|
National Saving
In economics, a country's national saving is the sum of private and public saving. It equals a nation's income minus consumption and the government spending. Economic model Closed economy with public deficit or surplus possible In this simple economic model with a closed economy there are three uses for GDP (the goods and services it produces in a year). If Y is national income (GDP), then the three uses of C consumption, I investment, and G government purchases can be expressed as: * Y = C + I + G National saving can be thought of as the amount of remaining income that is not consumed, or spent by government. In a simple model of a closed economy, anything that is not spent is assumed to be invested: * \text = Y - C - G = I National saving can be split into private saving and public saving. Denoting T for taxes paid by consumers that go directly to the government and TR for transfers paid by the government to the consumers as shown here: * (Y - T + TR - C) + (T - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is , with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people. The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of England (which included Wales, annexed in 1542) and the Kingdom of Scotland in 170 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Export
An export in international trade is a good produced in one country that is sold into another country or a service provided in one country for a national or resident of another country. The seller of such goods or the service provider is an ''exporter''; the foreign buyer is an '' importer''. Services that figure in international trade include financial, accounting and other professional services, tourism, education as well as intellectual property rights. Exportation of goods often requires the involvement of customs authorities. Firms Many manufacturing firms begin their global expansion as exporters and only later switch to another mode for serving a foreign market. Barriers There are four main types of export barriers: motivational, informational, operational/resource-based, and knowledge. Trade barriers are laws, regulations, policy, or practices that protect domestically made products from foreign competition. While restrictive business practices sometimes hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sectoral Balances
The sectoral balances (also called sectoral financial balances) are a sectoral analysis framework for macroeconomic analysis of national economies developed by British economist Wynne Godley. Sectoral analysis is based on the insight that when the government sector has a budget deficit, the non-government sectors (private domestic sector and foreign sector) together must have a surplus, and vice versa. In other words, if the government sector is borrowing, the other sectors taken together must be lending. The balances represent an accounting identity resulting from rearranging the components of aggregate demand, showing how the flow of funds affects the financial balances of the three sectors. This corresponds approximately to Balances Mechanics developed by Wolfgang Stützel in the 1950s. The approach is used by scholars at the Levy Economics Institute to support macroeconomic modelling and by Modern Monetary Theorists to illustrate the relationship between government budget def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reduction in the purchasing power of money. The opposite of inflation is deflation, a sustained decrease in the general price level of goods and services. The common measure of inflation is the inflation rate, the annualized percentage change in a general price index. As prices do not all increase at the same rate, the consumer price index (CPI) is often used for this purpose. The employment cost index is also used for wages in the United States. Most economists agree that high levels of inflation as well as hyperinflation—which have severely disruptive effects on the real economy—are caused by persistent excessive growth in the money supply. Views on low to moderate rates of inflation are more varied. Low or moderate inflation may be attri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Debt
A country's gross government debt (also called public debt, or sovereign debt) is the financial liabilities of the government sector. Changes in government debt over time reflect primarily borrowing due to past government deficits. A deficit occurs when a government's expenditures exceed revenues. Government debt may be owed to domestic residents, as well as to foreign residents. If owed to foreign residents, that quantity is included in the country's external debt. In 2020, the value of government debt worldwide was $87.4 US trillion, or 99% measured as a share of gross domestic product (GDP). Government debt accounted for almost 40% of all debt (which includes corporate and household debt), the highest share since the 1960s. The rise in government debt since 2007 is largely attributable to the global financial crisis of 2007–2008, and the COVID-19 pandemic. The ability of government to issue debt has been central to state formation and to state building. Public debt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolfgang Stützel
Wolfgang Stützel (23 January 1925, in Aalen, Germany – 1 March 1987, in Saarbrücken, West Germany) was a German economist and professor of economics at the Saarland University, Germany. From 1966 to 1968 he was member of the German Council of Economic Experts (german: Sachverständigenrat zur Begutachtung der gesamtwirtschaftlichen Entwicklung). He coined the concept of '' Macroeconomic Mechanics of Balances'' (german: Volkswirtschaftliche Saldenmechanik). Among other things, balances mechanics enabled the theories of John Maynard Keynes in which he argued that government deficit spending can be necessary during a deflationary depression to be placed on a formal, structural arithmetic foundation based on accounting identities. Stützel used balances mechanics to explain how a deflationary depression results from aggregate planned revenues from sales of goods being greater than aggregate planned expenditures on purchasing goods. He also showed on the same basis how an inflati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balances Mechanics
The Balances Mechanics (german: Saldenmechanik; from balances of bookkeeping respectively the credit system and mechanics to characterize the strict universal identities) is a work and mean of economics, comparable with Stock-Flow Consistent Modelling. Statements of Balances Mechanics are not based on assumptions and preconditions of a model but are of trivial arithmetic nature, usually shaped as equation and universal without restrictions. Balances Mechanics were developed by Wolfgang Stützel and published in his books ''Paradoxa der Geld- und Konkurrenzwirtschaft'' ''(Paradoxes of Competition-Based Monetary Economies)'' and ''Volkswirtschaftliche Saldenmechanik'' ''(Balances Mechanics of Economics)''. Overview Balances Mechanics deals with interrelations, the validity of which – contrary to most economics postulates – does not depend on assumptions about human behaviour. Balances Mechanics allows to put these frequently necessary assumptions of economic theories and postu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wynne Godley
Wynne Godley (26 September 192613 May 2010) was an economist famous for his pessimism about the British economy and his criticism of the British government. In 2007, he and Marc Lavoie wrote a book about the " Stock-Flow Consistent" model, an analysis that predicted the global financial crisis of 2008. Life Godley was born in London to Hugh Godley, 2nd Baron Kilbracken and his wife Elizabeth Usborn. He was born six years after his older brother, John who was to become John Godley, 3rd Baron Kilbracken. Godley attended Sandroyd School in Wiltshire before attending Rugby School then read politics, philosophy and economics at New College, Oxford where Isaiah Berlin and Philip Andrews, one of the main economists of the Oxford Economic Research Group, were two of his most important mentors. Godley trained to become a professional musician, studying at the Paris Conservatoire for three years, and then becoming principal oboist at the BBC Welsh Orchestra. He was however continuously ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sectoral Balances
The sectoral balances (also called sectoral financial balances) are a sectoral analysis framework for macroeconomic analysis of national economies developed by British economist Wynne Godley. Sectoral analysis is based on the insight that when the government sector has a budget deficit, the non-government sectors (private domestic sector and foreign sector) together must have a surplus, and vice versa. In other words, if the government sector is borrowing, the other sectors taken together must be lending. The balances represent an accounting identity resulting from rearranging the components of aggregate demand, showing how the flow of funds affects the financial balances of the three sectors. This corresponds approximately to Balances Mechanics developed by Wolfgang Stützel in the 1950s. The approach is used by scholars at the Levy Economics Institute to support macroeconomic modelling and by Modern Monetary Theorists to illustrate the relationship between government budget def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
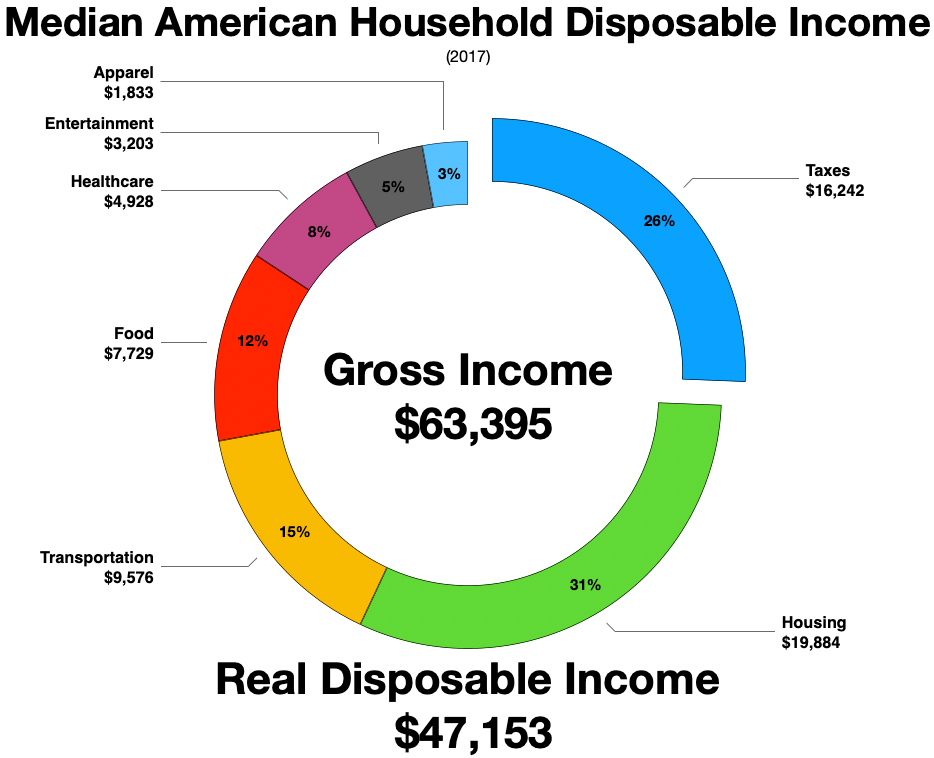
Disposable Income
Disposable income is total personal income minus current income taxes. In national accounts definitions, personal income minus personal current taxes equals disposable personal income. Subtracting personal outlays (which includes the major category of personal r privateconsumption expenditure) yields personal (or, private) savings, hence the income left after paying away all the taxes is referred to as disposable income. Restated, consumption expenditure plus savings equals disposable income after accounting for transfers such as payments to children in school or elderly parents’ living and care arrangements. The marginal propensity to consume (MPC) is the fraction of a change in disposable income that is consumed. For example, if disposable income rises by $100, and $65 of that $100 is consumed, the MPC is 65%. Restated, the marginal propensity to save is 35%. For the purposes of calculating the amount of income subject to garnishments, United States' federal law defin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Budget
A government budget is a document prepared by the government and/or other political entity presenting its anticipated tax revenues (Inheritance tax, income tax, corporation tax, import taxes) and proposed spending/expenditure (Healthcare, Education, Defence, Roads, State Benefit) for the coming financial year. In most parliamentary systems, the budget is presented to the legislature and often requires approval of the legislature. Through this budget, the government implements economic policy and realizes its program priorities. Once the budget is approved, the use of funds from individual chapters is in the hands of government ministries and other institutions. Revenues of the state budget consist mainly of taxes, customs duties, fees and other revenues. State budget expenditures cover the activities of the state, which are either given by law or the constitution. The budget in itself does not appropriate funds for government programs, hence need for additional legislative measur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)