|
Neural Correlates Of Consciousness
The neural correlates of consciousness (NCC) refer to the relationships between mental states and neural states and constitute the minimal set of neuronal events and mechanisms sufficient for a specific conscious percept. Neuroscientists use empirical approaches to discover neural correlates of subjective phenomena; that is, neural changes which necessarily and regularly correlate with a specific experience. The set should be ''minimal'' because, under the materialist assumption that the brain is sufficient to give rise to any given conscious experience, the question is which of its components is necessary to produce it. Neurobiological approach to consciousness A science of consciousness must explain the exact relationship between subjective mental states and brain states, the nature of the relationship between the conscious mind and the electro-chemical interactions in the body (mind–body problem). Progress in neuropsychology and neurophilosophy has come from focusing on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Oscillations
Neural oscillations, or brainwaves, are rhythmic or repetitive patterns of neural activity in the central nervous system. Neural tissue can generate oscillatory activity in many ways, driven either by mechanisms within individual neurons or by interactions between neurons. In individual neurons, oscillations can appear either as oscillations in membrane potential or as rhythmic patterns of action potentials, which then produce oscillatory activation of post-synaptic neurons. At the level of neural ensembles, synchronized activity of large numbers of neurons can give rise to macroscopic oscillations, which can be observed in an electroencephalogram. Oscillatory activity in groups of neurons generally arises from feedback connections between the neurons that result in the synchronization of their firing patterns. The interaction between neurons can give rise to oscillations at a different frequency than the firing frequency of individual neurons. A well-known example of macrosc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tononi2016
Carlo Annibale Tononi (1675–1730) was a luthier who trained and worked with his father in the Tononi family workshop in Bologna, Italy until his father, Johannes Tononi, died in 1713. After his father's death, Tononi moved to the more important center of music in Italy, Venice. In the late 17th century, Bologna was a great centre for art and especially of string playing, being Arcangelo Corelli's home town. By the early 18th century, Venice had become a more important cultural centre (for music and lutherie and instrument making). Carlo Tononi moved to Venice between 1713 and 1716, where he became one of the foremost makers of the new Venetian School. Before his death, Tononi modified his will to provide for his funeral. He requested that the proceeds from the sale of one of his cellos be used to pay for a mass to be said for his soul. On 21 April 1730, his executors published his will after his death. A genuine Tononi violin ranges in value from $45,000 to $450,000 depending ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
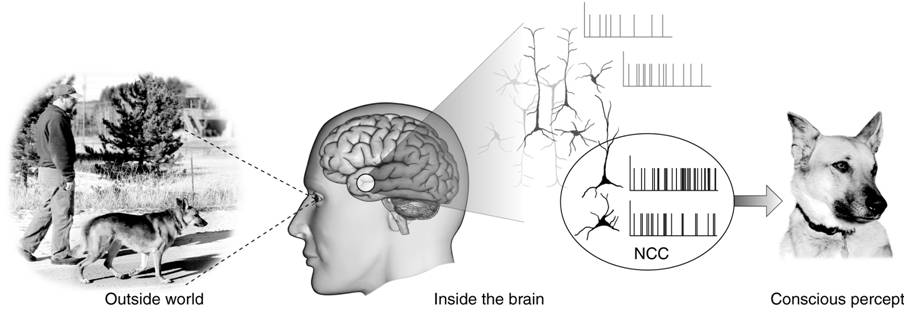
Integrated Information Theory
Integrated information theory (IIT) attempts to provide a framework capable of explaining why some physical systems (such as human brains) are conscious, why they feel the particular way they do in particular states (e.g. why our visual field appears extended when we gaze out at the night sky), and what it would take for other physical systems to be conscious (Are other animals conscious? Might the whole Universe be?). In principle, once the theory is mature and has been tested extensively in controlled conditions, the IIT framework may be capable of providing a concrete inference about whether any physical system is conscious, to what degree it is conscious, and what particular experience it is having. In IIT, a system's consciousness (what it is like subjectively) is conjectured to be identical to its causal properties (what it is like objectively). Therefore it should be possible to account for the conscious experience of a physical system by unfolding its complete causal power ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schiff2004
Schiff is a Jewish and German surname meaning "ship". The Schiffs are known from "about 1370, the earliest date to which any contemporary Jewish family can be definitely traced". It may refer to: People * Adam Schiff (born 1960), American politician, California state Senator and US Representative * András Schiff (born 1953), Hungarian pianist * Arthur Schiff (1940–2006), American infomercial copywriter * Barry Schiff (born 1938), American pilot and journalist * David Schiff (born 1945), American composer * Don Schiff (born 1955), American composer and musician * Dorothy Schiff (1903–1989), American newspaper proprietor * Frieda Warburg (1876–1958), American philanthropist * Gary Schiff (born 1972), American politician * Heinrich Schiff (1951–2016), Austrian cellist * Hugo Schiff (1834–1915), German chemist who discovered Schiff base and Schiff test * Irwin Schiff (born 1928), American tax protestor * Jacob Schiff (1847–1920), German-born American banker * Jeff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epileptic
Epilepsy is a group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking due to abnormal electrical activity in the brain. These episodes can result in physical injuries, either directly such as broken bones or through causing accidents. In epilepsy, seizures tend to recur and may have no immediate underlying cause. Isolated seizures that are provoked by a specific cause such as poisoning are not deemed to represent epilepsy. People with epilepsy may be treated differently in various areas of the world and experience varying degrees of social stigma due to the alarming nature of their symptoms. The underlying mechanism of epileptic seizures is excessive and abnormal neuronal activity in the cortex of the brain which can be observed in the electroencephalogram (EEG) of an individual. The reason this occurs in most cases of epilepsy is u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimally Conscious State
A minimally conscious state (MCS) is a disorder of consciousness distinct from persistent vegetative state and locked-in syndrome. Unlike persistent vegetative state, patients with MCS have partial preservation of conscious awareness. MCS is a relatively new category of disorders of consciousness. The natural history and longer term outcome of MCS have not yet been thoroughly studied. The prevalence of MCS was estimated to be 9 times of PVS cases (adult and pediatric), or between 112,000 to 280,000 in the US by year 2000. Pathophysiology Neuroimaging Because minimally conscious state is a relatively new criterion for diagnosis, there are very few functional imaging studies of patients with this condition. Preliminary data has shown that overall cerebral metabolism is less than in those with conscious awareness (20–40% of normal) and is slightly higher but comparable to those in vegetative states. Activation in the medial parietal cortex and adjacent posterior cingulate cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persistent Vegetative State
A persistent vegetative state (PVS) or post-coma unresponsiveness (PCU) is a disorder of consciousness in which patients with severe brain damage are in a state of partial arousal rather than true awareness. After four weeks in a vegetative state (VS), the patient is classified as being in a persistent vegetative state. This diagnosis is classified as a permanent vegetative state some months (three in the US and six in the UK) after a non-traumatic brain injury or one year after a traumatic injury. The term unresponsive wakefulness syndrome may be alternatively used, as "vegetative state" has some negative connotations among the public. Definition There are several definitions that vary by technical versus layman's usage. There are different legal implications in different countries. Medical definition Per the British Royal College of Physicians of London, a persistent vegetative state is "a wakeful unconscious state that lasts longer than a few weeks is referred to as a pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal wake-sleep cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. Coma patients exhibit a complete absence of wakefulness and are unable to consciously feel, speak or move. Comas can be derived by natural causes, or can be medically induced. Clinically, a coma can be defined as the inability consistently to follow a one-step command. It can also be defined as a score of ≤ 8 on the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) lasting ≥ 6 hours. For a patient to maintain consciousness, the components of ''wakefulness'' and ''awareness'' must be maintained. Wakefulness describes the quantitative degree of consciousness, whereas awareness relates to the qualitative aspects of the functions mediated by the cortex, including cognitive abilities such as attention, sensory perception, explicit memory, language, the execution of tasks, tempora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasgow Coma Scale
The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) is a clinical scale used to reliably measure a person's level of consciousness after a brain injury. The GCS assesses a person based on their ability to perform eye movements, speak, and move their body. These three behaviours make up the three elements of the scale: eye, verbal, and motor. A person's GCS score can range from 3 (completely unresponsive) to 15 (responsive). This score is used to guide immediate medical care after a brain injury (such as a car accident) and also to monitor hospitalised patients and track their level of consciousness. Lower GCS scores are correlated with higher risk of death. However, the GCS score alone should not be used on its own to predict the outcome for an individual person with brain injury. Scoring The Glasgow Coma Scale is used for people above the age of two and composed of three tests: eye, verbal, and motor responses. The scores for each of these tests are indicated in the table below. The Glasgow Coma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circadian
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural, internal process that regulates the sleep–wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours. It can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., endogenous) and responds to the environment ( entrained by the environment). These 24-hour rhythms are driven by a circadian clock, and they have been widely observed in animals, plants, fungi and cyanobacteria. The term ''circadian'' comes from the Latin '' circa'', meaning "approximately", and ''dies'', meaning "day". Processes with 24-hour cycles are more generally called diurnal rhythms; diurnal rhythms should not be called circadian rhythms unless they can be confirmed as endogenous, and not environmental. Although circadian rhythms are endogenous, they are adjusted to the local environment by external cues called zeitgebers (German for "time givers"), which include light, temperature and redox cycles. In clinical settings, an abnormal circadian rhythm in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
REM Sleep
Rapid eye movement sleep (REM sleep or REMS) is a unique phase of sleep in mammals and birds, characterized by random rapid movement of the eyes, accompanied by low muscle tone throughout the body, and the propensity of the sleeper to dream vividly. The REM phase is also known as paradoxical sleep (PS) and sometimes desynchronized sleep or dreamy sleep, because of physiological similarities to waking states including rapid, low-voltage desynchronized brain waves. Electrical and chemical activity regulating this phase seems to originate in the brain stem, and is characterized most notably by an abundance of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, combined with a nearly complete absence of monoamine neurotransmitters histamine, serotonin and norepinephrine. Experiences of REM sleep are not transferred to permanent memory due to absence of norepinephrine. REM sleep is physiologically different from the other phases of sleep, which are collectively referred to as non-REM sleep (NRE ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |