|
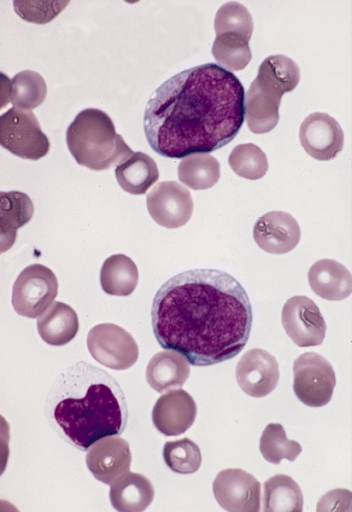
Myeloblast
The myeloblast is a unipotent stem cell which differentiates into the effectors of the granulocyte series. It is found in the bone marrow. Stimulation of myeloblasts by G-CSF and other cytokines triggers maturation, differentiation, proliferation and cell survival. Structure Myeloblasts reside extravascularly in the bone marrow. Hematopoiesis takes place in the extravascular cavities between the sinuses of the marrow. The wall of the sinuses is composed of two different types of cells, endothelial cells and adventitial reticular cells. The hemopoietic cells are aligned in cords or wedges between these sinuses, with myeloblasts and other granular progenitors concentrated in the subcortical regions of these hemopoietic cords. Myeloblasts are rather small cells with a diameter between 14 and 18μm. The major part is occupied by a large oval nucleus composed of very fine nonaggregated chromatin and possessing 3 or more nucleoli. The cytoplasm has a basophilic character and is devoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Myeloblastic Leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells, characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal cells that build up in the bone marrow and blood and interfere with normal blood cell production. Symptoms may include feeling tired, shortness of breath, easy bruising and bleeding, and increased risk of infection. Occasionally, spread may occur to the brain, skin, or gums. As an acute leukemia, AML progresses rapidly, and is typically fatal within weeks or months if left untreated. Risk factors include smoking, previous chemotherapy or radiation therapy, myelodysplastic syndrome, and exposure to the chemical benzene. The underlying mechanism involves replacement of normal bone marrow with leukemia cells, which results in a drop in red blood cells, platelets, and normal white blood cells. Diagnosis is generally based on bone marrow aspiration and specific blood tests. AML has several subtypes for which treatments and outcomes may vary. The first-lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granulopoiesis
Granulopoiesis (or granulocytopoiesis) is a part of haematopoiesis, that leads to the production of granulocytes. A granulocyte, also referred to as a polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMN), is a type of white blood cell that has multi lobed nuclei, usually containing three lobes, and has a significant amount of cytoplasmic granules within the cell. Granulopoiesis takes place in the bone marrow. It leads to the production of three types of mature granulocytes: neutrophils (most abundant, making up to 60% of all white blood cells), eosinophils (up to 4%) and basophils (up to 1%). Stages of granulocyte development Granulopoiesis is often divided into two parts; 1) Granulocyte lineage determination and 2) Commited granulopoiesis. Granulocyte lineage determination Granulopoiesis, as well as the rest of haematopoiesis, begins from a haematopoietic stem cells. These are multipotent cells that reside in the bone marrow niche and have the ability to give rise to all haematopoietic c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Promyelocyte
A promyelocyte (or progranulocyte) is a granulocyte precursor, developing from the myeloblast and developing into the myelocyte. Promyelocytes measure 12-20 microns in diameter. The nucleus of a promyelocyte is approximately the same size as a myeloblast but their cytoplasm is much more abundant. They also have less prominent nucleoli than myeloblasts and their chromatin is more coarse and clumped. The cytoplasm is basophilic and contains primary red/purple granules. Additional images File:Cytology of acute promyelocytic leukemia, annotated.png, Bone marrow smear from a patient with acute promyelocytic leukemia, showing characteristic abnormal promyelocytes.Image by Mikael Häggström, MD. Reference for findings: Last author update: 1 February 2013Source image: :File:Faggot cell in AML-M3.jpg froPEIR Digital Library (Pathology image database)(Public Domain) File:Hematopoiesis (human) diagram en.svg, Hematopoiesis File:Basophilic promyelocyte.png, Basophilic promyelocyte File: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granulocyte
Granulocytes are cells in the innate immune system characterized by the presence of specific granules in their cytoplasm. Such granules distinguish them from the various agranulocytes. All myeloblastic granulocytes are polymorphonuclear. They have varying shapes (morphology) of the nucleus (segmented, irregular; often lobed into three segments); and are referred to as polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN, PML, or PMNL). In common terms, ''polymorphonuclear granulocyte'' refers specifically to "neutrophil granulocytes", the most abundant of the granulocytes; the other types (eosinophils, basophils, and mast cells) have varying morphology. Granulocytes are produced via granulopoiesis in the bone marrow. Types There are four types of granulocytes (full name polymorphonuclear granulocytes): * Basophils * Eosinophils * Neutrophils * Mast cells Except for the mast cells, their names are derived from their staining characteristics; for example, the most abundant granulocyte is the neut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphoblast
__NOTOC__ A lymphoblast is a modified naive lymphocyte with altered cell morphology. It occurs when the lymphocyte is activated by an antigen (from antigen-presenting cells) and increased in volume by nucleus and cytoplasm growth as well as new mRNA and protein synthesis. The lymphoblast then starts dividing two to four times every 24 hours for three to five days, with a single lymphoblast making approximately 1000 clones of its original naive lymphocyte, with each clone sharing the originally unique antigen specificity. Finally the dividing cells differentiate into effector cells, known as plasma cells (for B cells), cytotoxic T cells, and helper T cells. Lymphoblasts can also refer to immature cells which typically differentiate to form mature lymphocytes. Normally lymphoblasts are found in the bone marrow, but in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), lymphoblasts proliferate uncontrollably and are found in large numbers in the peripheral blood. The size is between 10 and 20 μm. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myelocyte
A myelocyte is a young cell of the granulocytic series, occurring normally in bone marrow (can be found in circulating blood when caused by certain diseases). Structure When stained with the usual dyes, the cytoplasm is distinctly basophilic and relatively more abundant than in myeloblasts or promyelocytes, even though myelocytes are smaller cells. Numerous cytoplasmic granules are present in the more mature forms of myelocytes. Neutrophilic and eosinophilic granules are peroxidase-positive, while basophilic granules are not. The nuclear chromatin is coarser than that observed in a promyelocyte, but it is relatively faintly stained and lacks a well-defined membrane. The nucleus is fairly regular in contour (not indented), and seems to be 'buried' beneath the numerous cytoplasmic granules. (If the nucleus were indented, it would likely be a metamyelocyte.) Measurement There is an internationally agreed method of counting blasts, with results from M1 upwards. Development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemopoiesis
Haematopoiesis (, from Greek , 'blood' and 'to make'; also hematopoiesis in American English; sometimes also h(a)emopoiesis) is the formation of blood cellular components. All cellular blood components are derived from haematopoietic stem cells. In a healthy adult person, approximately – new blood cells are produced daily in order to maintain steady state levels in the peripheral circulation.Semester 4 medical lectures at Uppsala University 2008 by Leif Jansson Process Haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) Haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) reside in the medulla of the bone (bone marrow) and have the unique ability to give rise to all of the different mature blood cell types and tissues. HSCs are self-renewing cells: when they differentiate, at least some of their daughter cells remain as HSCs so the pool of stem cells is not depleted. This phenomenon is called asymmetric division. The other daughters of HSCs ( myeloid and lymphoid progenitor cells) can follow any of the other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
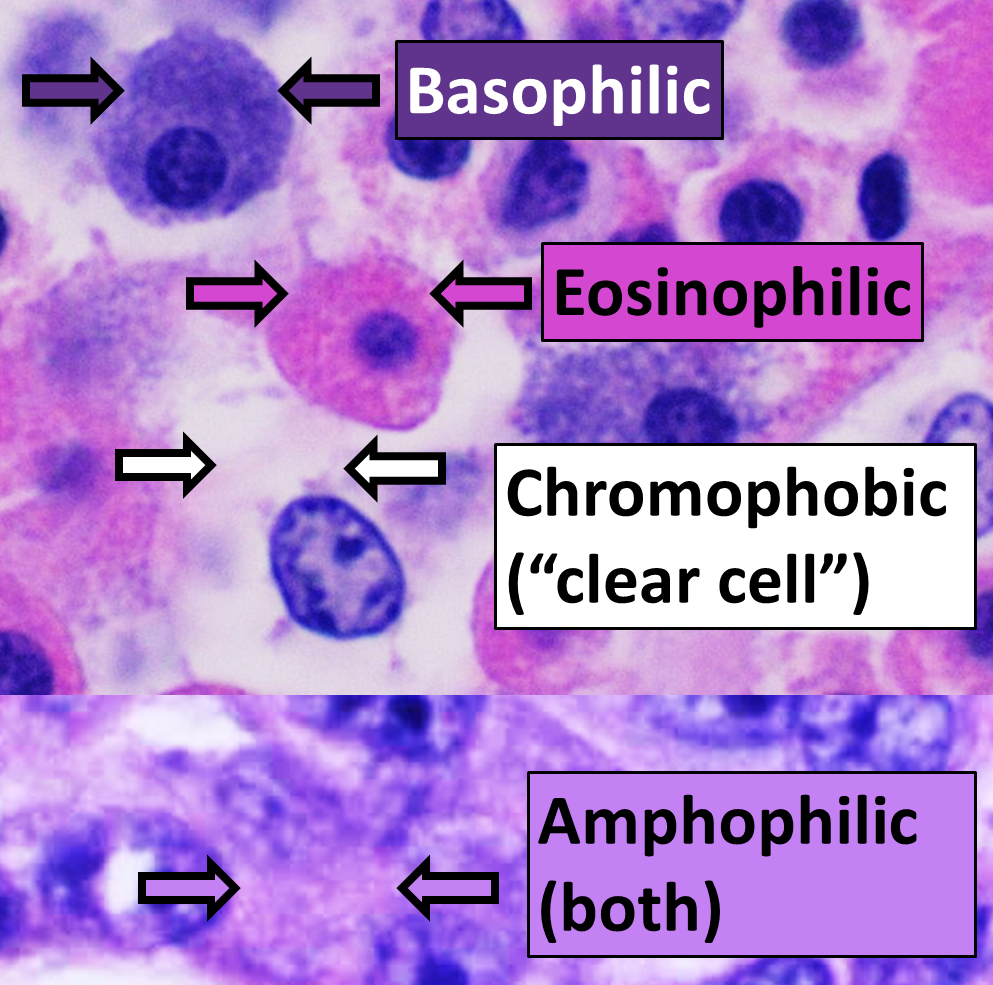
Eosinophilic
Eosinophilic (Greek suffix -phil-, meaning ''loves eosin'') is the staining of tissues, cells, or organelles after they have been washed with eosin, a dye. Eosin is an acidic dye for staining cell cytoplasm, collagen, and muscle fibers. ''Eosinophilic'' describes the appearance of cells and structures seen in histological sections that take up the staining dye eosin. Such eosinophilic structures are, in general, composed of protein. Eosin is usually combined with a stain called hematoxylin to produce a hematoxylin- and eosin-stained section (also called an H&E stain, HE or H+E section). It is the most widely used histological stain for a medical diagnosis. When a pathologist examines a biopsy of a suspected cancer, they will stain the biopsy with H&E. Some structures seen inside cells are described as being eosinophilic; for example, Lewy and Mallory bodies. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrophilic
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying in different animals. They are formed from stem cells in the bone marrow and differentiated into subpopulations of neutrophil-killers and neutrophil-cagers. They are short-lived and highly mobile, as they can enter parts of tissue where other cells/molecules cannot. Neutrophils may be subdivided into segmented neutrophils and banded neutrophils (or bands). They form part of the polymorphonuclear cells family (PMNs) together with basophils and eosinophils. The name ''neutrophil'' derives from staining characteristics on hematoxylin and eosin ( H&E) histological or cytological preparations. Whereas basophilic white blood cells stain dark blue and eosinophilic white blood cells stain bright red, neutrophils stain a neutral pink. Normally, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoblast
Monoblasts are the committed progenitor cells that differentiated from a committed macrophage or dendritic cell precursor (MDP) in the process of hematopoiesis. They are the first developmental stage in the monocyte series leading to a macrophage. Their myeloid cell fate is induced by the concentration of cytokines they are surrounded by during development. These cytokines induce the activation of transcription factors which push completion of the monoblast's myeloid cell fate. Monoblasts are normally found in bone marrow and do not appear in the normal peripheral blood. They mature into monocytes which, in turn, develop into macrophages. They then are seen as macrophages in the normal peripheral blood and many different tissues of the body. Macrophages can produce a variety of effector molecules that initiate local, systemic inflammatory responses. These monoblast differentiated cells are equipped to fight off foreign invaders using pattern recognition receptors to detect antigen as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematopoiesis (human) Diagram En
Haematopoiesis (, from Greek , 'blood' and 'to make'; also hematopoiesis in American English; sometimes also h(a)emopoiesis) is the formation of blood cellular components. All cellular blood components are derived from haematopoietic stem cells. In a healthy adult person, approximately – new blood cells are produced daily in order to maintain steady state levels in the peripheral circulation.Semester 4 medical lectures at Uppsala University 2008 by Leif Jansson Process Haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) Haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) reside in the medulla of the bone (bone marrow) and have the unique ability to give rise to all of the different mature blood cell types and tissues. HSCs are self-renewing cells: when they differentiate, at least some of their daughter cells remain as HSCs so the pool of stem cells is not depleted. This phenomenon is called asymmetric division. The other daughters of HSCs (myeloid and lymphoid progenitor cells) can follow any of the other d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin 3
Interleukin 3 (IL-3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IL3'' gene localized on chromosome 5q31.1. Sometimes also called colony-stimulating factor, multi-CSF, mast cell growth factor, MULTI-CSF, MCGF; MGC79398, MGC79399: the protein contains 152 amino acids and its molecular weight is 17 kDa. IL-3 is produced as a monomer by activated T cells, monocytes/macrophages and stroma cells. The major function of IL-3 cytokine is to regulate the concentrations of various blood-cell types. It induces proliferation and differentiation in both early pluripotent stem cells and committed progenitors. It also has many more specific effects like the regeneration of platelets and potentially aids in early antibody isotype switching. Function Interleukin 3 is an interleukin, a type of biological signal (cytokine) that can improve the body's natural response to disease as part of the immune system. In conjunction with other β common chain cytokines GM-CSF and IL-5, IL-3 works to re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |