|
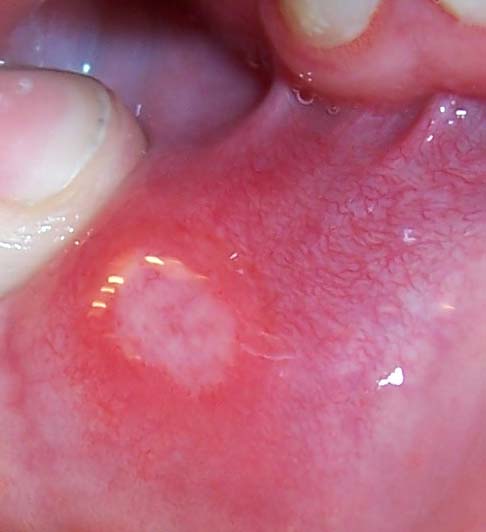
Necrolytic Migratory Erythema
Necrolytic migratory erythema is a red, blistering rash that spreads across the skin. It particularly affects the skin around the mouth and distal extremities; but may also be found on the lower abdomen, buttocks, perineum, and groin. It is strongly associated with glucagonoma, a glucagon-producing tumor of the pancreas, but is also seen in a number of other conditions including liver disease and intestinal malabsorption. Signs and symptoms Clinical features NME features a characteristic skin eruption of red patches with irregular borders, intact and ruptured vesicles, and crust formation. It commonly affects the limbs and skin surrounding the lips, although less commonly the abdomen, perineum, thighs, buttocks, and groin may be affected. Frequently these areas may be left dry or fissured as a result. All stages of lesion development may be observed synchronously. The initial eruption may be exacerbated by pressure or trauma to the affected areas. Associated conditions Will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucagonoma
Glucagonoma is a very rare tumor of the pancreatic alpha cells that results in the overproduction of the hormone, glucagon. Typically associated with a rash called necrolytic migratory erythema, weight loss, and mild diabetes mellitus, most people with glucagonoma contract it spontaneously. However, about 10% of cases are associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN-1) syndrome. Causes Although the cause of glucagonoma is unknown, some genetic factors may lead to the condition. A family history of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) is a risk factor. Additionally, those with Mahvash disease have an increased risk for glucagonoma, as the glucagon receptor gene (GCGR) is mutated. Mechanism Glucagonoma results from the overproduction of glucagon, a peptide hormone located in the pancreatic alpha cells. Classic symptoms include, but are not limited to, necrolytic migratory erythema (NME), diabetes mellitus, and weight loss. NME presents in about 70% of cases of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crohn's Disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea (which may be bloody if inflammation is severe), fever, abdominal distension, and weight loss. Complications outside of the gastrointestinal tract may include anemia, skin rashes, arthritis, inflammation of the eye, and fatigue. The skin rashes may be due to infections as well as pyoderma gangrenosum or erythema nodosum. Bowel obstruction may occur as a complication of chronic inflammation, and those with the disease are at greater risk of colon cancer and small bowel cancer. While the precise causes of Crohn's disease (CD) are unknown, it is believed to be caused by a combination of environmental, immune, and bacterial factors in genetically susceptible individuals. It results in a chronic inflammatory disorder, in which the body's immune system defends the gastrointestinal tract, possibly targeting microbial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cutaneous Conditions
Many skin conditions affect the human integumentary system—the organ system covering the entire surface of the body and composed of skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment. The skin weighs an average of four kilograms, covers an area of two square metres, and is made of three distinct layers: the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. The two main types of human skin are: glabrous skin, the hairless skin on the palms and soles (also referred to as the "palmoplantar" surfaces), and hair-bearing skin.Burns, Tony; ''et al''. (2006) ''Rook's Textbook of Dermatology CD-ROM''. Wiley-Blackwell. . Within the latter type, the hairs occur in structures called pilosebaceous units, each with hair follicle, sebaceous gland, and associated arrector pili muscle. In the embryo, the epidermis, hair, and glands form from the ectoderm, which is chemically influenced by the underlying mesoderm th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octreotide
Octreotide, sold under the brand name Sandostatin among others, is an octapeptide that mimics natural somatostatin pharmacologically, though it is a more potent inhibitor of growth hormone, glucagon, and insulin than the natural hormone. It was first synthesized in 1979 by the chemist Wilfried Bauer, and binds predominantly to the somatostatin receptors SSTR2 and SSTR5. It was approved for use in the United States in 1988. Octreotide (Mycapssa) was approved for medical use in the European Union in 2022. , octreotide (Mycapssa) is the first and only oral somatostatin analog (SSA) approved by the FDA. Medical uses Tumors Octreotide is used for the treatment of growth hormone producing tumors ( acromegaly and gigantism), when surgery is contraindicated, pituitary tumors that secrete thyroid-stimulating hormone (thyrotropinomata), diarrhea and flushing episodes associated with carcinoid syndrome, and diarrhea in people with vasoactive intestinal peptide-secreting tumors (VIPomas) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
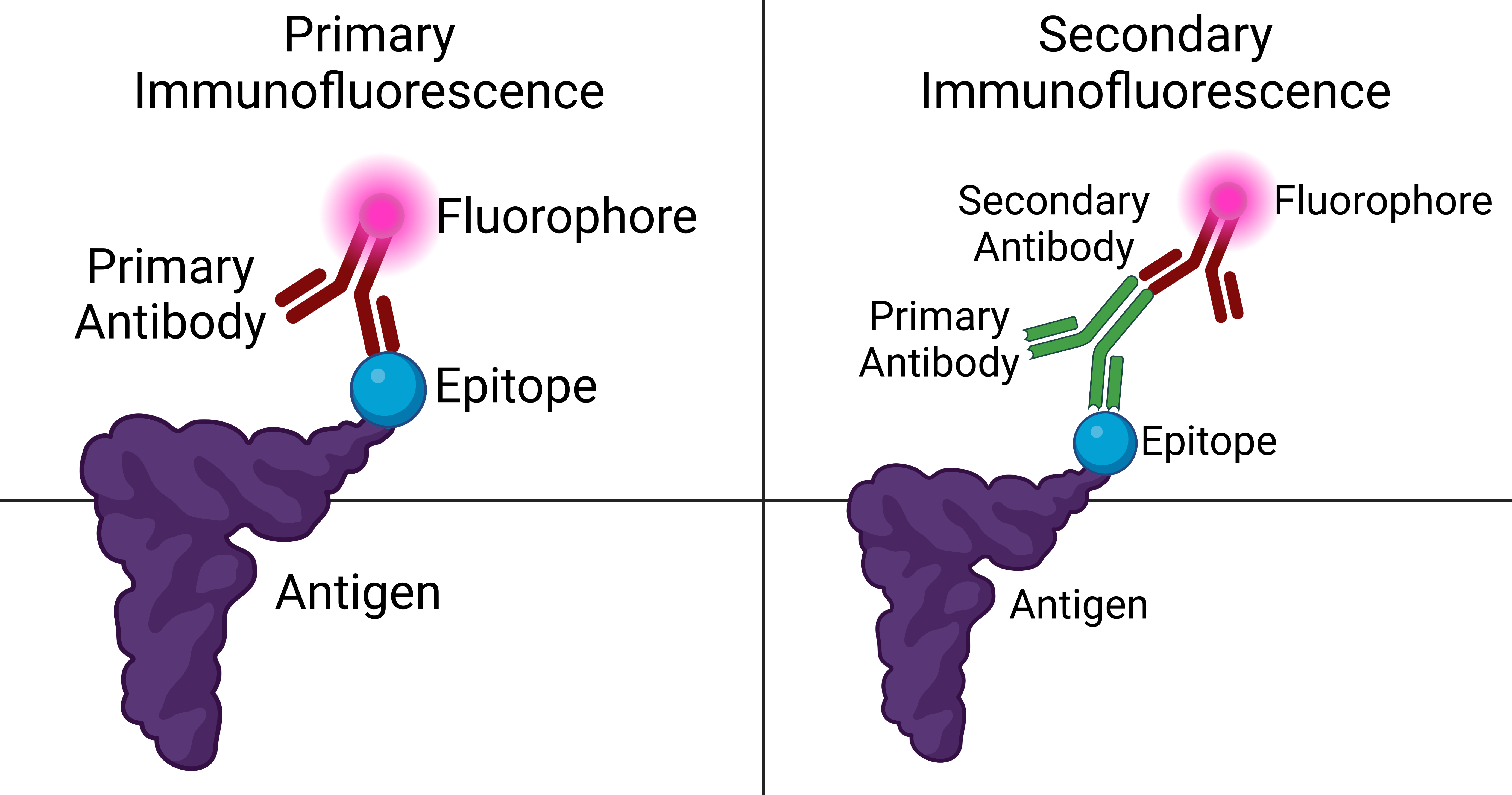
Immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence is a technique used for light microscopy with a fluorescence microscope and is used primarily on microbiological samples. This technique uses the specificity of antibodies to their antigen to target fluorescent dyes to specific biomolecule targets within a cell, and therefore allows visualization of the distribution of the target molecule through the sample. The specific region an antibody recognizes on an antigen is called an epitope. There have been efforts in epitope mapping since many antibodies can bind the same epitope and levels of binding between antibodies that recognize the same epitope can vary. Additionally, the binding of the fluorophore to the antibody itself cannot interfere with the immunological specificity of the antibody or the binding capacity of its antigen. Immunofluorescence is a widely used example of immunostaining (using antibodies to stain proteins) and is a specific example of immunohistochemistry (the use of the antibody-antigen rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are a major component of the lipids (up to 70% by weight) in some species such as microalgae but in some other organisms are not found in their standalone form, but instead exist as three main classes of esters: triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesteryl esters. In any of these forms, fatty acids are both important dietary sources of fuel for animals and important structural components for cells. History The concept of fatty acid (''acide gras'') was introduced in 1813 by Michel Eugène Chevreul, though he initially used some variant terms: ''graisse acide'' and ''acide huileux'' ("acid fat" and "oily acid"). Types of fatty acids Fatty acids are classified in many ways: by length, by saturation vs unsaturati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc Deficiency
Zinc deficiency is defined either as insufficient zinc to meet the needs of the body, or as a serum zinc level below the normal range. However, since a decrease in the serum concentration is only detectable after long-term or severe depletion, serum zinc is not a reliable biomarker for zinc status. Common symptoms include increased rates of diarrhea. Zinc deficiency affects the skin and gastrointestinal tract; brain and central nervous system, immune, skeletal, and reproductive systems. Zinc deficiency in humans is caused by reduced dietary intake, inadequate absorption, increased loss, or increased body system use. The most common cause is reduced dietary intake. In the U.S., the Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) is 8 mg/day for women and 11 mg/day for men."Zinc" , pp. 442–501 in ''Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arseni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duodenal Cancer
Duodenal cancer is a cancer in the first section of the small intestine known as the duodenum. Cancer of the duodenum is relatively rare compared to stomach cancer and colorectal cancer. Its histology is usually adenocarcinoma. Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), Gardner syndrome, Lynch syndrome, Muir–Torre syndrome, celiac disease, Peutz–Jeghers syndrome, Crohn's disease and juvenile polyposis syndrome are risk factors for developing this cancer. The duodenum is the first part of the small intestine. It is located between the stomach and the jejunum. After foods combine with stomach acid, they descend into the duodenum where they mix with bile from the gallbladder and digestive fluid from the pancreas. Signs and symptoms The cancerous mass tends to block food from getting to the small intestine. If food cannot get to the intestines, it will cause pain, acid reflux, and weight loss because the food cannot get to where it is supposed to be processed and absorbed by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin-like Growth Factor 2
Insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF-2) is one of three protein hormones that share structural similarity to insulin. The MeSH definition reads: "A well-characterized neutral peptide believed to be secreted by the liver and to circulate in the blood. It has growth-regulating, insulin-like and mitogenic activities. The growth factor has a major, but not absolute, dependence on somatotropin. It is believed to be a major fetal growth factor in contrast to insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), which is a major growth factor in adults." Gene structure In humans, the gene is located on chromosome 11p15.5, a region which contains numerous imprinted genes. In mice this homologous region is found at distal chromosome 7. In both organisms, ''IGF2'' is imprinted, with expression resulting favourably from the paternally inherited allele. However, in some human brain regions a loss of imprinting occurs resulting in both ''IGF2'' and being transcribed from both parental alleles. The prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and protein by promoting the absorption of glucose from the blood into liver, fat and skeletal muscle cells. In these tissues the absorbed glucose is converted into either glycogen via glycogenesis or fats (triglycerides) via lipogenesis, or, in the case of the liver, into both. Glucose production and secretion by the liver is strongly inhibited by high concentrations of insulin in the blood. Circulating insulin also affects the synthesis of proteins in a wide variety of tissues. It is therefore an anabolic hormone, promoting the conversion of small molecules in the blood into large molecules inside the cells. Low insulin levels in the blood have the opposite effect by promoting widespread catabolism, especially o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
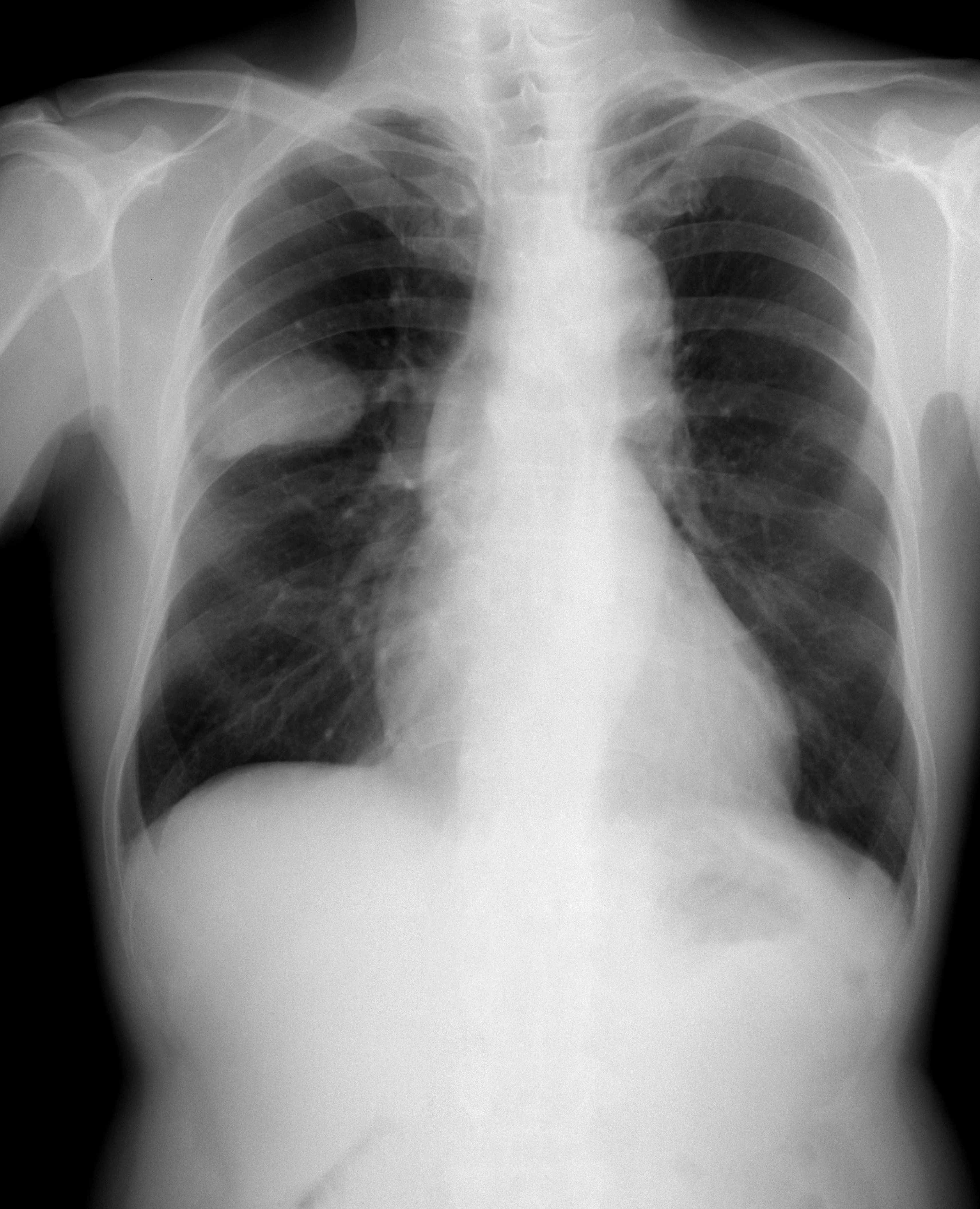
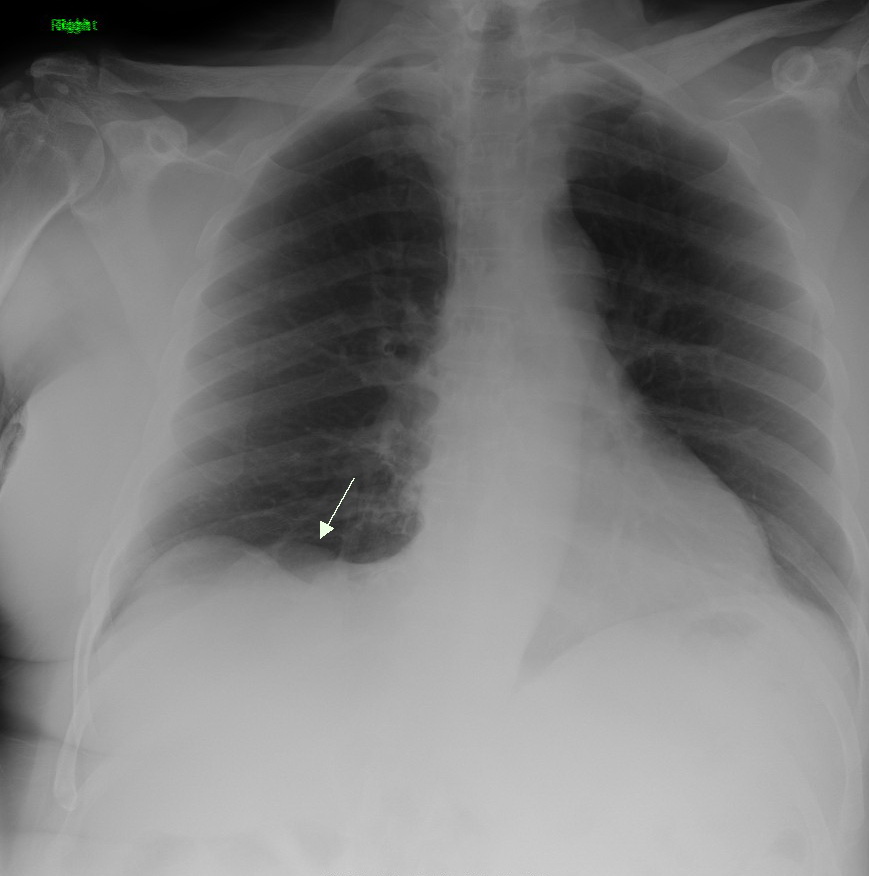
Small Cell Lung Cancer
Small-cell carcinoma is a type of highly malignant cancer that most commonly arises within the lung, although it can occasionally arise in other body sites, such as the cervix, prostate, and gastrointestinal tract. Compared to non-small cell carcinoma, small cell carcinoma has a shorter doubling time, higher growth fraction, and earlier development of metastases. Extensive stage small cell lung cancer is classified as a rare disorder. Ten-year relative survival rate is 3.5%; however, women have a higher survival rate, 4.3%, and men lower, 2.8%. Survival can be higher or lower based on a combination of factors including stage, age, gender and race. Types of SCLC Small-cell lung carcinoma has long been divided into two clinicopathological stages, termed ''limited stage'' (LS) and ''extensive stage'' (ES). The stage is generally determined by the presence or absence of metastases, whether or not the tumor appears limited to the thorax, and whether or not the entire tumor burden wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lung Cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma (since about 98–99% of all lung cancers are carcinomas), is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissue (biology), tissues of the lung. Lung carcinomas derive from transformed, malignant cells that originate as epithelial cells, or from tissues composed of epithelial cells. Other lung cancers, such as the rare sarcomas of the lung, are generated by the malignant transformation of connective tissues (i.e. nerve, fat, muscle, bone), which arise from mesenchymal cells. Lymphomas and melanomas (from lymphoid and melanocyte cell lineages) can also rarely result in lung cancer. In time, this uncontrolled neoplasm, growth can metastasis, metastasize (spreading beyond the lung) either by direct extension, by entering the lymphatic circulation, or via hematogenous, bloodborne spread – into nearby tissue or other, more distant parts of the body. Most cancers that originate from within the lungs, known as primary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |