|
Mutation Testing
Mutation testing (or ''mutation analysis'' or ''program mutation'') is used to design new software tests and evaluate the quality of existing software tests. Mutation testing involves modifying a program in small ways. Each mutated version is called a ''mutant'' and tests detect and reject mutants by causing the behaviour of the original version to differ from the mutant. This is called ''killing'' the mutant. Test suites are measured by the percentage of mutants that they kill. New tests can be designed to kill additional mutants. Mutants are based on well-defined ''mutation operators'' that either mimic typical programming errors (such as using the wrong operator or variable name) or force the creation of valuable tests (such as dividing each expression by zero). The purpose is to help the tester develop effective tests or locate weaknesses in the test data used for the program or in sections of the code that are seldom or never accessed during Execution (computers), execution. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Execution (computers)
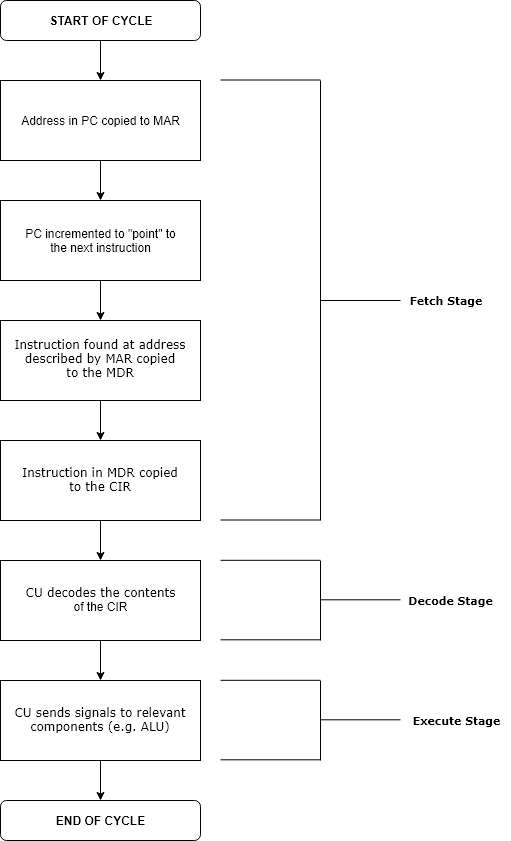
Execution in computer engineering, computer and software engineering is the process by which a computer or virtual machine interprets and acts on the instructions of a computer program. Each instruction of a program is a description of a particular action which must be carried out, in order for a specific problem to be solved. Execution involves repeatedly following a "Instruction cycle, fetch–decode–execute" cycle for each instruction done by the control unit. As the executing machine follows the instructions, specific effects are produced in accordance with the Formal semantics of programming languages, semantics of those instructions. Programs for a computer may be executed in a Batch processing, batch process without human interaction or a User (computing), user may type Command (computing), commands in an Session (computer science), interactive session of an Interpreter (computing), interpreter. In this case, the "commands" are simply program instructions, whose executio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Synopsys
Synopsys, Inc. is an American electronic design automation (EDA) company headquartered in Sunnyvale, California, that focuses on silicon design and verification, silicon intellectual property and software security and quality. Synopsys supplies tools and services to the semiconductor design and manufacturing industry. Products include tools for logic synthesis and physical design of integrated circuits, simulators for development, and debugging environments that assist in the design of the logic for chips and computer systems. History Synopsys was founded by Aart de Geus, David Gregory, Alberto Sangiovanni-Vincentelli and Bill Krieger in 1986 in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina. The company was initially established as Optimal Solutions with a charter to develop and market logic synthesis technology developed by the team at General Electric's Advanced Computer-Aided Engineering Group. The company changed its name to Synopsys and moved to Mountain View, Califo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sanity Testing
A sanity check or sanity test is a basic test to quickly evaluate whether a claim or the result of a calculation can possibly be true. It is a simple check to see if the produced material is rational (that the material's creator was thinking rationally, applying sanity). The point of a sanity test is to rule out certain classes of obviously false results, not to catch every possible error. A rule-of-thumb or back-of-the-envelope calculation may be checked to perform the test. The advantage of performing an initial sanity test is that of speedily evaluating basic function. In arithmetic, for example, when multiplying by 9, using the divisibility rule for 9 to verify that the sum of digits of the result is divisible by 9 is a sanity test—it will not catch ''every'' multiplication error, but is a quick and simple method to discover ''many'' possible errors. In computer science, a ''sanity test'' is a very brief run-through of the functionality of a computer program, system, calc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |