueing component, and logging subsystem. nft Command-line syntax A command to drop any packets with destination IP address 1.2.3.4: nft add rule ip filter output ip daddr 1.2.3.4 drop Note that the new syntax differs significantly from that of iptables, in which the same r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netfilter
Netfilter is a framework provided by the Linux kernel that allows various networking-related operations to be implemented in the form of customized handlers. Netfilter offers various functions and operations for packet filtering, network address translation, and port translation, which provide the functionality required for directing packets through a network and prohibiting packets from reaching sensitive locations within a network. Netfilter represents a set of hooks inside the Linux kernel, allowing specific kernel modules to register callback functions with the kernel's networking stack. Those functions, usually applied to the traffic in the form of filtering and modification rules, are called for every packet that traverses the respective hook within the networking stack. History Rusty Russell started the ''netfilter/iptables project'' in 1998; he had also authored the project's predecessor, ipchains. As the project grew, he founded the ''Netfilter Core Team'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iptables
iptables is a user-space utility program that allows a system administrator to configure the IP packet filter rules of the Linux kernel firewall, implemented as different Netfilter modules. The filters are organized in different tables, which contain chains of rules for how to treat network traffic packets. Different kernel modules and programs are currently used for different protocols; ''iptables'' applies to IPv4, ''ip6tables'' to IPv6, ''arptables'' to ARP, and ' to Ethernet frames. iptables requires elevated privileges to operate and must be executed by user root, otherwise it fails to function. On most Linux systems, iptables is installed as and documented in its man pages, which can be opened using man iptables when installed. It may also be found in /sbin/iptables, but since iptables is more like a service rather than an "essential binary", the preferred location remains . The term ''iptables'' is also commonly used to inclusively refer to the kernel-level componen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C (programming Language)
C (''pronounced like the letter c'') is a General-purpose language, general-purpose computer programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie, and remains very widely used and influential. By design, C's features cleanly reflect the capabilities of the targeted CPUs. It has found lasting use in operating systems, device drivers, protocol stacks, though decreasingly for application software. C is commonly used on computer architectures that range from the largest supercomputers to the smallest microcontrollers and embedded systems. A successor to the programming language B (programming language), B, C was originally developed at Bell Labs by Ritchie between 1972 and 1973 to construct utilities running on Unix. It was applied to re-implementing the kernel of the Unix operating system. During the 1980s, C gradually gained popularity. It has become one of the measuring programming language popularity, most widely used programming languages, with C compilers avail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IPv4
Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) is the fourth version of the Internet Protocol (IP). It is one of the core protocols of standards-based internetworking methods in the Internet and other packet-switched networks. IPv4 was the first version deployed for production on SATNET in 1982 and on the ARPANET in January 1983. It is still used to route most Internet traffic today, even with the ongoing deployment of Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6), its successor. IPv4 uses a 32-bit address space which provides 4,294,967,296 (232) unique addresses, but large blocks are reserved for special networking purposes. History Internet Protocol version 4 is described in IETF publication RFC 791 (September 1981), replacing an earlier definition of January 1980 (RFC 760). In March 1982, the US Department of Defense decided on the Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP) as the standard for all military computer networking. Purpose The Internet Protocol is the protocol that defines and enables in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firewall Software
In computing, a firewall is a network security system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. A firewall typically establishes a barrier between a trusted network and an untrusted network, such as the Internet. History The term ''firewall'' originally referred to a wall intended to confine a fire within a line of adjacent buildings. Later uses refer to similar structures, such as the metal sheet separating the engine compartment of a vehicle or aircraft from the passenger compartment. The term was applied in the late 1980s to network technology that emerged when the Internet was fairly new in terms of its global use and connectivity. The predecessors to firewalls for network security were routers used in the late 1980s. Because they already segregated networks, routers could apply filtering to packets crossing them. Before it was used in real-life computing, the term appeared in the 1983 computer-hacking movie ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenDocument
The Open Document Format for Office Applications (ODF), also known as OpenDocument, is an open file format for word processing documents, spreadsheets, presentations and graphics and using ZIP-compressed XML files. It was developed with the aim of providing an open, XML-based file format specification for office applications. It is also the default format for documents in typical Linux distributions. The standard is developed and maintained by a technical committee in the Organization for the Advancement of Structured Information Standards (OASIS) consortium. It was based on the Sun Microsystems specification for OpenOffice.org XML, the default format for OpenOffice.org and LibreOffice. It was originally developed for StarOffice "to provide an open standard for office documents." In addition to being an OASIS standard, it is published as an ISO/ IEC international standard ISO/IEC 26300 Open Document Format for Office Applications (OpenDocument). In 2021 the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netlink
Netlink is a socket family used for inter-process communication (IPC) between both the kernel and userspace processes, and between different userspace processes, in a way similar to the Unix domain sockets available on certain Unix-like operating systems, including its original incarnation as a Linux kernel interface, as well as in the form of a later implementation on FreeBSD. Similarly to the Unix domain sockets, and unlike INET sockets, Netlink communication cannot traverse host boundaries. However, while the Unix domain sockets use the file system namespace, Netlink sockets are usually addressed by process identifiers (PIDs). Netlink is designed and used for transferring miscellaneous networking information between the kernel space and userspace processes. Networking utilities, such as the iproute2 family and the utilities used for configuring mac80211-based wireless drivers, use Netlink to communicate with the Linux kernel from userspace. Netlink provides a standard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Operation
In concurrent programming, an operation (or set of operations) is linearizable if it consists of an ordered list of invocation and response events ( event), that may be extended by adding response events such that: # The extended list can be re-expressed as a sequential history (is serializable). # That sequential history is a subset of the original unextended list. Informally, this means that the unmodified list of events is linearizable if and only if its invocations were serializable, but some of the responses of the serial schedule have yet to return. In a concurrent system, processes can access a shared object at the same time. Because multiple processes are accessing a single object, there may arise a situation in which while one process is accessing the object, another process changes its contents. Making a system linearizable is one solution to this problem. In a linearizable system, although operations overlap on a shared object, each operation appears to take place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
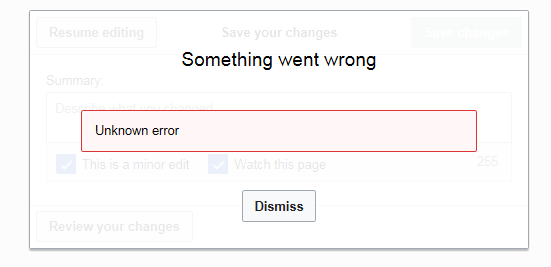
Error Message
An error message is information displayed when an unforeseen occurs, usually on a computer or other device. On modern operating systems with graphical user interfaces, error messages are often displayed using dialog boxes. Error messages are used when user intervention is required, to indicate that a desired operation has failed, or to relay important warnings (such as warning a computer user that they are almost out of hard disk space). Error messages are seen widely throughout computing, and are part of every operating system or computer hardware device. Proper design of error messages is an important topic in usability and other fields of human–computer interaction. Common error messages The following error messages are commonly seen by modern computer users: ;Access denied :This error occurs if the user doesn't have privileges to a file, or if it has been locked by some program or user. ;Device not ready :This error most often occurs when there is no floppy disk (o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duplicate Code
In computer programming, duplicate code is a sequence of source code that occurs more than once, either within a program or across different programs owned or maintained by the same entity. Duplicate code is generally considered undesirable for a number of reasons. A minimum requirement is usually applied to the quantity of code that must appear in a sequence for it to be considered duplicate rather than coincidentally similar. Sequences of duplicate code are sometimes known as code clones or just clones, the automated process of finding duplications in source code is called clone detection. Two code sequences may be duplicates of each other without being character-for-character identical, for example by being character-for-character identical only when white space characters and comments are ignored, or by being token-for-token identical, or token-for-token identical with occasional variation. Even code sequences that are only functionally identical may be considered duplicate code ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Application Binary Interface
In computer software, an application binary interface (ABI) is an interface between two binary program modules. Often, one of these modules is a library or operating system facility, and the other is a program that is being run by a user. An ''ABI'' defines how data structures or computational routines are accessed in machine code, which is a low-level, hardware-dependent format. In contrast, an ''API'' defines this access in source code, which is a relatively high-level, hardware-independent, often human-readable format. A common aspect of an ABI is the calling convention, which determines how data is provided as input to, or read as output from, computational routines. Examples of this are the x86 calling conventions. Adhering to an ABI (which may or may not be officially standardized) is usually the job of a compiler, operating system, or library author. However, an application programmer may have to deal with an ABI directly when writing a program in a mix of programm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |