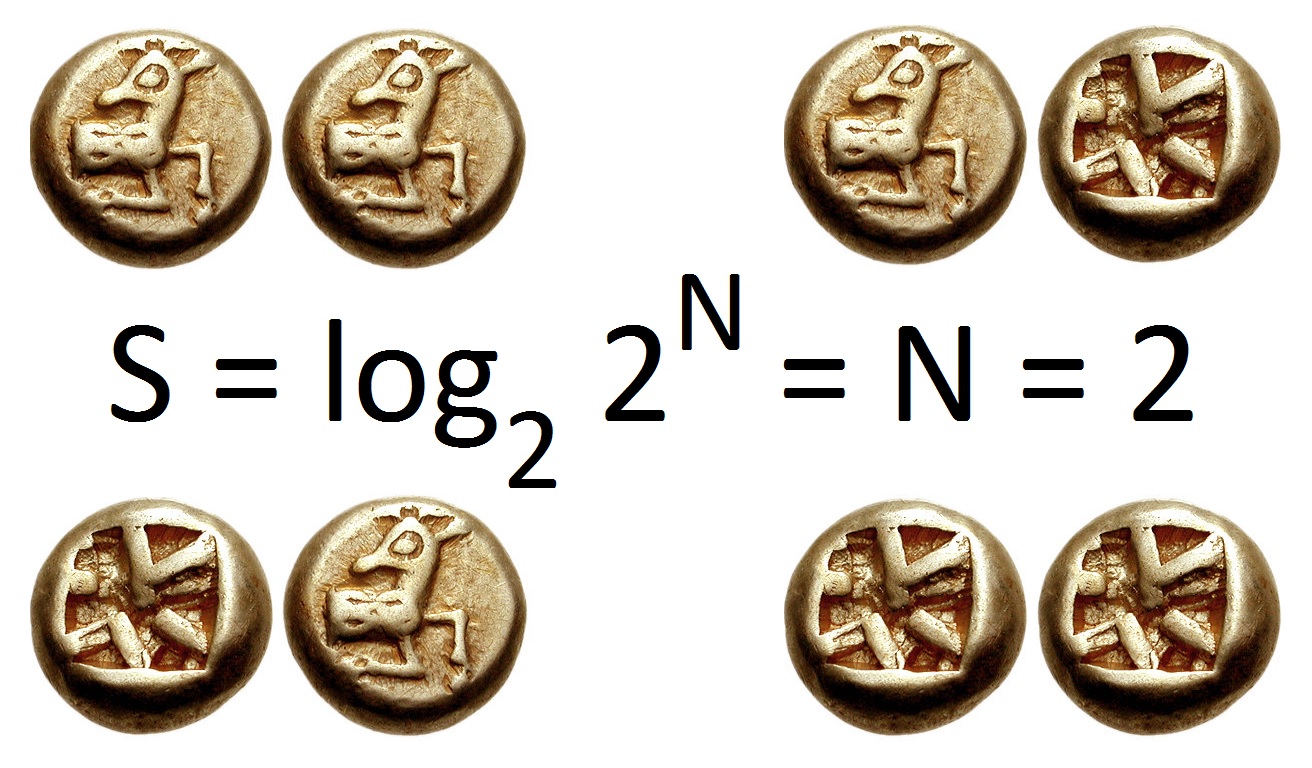|
Munged Password
In computing, the term munge means to attempt to create a strong, secure password through character substitution. "Munge" is sometimes backronymmed as Modify Until Not Guessed Easily. The usage differs significantly from Mung (Mash Until No Good), because munging implies destruction of data, while mungeing implies creation of strong protection for data. Rationale Passwords are used to gain access to computer resources, and computer users generally choose passwords that are easy to remember, but therefore insecure. Simple passwords are easily hacked by dictionary attacking software. If a network administrator supplies a password that is too difficult to remember, or requires that passwords be changed frequently, users tend to write their passwords down to help them remember. Many times passwords can be found on sticky notes under keyboards, behind pictures, or hidden among other desktop items—another security risk. Mungeing helps to create a strong password that the user can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Password
A password, sometimes called a passcode (for example in Apple devices), is secret data, typically a string of characters, usually used to confirm a user's identity. Traditionally, passwords were expected to be memorized, but the large number of password-protected services that a typical individual accesses can make memorization of unique passwords for each service impractical. Using the terminology of the NIST Digital Identity Guidelines, the secret is held by a party called the ''claimant'' while the party verifying the identity of the claimant is called the ''verifier''. When the claimant successfully demonstrates knowledge of the password to the verifier through an established authentication protocol, the verifier is able to infer the claimant's identity. In general, a password is an arbitrary string of characters including letters, digits, or other symbols. If the permissible characters are constrained to be numeric, the corresponding secret is sometimes called a personal i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backronym
A backronym is an acronym formed from an already existing word by expanding its letters into the words of a phrase. Backronyms may be invented with either serious or humorous intent, or they may be a type of false etymology or folk etymology. The word is a portmanteau of ''back'' and ''acronym''. An acronym is a word derived from the initial letters of the words of a phrase, such as ''radar'' from "''ra''dio ''d''etection ''a''nd ''r''anging". By contrast, a backronym is "an acronym deliberately formed from a phrase whose initial letters spell out a particular word or words, either to create a memorable name or as a fanciful explanation of a word's origin." Many fictional espionage organizations are backronyms, such as SPECTRE (''sp''ecial ''e''xecutive for ''c''ounterintelligence, ''t''errorism, ''r''evenge and ''e''xtortion) from the James Bond franchise. For example, the Amber Alert missing-child program was named after Amber Hagerman, a nine-year-old girl who was abducted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mung (computer Term)
Mung is computer jargon for a series of potentially destructive or irrevocable changes to a piece of data or a file. It is sometimes used for vague data transformation steps that are not yet clear to the speaker. Common munging operations include removing punctuation or HTML tags, data parsing, filtering, and transformation. The term was coined in 1958 in the Tech Model Railroad Club at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. In 1960 the backronym "Mash Until No Good" was created to describe Mung, and by 1976 it was revised to "Mung Until No Good", making it one of the first recursive acronyms. It lived on as a recursive command in the editing language Text Editor and Corrector, TECO. It differs from the very similar term munged password, munge, because munging usually implies destruction of data, while mungeing usually implies modifying data (simple passwords) in order to create protection related to that data. Munging may also describe the constructive operation of tying to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dictionary Attack
In cryptanalysis and computer security, a dictionary attack is an attack using a restricted subset of a keyspace to defeat a cipher or authentication mechanism by trying to determine its decryption key or passphrase, sometimes trying thousands or millions of likely possibilities often obtained from lists of past security breaches. Technique A dictionary attack is based on trying all the strings in a pre-arranged listing. Such attacks originally used words found in a dictionary (hence the phrase ''dictionary attack''); however, now there are much larger lists available on the open Internet containing hundreds of millions of passwords recovered from past data breaches. There is also cracking software that can use such lists and produce common variations, such as substituting numbers for similar-looking letters. A dictionary attack tries only those possibilities which are deemed most likely to succeed. Dictionary attacks often succeed because many people have a tendency to choose sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Password Strength
Password strength is a measure of the effectiveness of a password against guessing or brute-force attacks. In its usual form, it estimates how many trials an attacker who does not have direct access to the password would need, on average, to guess it correctly. The strength of a password is a function of length, complexity, and unpredictability. Using strong passwords lowers overall risk of a security breach, but strong passwords do not replace the need for other effective security controls. The effectiveness of a password of a given strength is strongly determined by the design and implementation of the factors (knowledge, ownership, inherence). The first factor is the main focus in this article. The rate at which an attacker can submit guessed passwords to the system is a key factor in determining system security. Some systems impose a time-out of several seconds after a small number (e.g. three) of failed password entry attempts. In the absence of other vulnerabilities, such s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropy (information Theory)
In information theory, the entropy of a random variable is the average level of "information", "surprise", or "uncertainty" inherent to the variable's possible outcomes. Given a discrete random variable X, which takes values in the alphabet \mathcal and is distributed according to p: \mathcal\to , 1/math>: \Eta(X) := -\sum_ p(x) \log p(x) = \mathbb \log p(X), where \Sigma denotes the sum over the variable's possible values. The choice of base for \log, the logarithm, varies for different applications. Base 2 gives the unit of bits (or " shannons"), while base ''e'' gives "natural units" nat, and base 10 gives units of "dits", "bans", or " hartleys". An equivalent definition of entropy is the expected value of the self-information of a variable. The concept of information entropy was introduced by Claude Shannon in his 1948 paper "A Mathematical Theory of Communication",PDF archived froherePDF archived frohere and is also referred to as Shannon entropy. Shannon's theory defi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moore's Law
Moore's law is the observation that the number of transistors in a dense integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years. Moore's law is an observation and projection of a historical trend. Rather than a law of physics, it is an empirical relationship linked to gains from experience in production. The observation is named after Gordon Moore, the co-founder of Fairchild Semiconductor and Intel (and former CEO of the latter), who in 1965 posited a doubling every year in the number of components per integrated circuit, and projected this rate of growth would continue for at least another decade. In 1975, looking forward to the next decade, he revised the forecast to doubling every two years, a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 41%. While Moore did not use empirical evidence in forecasting that the historical trend would continue, his prediction held since 1975 and has since become known as a "law". Moore's prediction has been used in the semiconductor industry to g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leet
Leet (or "1337"), also known as eleet or leetspeak, is a system of modified spellings used primarily on the Internet. It often uses character replacements in ways that play on the similarity of their glyphs via reflection or other resemblance. Additionally, it modifies certain words based on a system of suffixes and alternate meanings. There are many dialects or linguistic varieties in different online communities. The term "leet" is derived from the word ''elite'', used as an adjective to describe skill or accomplishment, especially in the fields of online gaming and computer hacking. The leet lexicon includes spellings of the word as ''1337'' or ''leet''. History Leet originated within bulletin board systems (BBS) in the 1980s,Mitchell.An Explanation of l33t Speak. where having "elite" status on a BBS allowed a user access to file folders, games, and special chat rooms. The Cult of the Dead Cow hacker collective has been credited with the original coining of the term, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Password Authentication
A password, sometimes called a passcode (for example in Apple devices), is secret data, typically a string of characters, usually used to confirm a user's identity. Traditionally, passwords were expected to be memorized, but the large number of password-protected services that a typical individual accesses can make memorization of unique passwords for each service impractical. Using the terminology of the NIST Digital Identity Guidelines, the secret is held by a party called the ''claimant'' while the party verifying the identity of the claimant is called the ''verifier''. When the claimant successfully demonstrates knowledge of the password to the verifier through an established authentication protocol, the verifier is able to infer the claimant's identity. In general, a password is an arbitrary string of characters including letters, digits, or other symbols. If the permissible characters are constrained to be numeric, the corresponding secret is sometimes called a personal i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |