|
Neuropeptide
Neuropeptides are chemical messengers made up of small chains of amino acids that are synthesized and released by neurons. Neuropeptides typically bind to G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) to modulate neural activity and other tissues like the gut, muscles, and heart. There are over 100 known neuropeptides, representing the largest and most diverse class of signaling molecules in the nervous system. Neuropeptides are synthesized from large precursor proteins which are cleaved and post-translationally processed then packaged into dense core vesicles. Neuropeptides are often co-released with other neuropeptides and neurotransmitters in a single neuron, yielding a multitude of effects. Once released, neuropeptides can diffuse widely to affect a broad range of targets. Synthesis Neuropeptides are synthesized from large, inactive precursor proteins called prepropeptides. Prepropeptides contain sequences for a family of distinct peptides and often contain repeated copies of the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
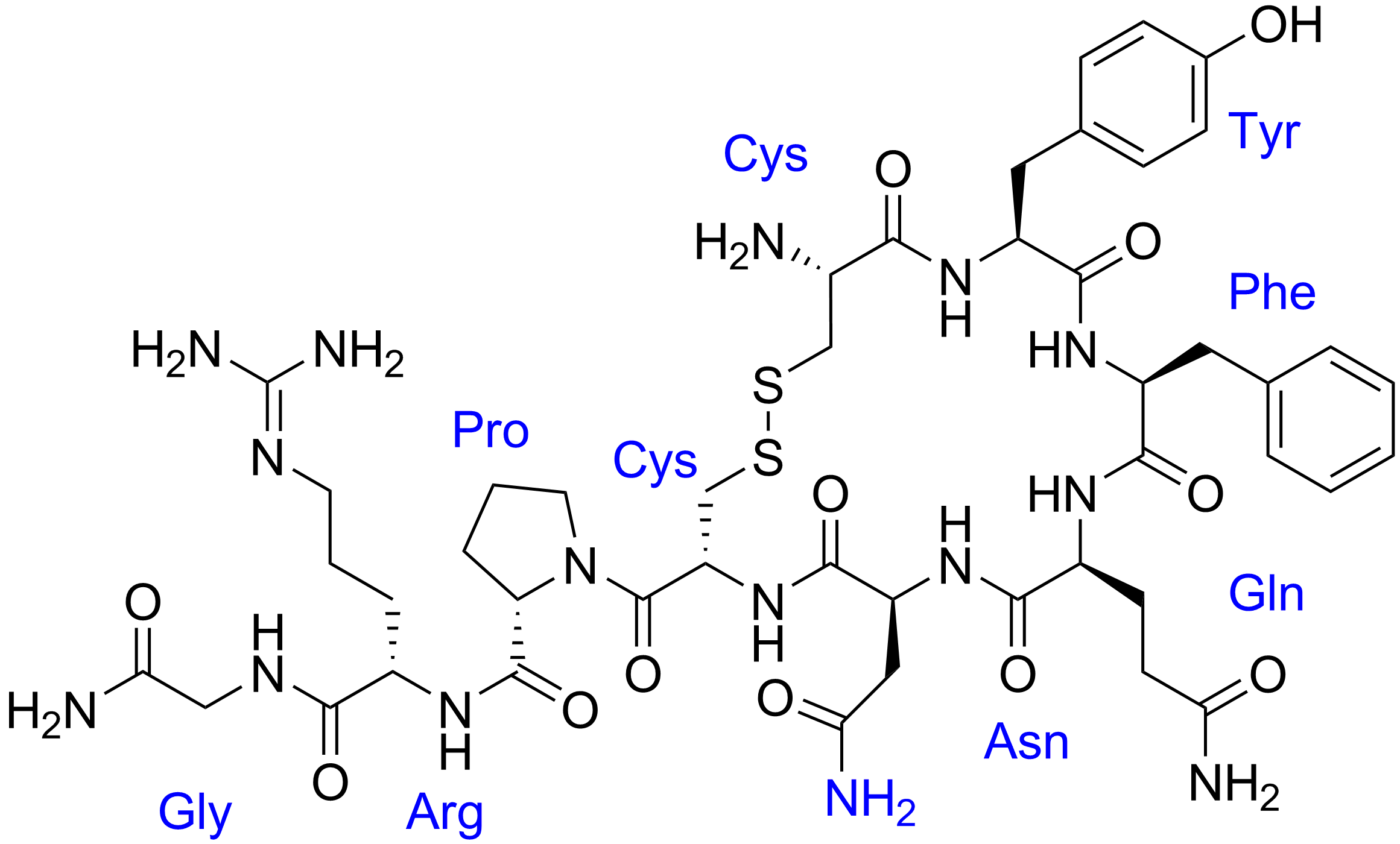
Neuropeptide Y
Neuropeptide Y (NPY) is a 36 amino-acid neuropeptide that is involved in various physiological and homeostatic processes in both the central and peripheral nervous systems. NPY has been identified as the most abundant peptide present in the mammalian central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord. It is secreted alongside other neurotransmitters such as GABA and glutamate. In the autonomic system it is produced mainly by neurons of the sympathetic nervous system and serves as a strong vasoconstrictor and also causes growth of fat tissue. In the brain, it is produced in various locations including the hypothalamus, and is thought to have several functions, including: increasing food intake and storage of energy as fat, reducing anxiety and stress, reducing pain perception, affecting the circadian rhythm, reducing voluntary alcohol intake, lowering blood pressure, and controlling epileptic seizures. Function Neuropeptide Y has been identified as bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuropeptide Y
Neuropeptide Y (NPY) is a 36 amino-acid neuropeptide that is involved in various physiological and homeostatic processes in both the central and peripheral nervous systems. NPY has been identified as the most abundant peptide present in the mammalian central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord. It is secreted alongside other neurotransmitters such as GABA and glutamate. In the autonomic system it is produced mainly by neurons of the sympathetic nervous system and serves as a strong vasoconstrictor and also causes growth of fat tissue. In the brain, it is produced in various locations including the hypothalamus, and is thought to have several functions, including: increasing food intake and storage of energy as fat, reducing anxiety and stress, reducing pain perception, affecting the circadian rhythm, reducing voluntary alcohol intake, lowering blood pressure, and controlling epileptic seizures. Function Neuropeptide Y has been identified as bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cocaine-and-amphetamine-regulated Transcript
Cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript, also known as CART, is a neuropeptide protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CARTPT'' gene. CART appears to have roles in reward, feeding, and stress, and it has the functional properties of an endogenous psychostimulant. Function CART is a neuropeptide that produces similar behavior in animals as cocaine and amphetamine, but conversely blocks the effects of cocaine when they are co-administered. The peptide is found in several areas, among them the ventral tegmental area (VTA) of the brain. When CART was injected into rat VTA, increased locomotor activity was seen, which is one of the signs of "central stimulation" caused by psychostimulants, such as cocaine and amphetamine. The same rats also tended to return to the place where they were injected. This is called conditioned place preference and is also seen after injection of cocaine. CART peptides, in particular, CART(55–102), seem to have an important function in the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substance P
Substance P (SP) is an undecapeptide (a peptide composed of a chain of 11 amino acid residues) and a member of the tachykinin neuropeptide family. It is a neuropeptide, acting as a neurotransmitter and as a neuromodulator. Substance P and its closely related neurokinin A (NKA) are produced from a polyprotein precursor after differential splicing of the preprotachykinin A gene. The deduced amino acid sequence of substance P is as follows: * Arg Pro Lys Pro Gln Gln Phe Phe Gly Leu Met (RPKPQQFFGLM) with an amidation at the C-terminus. Substance P is released from the terminals of specific sensory nerves. It is found in the brain and spinal cord and is associated with inflammatory processes and pain. Discovery The original discovery of Substance P (SP) was in 1931 by Ulf von Euler and John H. Gaddum as a tissue extract that caused intestinal contraction ''in vitro''. Its tissue distribution and biologic actions were further investigated over the following decades. The ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide
Vasoactive intestinal peptide, also known as vasoactive intestinal polypeptide or VIP, is a peptide hormone that is vasoactive in the intestine. VIP is a peptide of 28 amino acid residues that belongs to a glucagon/secretin superfamily, the ligand of class II G protein–coupled receptors. VIP is produced in many tissues of vertebrates including the gut, pancreas, and suprachiasmatic nuclei of the hypothalamus in the brain. VIP stimulates contractility in the heart, causes vasodilation, increases glycogenolysis, lowers arterial blood pressure and relaxes the smooth muscle of trachea, stomach and gallbladder. In humans, the vasoactive intestinal peptide is encoded by the ''VIP'' gene. VIP has a half-life (t½) in the blood of about two minutes. Function In the body VIP has an effect on several tissues: In the digestive system, VIP seems to induce smooth muscle relaxation (lower esophageal sphincter, stomach, gallbladder), stimulate secretion of water into pancreatic juice a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galanin-like Peptide
Galanin-like peptide (GALP) is a neuropeptide present in humans and other mammals. It is a 60-amino acid polypeptide produced in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus and the posterior pituitary gland The posterior pituitary (or neurohypophysis) is the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland which is part of the endocrine system. The posterior pituitary is not glandular as is the anterior pituitary. Instead, it is largely a collection of axona .... It is involved in the regulation of appetite and may also have other roles such as in inflammation, sex behavior, and stress. Notes Neuropeptides {{biochem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcuate Nucleus
The arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus (also known as ARH, ARC, or infundibular nucleus) is an aggregation of neurons in the mediobasal hypothalamus, adjacent to the third ventricle and the median eminence. The arcuate nucleus includes several important and diverse populations of neurons that help mediate different neuroendocrine and physiological functions, including neuroendocrine neurons, centrally projecting neurons, and astrocytes. The populations of neurons found in the arcuate nucleus are based on the hormones they secrete or interact with and are responsible for hypothalamic function, such as regulating hormones released from the pituitary gland or secreting their own hormones. Neurons in this region are also responsible for integrating information and providing inputs to other nuclei in the hypothalamus or inputs to areas outside this region of the brain. These neurons, generated from the ventral part of the periventricular epithelium during embryonic development, locat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasopressin
Human vasopressin, also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH), arginine vasopressin (AVP) or argipressin, is a hormone synthesized from the AVP gene as a peptide prohormone in neurons in the hypothalamus, and is converted to AVP. It then travels down the axon terminating in the posterior pituitary, and is released from vesicles into the circulation in response to extracellular fluid hypertonicity (hyperosmolality). AVP has two primary functions. First, it increases the amount of solute-free water reabsorbed back into the circulation from the filtrate in the kidney tubules of the nephrons. Second, AVP constricts arterioles, which increases peripheral vascular resistance and raises arterial blood pressure. A third function is possible. Some AVP may be released directly into the brain from the hypothalamus, and may play an important role in social behavior, sexual motivation and pair bonding, and maternal responses to stress. Vasopressin induces differentiation of stem cells in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agouti-related Peptide
Agouti-related protein (AgRP), also called agouti-related peptide, is a neuropeptide produced in the brain by the AgRP/NPY neuron. It is synthesized in neuropeptide Y (NPY)-containing cell bodies located in the ventromedial part of the arcuate nucleus in the hypothalamus. AgRP is co-expressed with NPY and acts to increase appetite and decrease metabolism and energy expenditure. It is one of the most potent and long-lasting of appetite stimulators. In humans, the agouti-related peptide is encoded by the ''AGRP'' gene. Structure AgRP is a paracrine signaling molecule made of 112 amino acids (the gene product of 132 amino acids is processed by removal of the N-terminal 20-residue signal peptide domain). It was independently identified by two teams in 1997 based on its sequence similarity with agouti signalling peptide (ASIP), a protein synthesized in the skin controlling coat colour. AgRP is approximately 25% identical to ASIP. The murine homologue of AgRP consists of 111 amino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha-Melanocyte-stimulating Hormone
α-Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH) is an endogenous peptide hormone and neuropeptide of the melanocortin family, with a tridecapeptide structure and the amino acid sequence Ac-Ser-Tyr-Ser-Met-Glu-His-Phe-Arg-Trp-Gly-Lys-Pro-Val-NH2. It is the most important of the melanocyte-stimulating hormones (MSHs) (also known as melanotropins) in stimulating melanogenesis, a process that in mammals (including humans) is responsible for pigmentation primarily of the hair and skin. It also plays a role in feeding behavior, energy homeostasis, sexual activity, and protection against ischemia and reperfusion injury. α-MSH is a non-selective full agonist of the melanocortin receptors MC1 (Ki = 0.230 nM), MC3 (Ki = 31.5 nM), MC4 (Ki = 900 nM), and MC5 (Ki = 7160 nM), but not MC2 (which is exclusive for adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)). Activation of the MC1 receptor is responsible for its effect on pigmentation, whereas its regulation of appetite, metabolism, and sexual behavior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proctolin
Proctolin is a neuropeptide present in insects and crustaceans. It was first found in ''Periplaneta americana'', a species of cockroach in 1975. Proctolin was extracted from 125,000 cockroaches and the Edman degradation was carried out on the sample to determine the amino acid sequence, which is Arg-Tyr-Leu-Pro-Thr. Proctolin was the first insect neuropeptide to be sequenced. Starratt and Brown identified it as a visceral muscle neurotransmitter. However, it now appears that there are many more functions of proctolin, and it is present in many more species. Localisation Proctolin is found in the following insect orders: * Orthoptera * Hemiptera * Diptera * Coleoptera Proctolin may also be present in molluscs, annelids, decapod crustaceans, and possibly even some mammals. Structure The proctolin structure is very highly conserved between species. Proctolin analogs have been synthesised in order to find out more about the structure of the molecule. It was found that eac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH; also adrenocorticotropin, corticotropin) is a polypeptide tropic hormone produced by and secreted by the anterior pituitary gland. It is also used as a medication and diagnostic agent. ACTH is an important component of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and is often produced in response to biological stress (along with its precursor corticotropin-releasing hormone from the hypothalamus). Its principal effects are increased production and release of cortisol by the cortex of the adrenal gland. ACTH is also related to the circadian rhythm in many organisms. Deficiency of ACTH is an indicator of secondary adrenal insufficiency (suppressed production of ACTH due to an impairment of the pituitary gland or hypothalamus, cf. hypopituitarism) or tertiary adrenal insufficiency (disease of the hypothalamus, with a decrease in the release of corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH)). Conversely, chronically elevated ACTH levels occur in primary ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |