|
Nanoreactor
Nanoreactors are a form of chemical reactor that are particularly in the disciplines of nanotechnology and nanobiotechnology. These special reactors are crucial in maintaining a working nanofoundry; which is essentially a foundry that manufactures products on a nanotechnological scale. Summary General information The term nanoreactor refers to an isolated system on the nanometer scale that is used to run chemical reactions in an environment that differs drastically from a reaction in bulk solution. The synthesis and analysis of these nanoreactors is a highly interdisciplinary subject, spanning from chemistry and physics to biology and materials science. These systems can be synthetic, such as nanopores and hollow nanoparticles, or they can be biological systems, including protein pores and channels. Generally, the effect of confinement provided by these nanoreactors results in novel chemistry. This field has only begun to receive significant attention in the last two decades, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Reactor
A chemical reactor is an enclosed volume in which a chemical reaction takes place. In chemical engineering, it is generally understood to be a process vessel used to carry out a chemical reaction, which is one of the classic unit operations in chemical process analysis. The design of a chemical reactor deals with multiple aspects of chemical engineering. Chemical engineers design reactors to maximize net present value for the given reaction. Designers ensure that the reaction proceeds with the highest efficiency towards the desired output product, producing the highest yield of product while requiring the least amount of money to purchase and operate. Normal operating expenses include energy input, energy removal, raw material costs, labor, etc. Energy changes can come in the form of heating or cooling, pumping to increase pressure, frictional pressure loss or agitation.Chemical reaction engineering is the branch of chemical engineering which deals with chemical reactors and their d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Shell
In chemistry and atomic physics, an electron shell may be thought of as an orbit followed by electrons around an atom's nucleus. The closest shell to the nucleus is called the "1 shell" (also called the "K shell"), followed by the "2 shell" (or "L shell"), then the "3 shell" (or "M shell"), and so on farther and farther from the nucleus. The shells correspond to the principal quantum numbers (''n'' = 1, 2, 3, 4 ...) or are labeled alphabetically with the letters used in X-ray notation (K, L, M, ...). A useful guide when understanding electron shells in atoms is to note that each row on the conventional periodic table of elements represents an electron shell. Each shell can contain only a fixed number of electrons: the first shell can hold up to two electrons, the second shell can hold up to eight (2 + 6) electrons, the third shell can hold up to 18 (2 + 6 + 10) and so on. The general formula is that the ''n''th shell can in principle hold up to 2( ''n''2) electrons. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cream (pharmaceutical)
A cream is a preparation usually for application to the skin. Creams for application to mucous membranes such as those of the rectum or vagina are also used. Creams may be considered pharmaceutical products as even cosmetic creams are based on techniques developed by pharmacy and unmedicated creams are highly used in a variety of skin conditions (dermatoses). The use of the finger tip unit concept may be helpful in guiding how much topical cream is required to cover different areas. Creams are semi-solid emulsions of oil and water. They are divided into two types: oil-in-water (O/W) creams which are composed of small droplets of oil dispersed in a continuous water phase, and water-in-oil (W/O) creams which are composed of small droplets of water dispersed in a continuous oily phase. Oil-in-water creams are more comfortable and cosmetically acceptable as they are less greasy and more easily washed off using water. Water-in-oil creams are more difficult to handle but many drugs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lotion
Lotion is a low-viscosity topical preparation intended for application to the skin. By contrast, creams and gels have higher viscosity, typically due to lower water content. Lotions are applied to external skin with bare hands, a brush, a clean cloth, or cotton wool. While a lotion may be used as a medicine delivery system, many lotions, especially hand lotions and body lotions and lotion for allergies are meant instead to simply smooth, moisturize, soften and, sometimes, perfume the skin. Some skincare products, such as sunscreen and moisturizer, may be available in multiple formats, such as lotions, gels, creams, or sprays. Medicine delivery Dermatologists can prescribe lotions to treat or prevent skin diseases. It is not unusual for the same drug ingredient to be formulated into a lotion, cream and ointment. Creams are the most convenient of the three but inappropriate for application to regions of hairy skin such as the scalp, while a lotion is less viscous and may b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Substance
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., without breaking chemical bonds. Chemical substances can be simple substances (substances consisting of a single chemical element), chemical compounds, or alloys. Chemical substances are often called 'pure' to set them apart from mixtures. A common example of a chemical substance is pure water; it has the same properties and the same ratio of hydrogen to oxygen whether it is isolated from a river or made in a laboratory. Other chemical substances commonly encountered in pure form are diamond (carbon), gold, table salt (sodium chloride) and refined sugar (sucrose). However, in practice, no substance is entirely pure, and chemical purity is specified according to the intended use of the chemical. Chemical substances exist as solids, liquids, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Fuel
Hydrogen fuel refers to hydrogen which is burned as fuel with oxygen. It is zero-carbon, provided that it is created in a process that does not involve carbon. It can be used in fuel cells or internal combustion engines (see HICEV). Regarding hydrogen vehicles, hydrogen has begun to be used in commercial fuel cell vehicles such as passenger cars, and has been used in fuel cell buses for many years. It is also used as a fuel for spacecraft propulsion and is being proposed for hydrogen-powered aircraft. Production Because pure hydrogen does not occur naturally on Earth in large quantities, it usually requires a primary energy input to be produced on an industrial scale. Hydrogen fuel can be produced from methane or by electrolysis of water. As of 2020, the majority of hydrogen (∼95%) is produced from fossil fuels by steam reforming or partial oxidation of methane and coal gasification with only a small quantity by other routes such as biomass gasification or electrolysis of water. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight, where it is used to make cellulose in cell walls, the most abundant carbohydrate in the world. In energy metabolism, glucose is the most important source of energy in all organisms. Glucose for metabolism is stored as a polymer, in plants mainly as starch and amylopectin, and in animals as glycogen. Glucose circulates in the blood of animals as blood sugar. The naturally occurring form of glucose is -glucose, while -glucose is produced synthetically in comparatively small amounts and is less biologically active. Glucose is a monosaccharide containing six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group, and is therefore an aldohexose. The glucose molecule can exist in an open-chain (acyclic) as well as ring (cyclic) form. Gluco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipase B
Lipase ( ) is a family of enzymes that catalyzes the hydrolysis of fats. Some lipases display broad substrate scope including esters of cholesterol, phospholipids, and of lipid-soluble vitamins and sphingomyelinases; however, these are usually treated separately from "conventional" lipases. Unlike esterases, which function in water, lipases "are activated only when adsorbed to an oil–water interface". Lipases perform essential roles in digestion, transport and processing of dietary lipids in most, if not all, organisms. Structure and catalytic mechanism Classically, lipases catalyse the hydrolysis of triglycerides: :triglyceride + H2O → fatty acid + diacylglycerol :diacylglycerol + H2O → fatty acid + monacylglycerol :monacylglycerol + H2O → fatty acid + glycerol Lipases are serine hydrolases, i.e. they function by transesterification generating an acyl serine intermediate. Most lipases act at a specific position on the glycerol backbone of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose Oxidase
The glucose oxidase enzyme (GOx or GOD) also known as notatin (EC number 1.1.3.4) is an oxidoreductase that catalyses the oxidation of glucose to hydrogen peroxide and D-glucono-δ-lactone. This enzyme is produced by certain species of fungi and insects and displays antibacterial activity when oxygen and glucose are present. Glucose oxidase is widely used for the determination of free glucose in body fluids (medical testing), in vegetal raw material, and in the food industry. It also has many applications in biotechnologies, typically enzyme assays for biochemistry including biosensors in nanotechnologies. It was first isolated by Detlev Müller in 1928 from ''Aspergillus niger''. Function Several species of fungi and insects synthesize glucose oxidase, which produces hydrogen peroxide, which kills bacteria. Notatin, extracted from antibacterial cultures of ''Penicillium notatum'', was originally named Penicillin A, but was renamed to avoid confusion with penicillin. Notati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
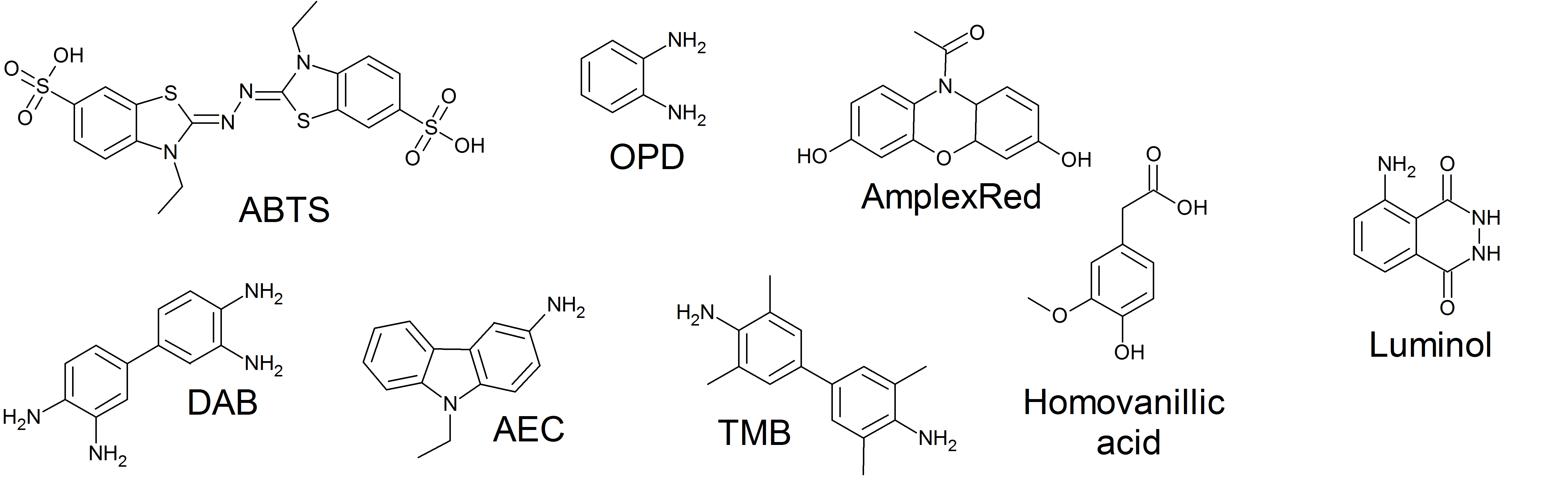
Horseradish Peroxidase
The enzyme horseradish peroxidase (HRP), found in the roots of horseradish, is used extensively in biochemistry applications. It is a metalloenzyme with many isoforms, of which the most studied type is C. It catalyzes the oxidation of various organic substrates by hydrogen peroxide. Structure The structure of the enzyme was first solved by X-ray crystallography in 1997; and has since been solved several times with various substrates. It is a large alpha-helical glycoprotein which binds heme as a redox cofactor. Substrates Alone, the HRP enzyme, or conjugates thereof, is of little value; its presence must be made visible using a substrate that, when oxidized by HRP using hydrogen peroxide as the oxidizing agent, yields a characteristic color change that is detectable by spectrophotometric methods. Numerous substrates for horseradish peroxidase have been described and commercialized to exploit the desirable features of HRP. These substrates fall into several distinct cat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptability, plus a wide range of other properties, such as being lightweight, durable, flexible, and inexpensive to produce, has led to its widespread use. Plastics typically are made through human industrial systems. Most modern plastics are derived from fossil fuel-based chemicals like natural gas or petroleum; however, recent industrial methods use variants made from renewable materials, such as corn or cotton derivatives. 9.2 billion tonnes of plastic are estimated to have been made between 1950 and 2017. More than half this plastic has been produced since 2004. In 2020, 400 million tonnes of plastic were produced. If global trends on plastic demand continue, it is estimated that by 2050 annual global plastic production will reach over 1, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reservoir
A reservoir (; from French ''réservoir'' ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, built to store fresh water or it may be a natural formation. Reservoirs can be created in a number of ways, including controlling a watercourse that drains an existing body of water, interrupting a watercourse to form an embayment within it, through excavation, or building any number of retaining walls or levees. In other contexts, "reservoirs" may refer to storage spaces for various fluids; they may hold liquids or gasses, including hydrocarbons. ''Tank reservoirs'' store these in ground-level, elevated, or buried tanks. Tank reservoirs for water are also called cisterns. Most underground reservoirs are used to store liquids, principally either water or petroleum. Types Dammed valleys Dammed reservoirs are artificial lakes created and controlled by a dam A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |