|
Neuroevolution
Neuroevolution, or neuro-evolution, is a form of artificial intelligence that uses evolutionary algorithms to generate artificial neural networks (ANN), parameters, and rules. It is most commonly applied in artificial life, general game playing and evolutionary robotics. The main benefit is that neuroevolution can be applied more widely than supervised learning algorithms, which require a syllabus of correct input-output pairs. In contrast, neuroevolution requires only a measure of a network's performance at a task. For example, the outcome of a game (i.e., whether one player won or lost) can be easily measured without providing labeled examples of desired strategies. Neuroevolution is commonly used as part of the reinforcement learning paradigm, and it can be contrasted with conventional deep learning techniques that use backpropagation (gradient descent on a neural network) with a fixed topology. Features Many neuroevolution algorithms have been defined. One common distinct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compositional Pattern-producing Network
Compositional pattern-producing networks (CPPNs) are a variation of artificial neural networks (ANNs) that have an architecture whose evolution is guided by genetic algorithms.Stanley, Kenneth O. "Compositional pattern producing networks: A novel abstraction of development." Genetic programming and evolvable machines 8.2 (2007): 131-162. While ANNs often contain only sigmoid functions and sometimes Gaussian functions, CPPNs can include both types of functions and many others. The choice of functions for the canonical set can be biased toward specific types of patterns and regularities. For example, periodic functions such as sine produce segmented patterns with repetitions, while symmetric functions such as Gaussian produce symmetric patterns. Linear functions can be employed to produce linear or fractal-like patterns. Thus, the architect of a CPPN-based genetic art system can bias the types of patterns it generates by deciding the set of canonical functions to include. Furthermore, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NeuroEvolution Of Augmenting Topologies
NeuroEvolution of Augmenting Topologies (NEAT) is a genetic algorithm (GA) for generating evolving artificial neural networks (a neuroevolution technique) developed by Kenneth Stanley and Risto Miikkulainen in 2002 while at The University of Texas at Austin. It alters both the weighting parameters and structures of networks, attempting to find a balance between the fitness of evolved solutions and their diversity. It is based on applying three key techniques: tracking genes with history markers to allow crossover among topologies, applying speciation (the evolution of species) to preserve innovations, and developing topologies incrementally from simple initial structures ("complexifying"). Performance On simple control tasks, the NEAT algorithm often arrives at effective networks more quickly than other contemporary neuro-evolutionary techniques and reinforcement learning methods, as of 2006.Kenneth O. Stanley and Risto Miikkulainen (2002). "Evolving Neural Networks Through Augm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Neural Network
In machine learning, a neural network (also artificial neural network or neural net, abbreviated ANN or NN) is a computational model inspired by the structure and functions of biological neural networks. A neural network consists of connected units or nodes called '' artificial neurons'', which loosely model the neurons in the brain. Artificial neuron models that mimic biological neurons more closely have also been recently investigated and shown to significantly improve performance. These are connected by ''edges'', which model the synapses in the brain. Each artificial neuron receives signals from connected neurons, then processes them and sends a signal to other connected neurons. The "signal" is a real number, and the output of each neuron is computed by some non-linear function of the sum of its inputs, called the '' activation function''. The strength of the signal at each connection is determined by a ''weight'', which adjusts during the learning process. Typically, ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HyperNEAT
Hypercube-based NEAT, or HyperNEAT, is a generative encoding that evolves artificial neural networks In machine learning, a neural network (also artificial neural network or neural net, abbreviated ANN or NN) is a computational model inspired by the structure and functions of biological neural networks. A neural network consists of connected ... (ANNs) with the principles of the widely used NeuroEvolution of Augmented Topologies (NEAT) algorithm developed by Kenneth Stanley. It is a novel technique for evolving large-scale neural networks using the geometric regularities of the task domain. It uses Compositional Pattern Producing Networks ( CPPNs), which are used to generate the images foPicbreeder.org and shapes foEndlessForms.com. HyperNEAT has recently been extended to also evolve plastic ANNs and to evolve the location of every neuron in the network. Applications to date * Multi-agent learning * Checkers board evaluation * Controlling Legged Robovideo* Comparing G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uber
Uber Technologies, Inc. is an American multinational transportation company that provides Ridesharing company, ride-hailing services, courier services, food delivery, and freight transport. It is headquartered in San Francisco, California, and operates in approximately 70 countries and 15,000 cities worldwide. It is the largest ridesharing company worldwide with over 150 million monthly active users and 6 million active drivers and couriers. It coordinates an average of 28 million trips per day, and has coordinated 47 billion trips since its inception in 2010. In 2023, the company had a take rate (revenue as a percentage of gross bookings) of 28.7% for mobility services and 18.3% for food delivery. History In 2009, Garrett Camp, a co-founder of StumbleUpon, came up with the idea to create Uber to make it easier and cheaper to procure direct transportation. Camp and Travis Kalanick had spent $800 hiring a private driver on New Year's Eve, which they deemed excessive, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of research in computer science that develops and studies methods and software that enable machines to machine perception, perceive their environment and use machine learning, learning and intelligence to take actions that maximize their chances of achieving defined goals. High-profile applications of AI include advanced web search engines (e.g., Google Search); recommendation systems (used by YouTube, Amazon (company), Amazon, and Netflix); virtual assistants (e.g., Google Assistant, Siri, and Amazon Alexa, Alexa); autonomous vehicles (e.g., Waymo); Generative artificial intelligence, generative and Computational creativity, creative tools (e.g., ChatGPT and AI art); and Superintelligence, superhuman play and analysis in strategy games (e.g., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fitness Function
A fitness function is a particular type of objective or cost function that is used to summarize, as a single figure of merit, how close a given candidate solution is to achieving the set aims. It is an important component of evolutionary algorithms (EA), such as genetic programming, evolution strategies or genetic algorithms. An EA is a metaheuristic that reproduces the basic principles of biological evolution as a computer algorithm in order to solve challenging optimization or planning tasks, at least approximately. For this purpose, many candidate solutions are generated, which are evaluated using a fitness function in order to guide the evolutionary development towards the desired goal. Similar quality functions are also used in other metaheuristics, such as ant colony optimization or particle swarm optimization. In the field of EAs, each candidate solution, also called an ''individual'', is commonly represented as a string of numbers (referred to as a chromosome). A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
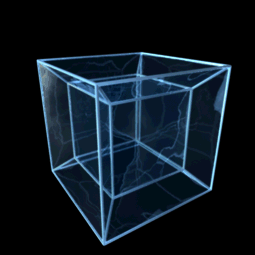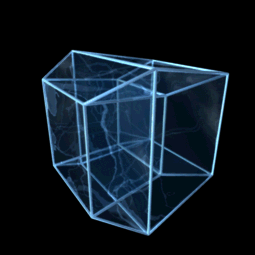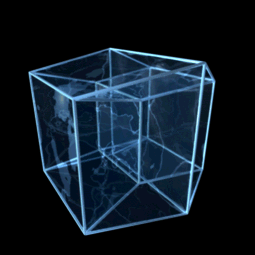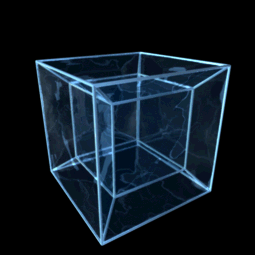
Hypercube
In geometry, a hypercube is an ''n''-dimensional analogue of a square ( ) and a cube ( ); the special case for is known as a ''tesseract''. It is a closed, compact, convex figure whose 1- skeleton consists of groups of opposite parallel line segments aligned in each of the space's dimensions, perpendicular to each other and of the same length. A unit hypercube's longest diagonal in ''n'' dimensions is equal to \sqrt. An ''n''-dimensional hypercube is more commonly referred to as an ''n''-cube or sometimes as an ''n''-dimensional cube. The term measure polytope (originally from Elte, 1912) is also used, notably in the work of H. S. M. Coxeter who also labels the hypercubes the γn polytopes. The hypercube is the special case of a hyperrectangle (also called an ''n-orthotope''). A ''unit hypercube'' is a hypercube whose side has length one unit. Often, the hypercube whose corners (or ''vertices'') are the 2''n'' points in R''n'' with each coordinate equal to 0 or 1 i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simulated Annealing
Simulated annealing (SA) is a probabilistic technique for approximating the global optimum of a given function. Specifically, it is a metaheuristic to approximate global optimization in a large search space for an optimization problem. For large numbers of local optima, SA can find the global optimum. It is often used when the search space is discrete (for example the traveling salesman problem, the boolean satisfiability problem, protein structure prediction, and job-shop scheduling). For problems where finding an approximate global optimum is more important than finding a precise local optimum in a fixed amount of time, simulated annealing may be preferable to exact algorithms such as gradient descent or branch and bound. The name of the algorithm comes from annealing in metallurgy, a technique involving heating and controlled cooling of a material to alter its physical properties. Both are attributes of the material that depend on their thermodynamic free energy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary Programming
Evolutionary programming is an evolutionary algorithm, where a share of new population is created by mutation of previous population without crossover. Evolutionary programming differs from evolution strategy ES(\mu+\lambda) in one detail. All individuals are selected for the new population, while in ES(\mu+\lambda), every individual has the same probability to be selected. It is one of the four major evolutionary algorithm paradigms. History It was first used by Lawrence J. Fogel in the US in 1960 in order to use simulated evolution as a learning process aiming to generate artificial intelligence. It was used to evolve finite-state machines as predictors. See also * Artificial intelligence * Genetic algorithm In computer science and operations research, a genetic algorithm (GA) is a metaheuristic inspired by the process of natural selection that belongs to the larger class of evolutionary algorithms (EA). Genetic algorithms are commonly used to g ... * Genetic opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Programming
Genetic programming (GP) is an evolutionary algorithm, an artificial intelligence technique mimicking natural evolution, which operates on a population of programs. It applies the genetic operators selection (evolutionary algorithm), selection according to a predefined fitness function, fitness measure, mutation (evolutionary algorithm), mutation and crossover (evolutionary algorithm), crossover. The crossover operation involves swapping specified parts of selected pairs (parents) to produce new and different offspring that become part of the new generation of programs. Some programs not selected for reproduction are copied from the current generation to the new generation. Mutation involves substitution of some random part of a program with some other random part of a program. Then the selection and other operations are recursively applied to the new generation of programs. Typically, members of each new generation are on average more fit than the members of the previous gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |