|
Neuroborreliosis
Neuroborreliosis is a disorder of the central nervous system. A neurological manifestation of Lyme disease, neuroborreliosis is caused by a systemic infection of spirochetes of the genus ''Borrelia.'' Symptoms of the disease include erythema migrans and flu-like symptoms. Signs and symptoms Neuroborreliosis is often preceded by the typical symptoms of Lyme disease, which include erythema migrans and flu-like symptoms such as fever and muscle aches. Neurologic symptoms of neuroborreliosis include the meningoradiculitis (which is more common in European patients), cranial nerve abnormalities, and altered mental status. Sensory findings may also be present. Rarely, a progressive form of encephalomyelitis may occur. In children, symptoms of neuroborreliosis include headache, sleep disturbance, and symptoms associated with increased intracranial pressure, such as papilledema. Less common childhood symptoms can include meningitis, myelitis, ataxia, and chorea. Ocular Lyme disease has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
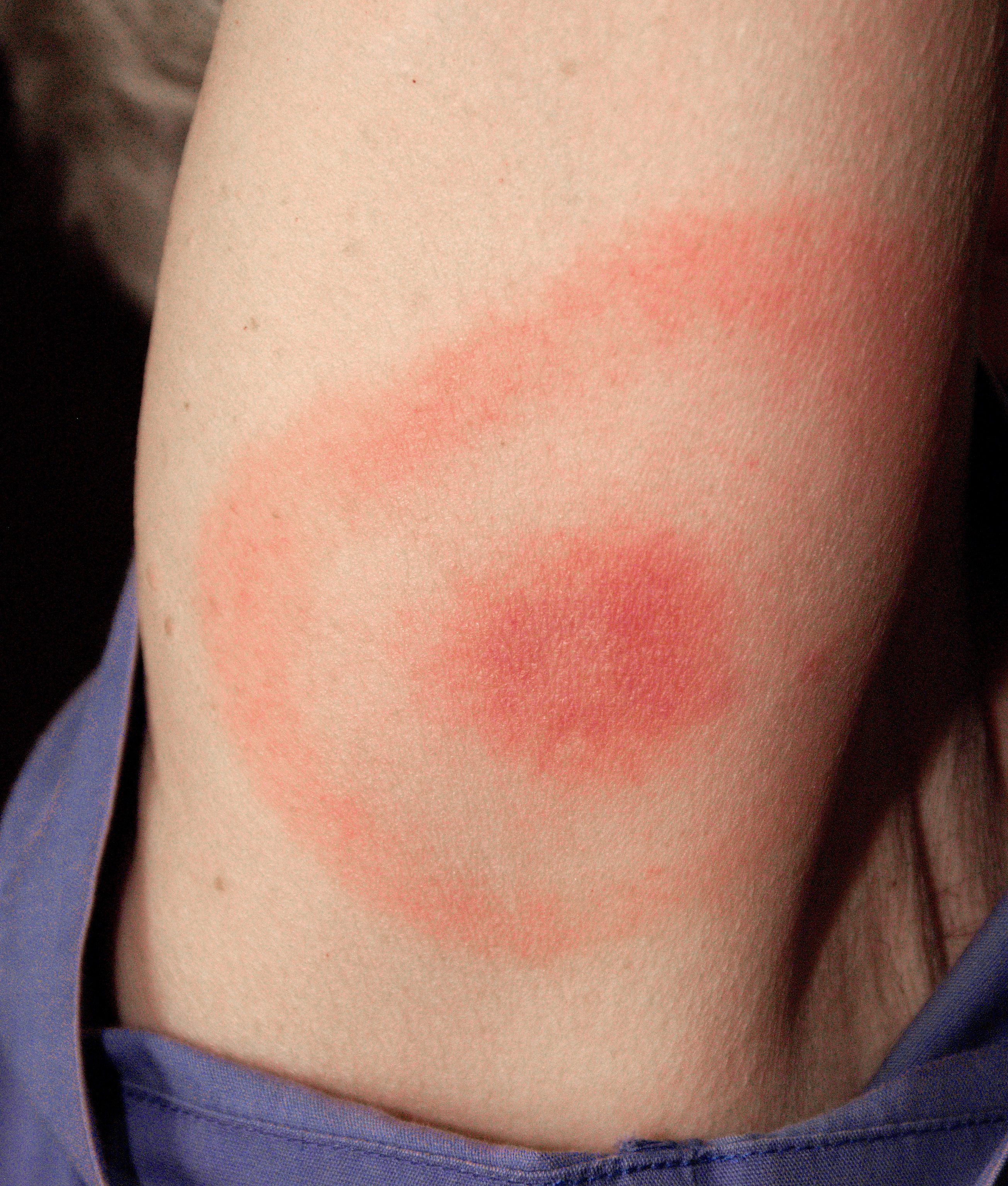
Lyme Disease
Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a vector-borne disease caused by the ''Borrelia'' bacterium, which is spread by ticks in the genus ''Ixodes''. The most common sign of infection is an expanding red rash, known as erythema migrans (EM), which appears at the site of the tick bite about a week afterwards. The rash is typically neither itchy nor painful. Approximately 70–80% of infected people develop a rash. Early diagnosis can be difficult. Other early symptoms may include fever, headaches and tiredness. If untreated, symptoms may include loss of the ability to move one or both sides of the face, joint pains, severe headaches with neck stiffness or heart palpitations. Months to years later repeated episodes of joint pain and swelling may occur. Occasionally shooting pains or tingling in the arms and legs may develop. Despite appropriate treatment about 10 to 20% of those affected develop joint pains, memory problems and tiredness for at least six months. Lym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphocytic Meningoradiculitis
Lymphocytic meningoradiculitis, also known as Bannwarth syndrome, is a neurological disease characterized as intense nerve pain radiating from the spine. The disease is caused by an infection of ''Borrelia burgdorferi'', a tick-borne spirochete bacterium also responsible for causing Lyme disease. Signs and symptoms Lymphocytic meningoradiculitis is characterized by an intense spinal pain in the lumbar and cervical regions, radiating to the extremities. Symptoms may include facial paralysis, abducens palsy, anorexia, tiredness, headache, double vision, paraesthesia, and erythema migrans. Treatment Lymphocytic meningoradiculitis is treated with antibiotics. Oral doxycycline or IV ceftriaxone are typically recommended for 14-21 days. History The disease was first reported in 1941 by German neurologist, Alfred Bannwarth, who described the main symptoms as intense radicular pain, facial palsy, severe headaches, and vomiting. A common feature he observed in his infected patients was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tick-borne Disease
Tick-borne diseases, which afflict humans and other animals, are caused by infectious agents transmitted by tick bites. They are caused by infection with a variety of pathogens, including rickettsia and other types of bacteria, viruses, and protozoa. The economic impact of tick-borne diseases is considered to be substantial in humans, and tick-borne diseases are estimated to affect ~80 % of cattle worldwide. 18 tick-borne pathogens have been identified in the United States according to the Centers for Disease Control and at least 27 are known globally. New tick-borne diseases have been discovered in the 21st century, due in part to the use of molecular assays and next-generation sequencing. The occurrence of ticks and tick-borne illnesses in humans is increasing. Tick populations are spreading into new areas, in part due to climate change. Tick populations are also affected by changes in the populations of their hosts (e.g. deer, cattle, mice, lizards) and those hosts' p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doxycycline
Doxycycline is a broad-spectrum tetracycline class antibiotic used in the treatment of infections caused by bacteria and certain parasites. It is used to treat bacterial pneumonia, acne, chlamydia infections, Lyme disease, cholera, typhus, and syphilis. It is also used to prevent malaria in combination with quinine. Doxycycline may be taken by mouth or by injection into a vein. Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and an increased risk of sunburn. Use during pregnancy is not recommended. Like other agents of the tetracycline class, it either slows or kills bacteria by inhibiting protein production. It kills malaria by targeting a plastid organelle, the apicoplast. Doxycycline was patented in 1957 and came into commercial use in 1967. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Doxycycline is available as a generic medicine. In 2020, it was the 79th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bismacine
Bismacine, also known as Chromacine, is a substance manufactured by American Biologics Corporation and marketed as a purported alternative treatment for Lyme disease. Bismacine contains high levels of bismuth, and two deaths are recorded following the use of intravenous bismacine to treat Lyme disease. In 2006, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ... warned consumers not to use bismacine, noting that it is ineffective and dangerous. References Bismuth Patent medicines Lyme disease {{Alt-med-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3%–6% by weight) in water for consumer use, and in higher concentrations for industrial use. Concentrated hydrogen peroxide, or " high-test peroxide", decomposes explosively when heated and has been used as a propellant in rocketry. Hydrogen peroxide is a reactive oxygen species and the simplest peroxide, a compound having an oxygen–oxygen single bond. It decomposes slowly when exposed to light, and rapidly in the presence of organic or reactive compounds. It is typically stored with a stabilizer in a weakly acidic solution in a dark bottle to block light. Hydrogen peroxide is found in biological systems including the human body. Enzymes that use or decompose hydrogen peroxide are classified as peroxidases. Properties The boiling poi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colloidal Silver
The medical uses of silver include its use in wound dressings, creams, and as an antibiotic coating on medical devices. Wound dressings containing silver sulfadiazine or silver nanomaterials may be used to treat external infections. The limited evidence available shows that silver coatings on endotracheal breathing tubes may reduce the incidence of ventilator-associated pneumonia. There is tentative evidence that using silver-alloy indwelling catheters for short-term catheterizing will reduce the risk of catheter-acquired urinary tract infections. Silver generally has low toxicity, and minimal risk is expected when silver is used in approved medical applications. Alternative medicine products such as colloidal silver are not safe or effective. Mechanism of action Silver and most silver compounds have an oligodynamic effect and are toxic for bacteria, algae, and fungi ''in vitro''. The antibacterial action of silver is dependent on the silver ion. The effectiveness of silver co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
Hyperbaric medicine is medical treatment in which an ambient pressure greater than sea level atmospheric pressure is a necessary component. The treatment comprises hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), the medical use of oxygen at an ambient pressure higher than atmospheric pressure, and therapeutic recompression for decompression illness, intended to reduce the injurious effects of systemic gas bubbles by physically reducing their size and providing improved conditions for elimination of bubbles and excess dissolved gas. The equipment required for hyperbaric oxygen treatment consists of a pressure chamber, which may be of rigid or flexible construction, and a means of delivering 100% oxygen. Operation is performed to a predetermined schedule by trained personnel who monitor the patient and may adjust the schedule as required. HBOT found early use in the treatment of decompression sickness, and has also shown great effectiveness in treating conditions such as gas gangrene and carbon mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malariotherapy
The malaria therapy (or malaria inoculation, and sometimes malariotherapy) is a medical procedure of treating diseases using artificial injection of malaria parasites. It is a type of pyrotherapy (or pyretotherapy) by which high fever is induced to stop or eliminate symptoms of certain diseases. In malaria therapy, malarial parasites (''Plasmodium'') are specifically used to cause fever, and an elevated body temperature reduces the symptoms of or cure the diseases. As the primary disease is treated, the malaria is then cured using antimalarial drugs. The method was developed by Austrian physician Julius Wagner-Jauregg in 1917 for the treatment of neurosyphilis for which he received the 1927 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Background The beneficial effects of infections in mental problems were known in the Ancient world. Hippocrates in the 4th century BCE recorded bacterial infections such as dysentery and dropsy reducing the symptoms of madness; and that malaria (quartan fev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borrelia Burgdorferi
''Borrelia burgdorferi'' is a bacterial species of the spirochete class in the genus ''Borrelia'', and is one of the causative agents of Lyme disease in humans. Along with a few similar genospecies, some of which also cause Lyme disease, it makes up the species complex of ''Borrelia burgdorferi'' sensu lato. The complex currently comprises 20 accepted and 3 proposed genospecies. ''B. burgdorferi'' sensu stricto exists in North America and Eurasia and until 2016 was the only known cause of Lyme disease in North America. ''Borrelia'' species are Gram-negative. Microbiology ''Borrelia burgdorferi'' is named after the researcher Willy Burgdorfer, who first isolated the bacterium in 1982. ''Borrelia burgdorferi'' is a microaerophile, requiring small amounts of oxygen in order to undergo glycolysis and survive. Like all other ''Borrelia'' sps., this bacterium is also gram-negative and a spirochete. Borrelia colonies are often smaller, rounded, and white with an elevated center. ''B. b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Randomized Controlled Trial
A randomized controlled trial (or randomized control trial; RCT) is a form of scientific experiment used to control factors not under direct experimental control. Examples of RCTs are clinical trials that compare the effects of drugs, surgical techniques, medical devices, diagnostic procedures or other medical treatments. Participants who enroll in RCTs differ from one another in known and unknown ways that can influence study outcomes, and yet cannot be directly controlled. By Random assignment, randomly allocating participants among compared treatments, an RCT enables ''statistical control'' over these influences. Provided it is designed well, conducted properly, and enrolls enough participants, an RCT may achieve sufficient control over these confounding factors to deliver a useful comparison of the treatments studied. Definition and examples An RCT in clinical research typically compares a proposed new treatment against an existing Standard of care#Medical standard of care, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cefotaxime
Cefotaxime is an antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections in human, other animals and plant tissue culture. Specifically in humans it is used to treat joint infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, meningitis, pneumonia, urinary tract infections, sepsis, gonorrhea, and cellulitis. It is given either by injection into a vein or muscle. Common side effects include nausea, allergic reactions, and inflammation at the site of injection. Another side effect may include ''Clostridium difficile'' diarrhea. It is not recommended in people who have had previous anaphylaxis to a penicillin. It is relatively safe for use during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It is in the third-generation cephalosporin family of medications and works by interfering with the bacteria's cell wall. Cefotaxime was discovered in 1976, and came into commercial use in 1980. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a generic medication. Medica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |