|
Motion System
{{refimprove, date=September 2007 Motion system in engineering and systems, is a component of a test and measurement system that provides motion to a load or loads in a one or many directions. Generally a motion system is made up of a set (or stack) of linear and rotational stages. A linear stage moves in a straight line, while a rotation stage moves in a partial or full circle. A stage can either be manually controlled with a knob control, or automated with a motion controller. A motion system generally is computer controlled and can perform fast, reliable, repeatable, and accurate positioning of loads. Most systems will support motion in X and Y directions, which is referred to as an XY stack. Often either a Z axis (up/down motion) or R axis (rotational motion) is placed on top of the XY stack. For automated stages, a scale can be attached to the internals of the stage and an encoder used to measure the position on the scale and report this to the controller, thereby determin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experiment
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into Causality, cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs when a particular factor is manipulated. Experiments vary greatly in goal and scale but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results. There also exist natural experiment, natural experimental studies. A child may carry out basic experiments to understand how things fall to the ground, while teams of scientists may take years of systematic investigation to advance their understanding of a phenomenon. Experiments and other types of hands-on activities are very important to student learning in the science classroom. Experiments can raise test scores and help a student become more engaged and interested in the material they are learning, especially when used over time. Experiments can vary from personal and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measurement
Measurement is the quantification of attributes of an object or event, which can be used to compare with other objects or events. In other words, measurement is a process of determining how large or small a physical quantity is as compared to a basic reference quantity of the same kind. The scope and application of measurement are dependent on the context and discipline. In natural sciences and engineering, measurements do not apply to nominal properties of objects or events, which is consistent with the guidelines of the ''International vocabulary of metrology'' published by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures. However, in other fields such as statistics as well as the social and behavioural sciences, measurements can have multiple levels, which would include nominal, ordinal, interval and ratio scales. Measurement is a cornerstone of trade, science, technology and quantitative research in many disciplines. Historically, many measurement systems existed fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System
A system is a group of Interaction, interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its environment (systems), environment, is described by its boundaries, structure and purpose and expressed in its functioning. Systems are the subjects of study of systems theory and other systems sciences. Systems have several common properties and characteristics, including structure, function(s), behavior and interconnectivity. Etymology The term ''system'' comes from the Latin word ''systēma'', in turn from Greek language, Greek ''systēma'': "whole concept made of several parts or members, system", literary "composition"."σύστημα" Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, ''A Greek–English Lexicon'', on Per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Load
A structural load or structural action is a force, deformation, or acceleration applied to structural elements. A load causes stress, deformation, and displacement in a structure. Structural analysis, a discipline in engineering, analyzes the effects of loads on structures and structural elements. Excess load may cause structural failure, so this should be considered and controlled during the design of a structure. Particular mechanical structures—such as aircraft, satellites, rockets, space stations, ships, and submarines—are subject to their own particular structural loads and actions. Engineers often evaluate structural loads based upon published regulations, contracts, or specifications. Accepted technical standards are used for acceptance testing and inspection. Types Dead loads are static forces that are relatively constant for an extended time. They can be in tension or compression. The term can refer to a laboratory test method or to the normal usage of a material ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear
Linearity is the property of a mathematical relationship (''function'') that can be graphically represented as a straight line. Linearity is closely related to '' proportionality''. Examples in physics include rectilinear motion, the linear relationship of voltage and current in an electrical conductor (Ohm's law), and the relationship of mass and weight. By contrast, more complicated relationships are ''nonlinear''. Generalized for functions in more than one dimension, linearity means the property of a function of being compatible with addition and scaling, also known as the superposition principle. The word linear comes from Latin ''linearis'', "pertaining to or resembling a line". In mathematics In mathematics, a linear map or linear function ''f''(''x'') is a function that satisfies the two properties: * Additivity: . * Homogeneity of degree 1: for all α. These properties are known as the superposition principle. In this definition, ''x'' is not necessarily a real ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotational
Rotation, or spin, is the circular movement of an object around a '' central axis''. A two-dimensional rotating object has only one possible central axis and can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. A three-dimensional object has an infinite number of possible central axes and rotational directions. If the rotation axis passes internally through the body's own center of mass, then the body is said to be ''autorotating'' or ''spinning'', and the surface intersection of the axis can be called a ''pole''. A rotation around a completely external axis, e.g. the planet Earth around the Sun, is called ''revolving'' or ''orbiting'', typically when it is produced by gravity, and the ends of the rotation axis can be called the ''orbital poles''. Mathematics Mathematically, a rotation is a rigid body movement which, unlike a translation, keeps a point fixed. This definition applies to rotations within both two and three dimensions (in a plane and in space, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
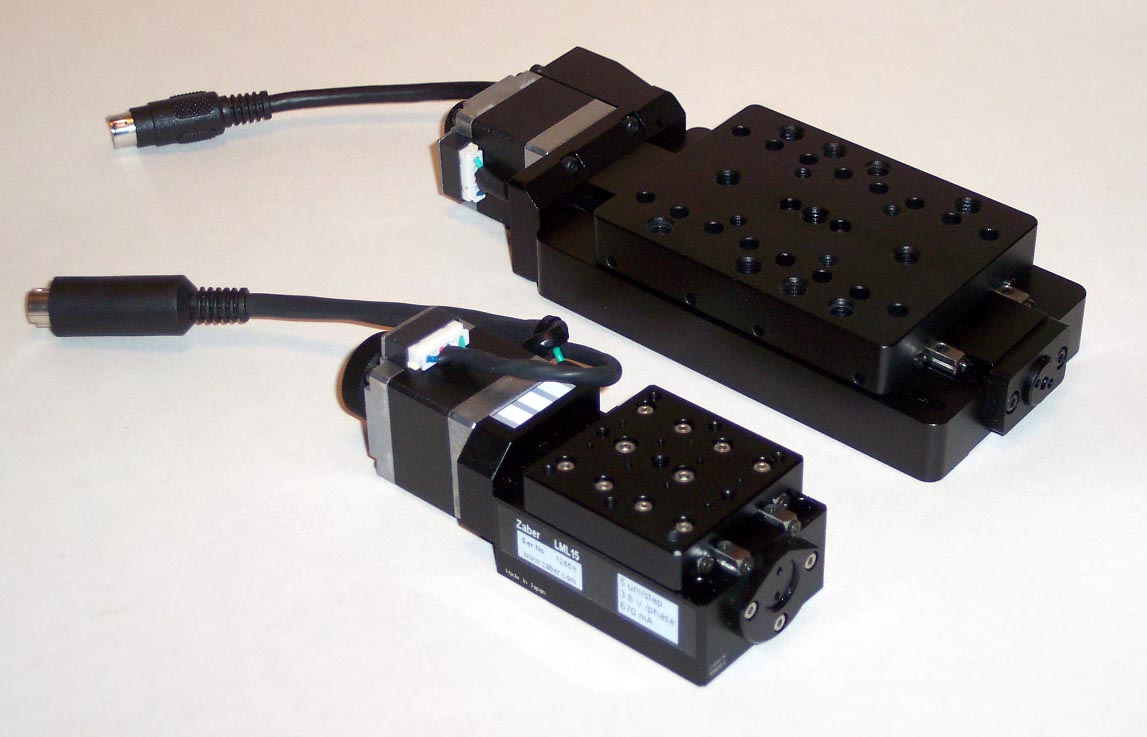
Linear Stage
A linear stage or translation stage is a component of a precise motion system used to restrict an object to a single axis of motion. The term linear slide is often used interchangeably with "linear stage", though technically "linear slide" refers to a linear motion bearing, which is only a component of a linear stage. All linear stages consist of a platform and a base, joined by some form of guide or linear bearing in such a way that the platform is restricted to linear motion with respect to the base. In common usage, the term linear stage may or may not also include the mechanism by which the position of the platform is controlled relative to the base. Principle of operation In three-dimensional space, an object may either rotate about, or translate along any of three axes. Thus the object is said to have six degrees of freedom (3 rotational and 3 translational). A linear stage exhibits only one degree of freedom (translation along one axis). In other words, linear stages opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Straight Line
In geometry, a line is an infinitely long object with no width, depth, or curvature. Thus, lines are One-dimensional space, one-dimensional objects, though they may exist in Two-dimensional Euclidean space, two, Three-dimensional space, three, or higher dimension spaces. The word ''line'' may also refer to a line segment in everyday life, which has two Point (geometry), points to denote its ends. Lines can be referred by two points that lay on it (e.g., \overleftrightarrow) or by a single letter (e.g., \ell). Euclid described a line as "breadthless length" which "lies evenly with respect to the points on itself"; he introduced several postulates as basic unprovable properties from which he constructed all of geometry, which is now called Euclidean geometry to avoid confusion with other geometries which have been introduced since the end of the 19th century (such as Non-Euclidean geometry, non-Euclidean, Projective geometry, projective and affine geometry). In modern mathematic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Stage
A linear stage or translation stage is a component of a precise motion system used to restrict an object to a single axis of motion. The term linear slide is often used interchangeably with "linear stage", though technically "linear slide" refers to a linear motion bearing, which is only a component of a linear stage. All linear stages consist of a platform and a base, joined by some form of guide or linear bearing in such a way that the platform is restricted to linear motion with respect to the base. In common usage, the term linear stage may or may not also include the mechanism by which the position of the platform is controlled relative to the base. Principle of operation In three-dimensional space, an object may either rotate about, or translate along any of three axes. Thus the object is said to have six degrees of freedom (3 rotational and 3 translational). A linear stage exhibits only one degree of freedom (translation along one axis). In other words, linear stages opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System Of Measurement
A system of measurement is a collection of units of measurement and rules relating them to each other. Systems of measurement have historically been important, regulated and defined for the purposes of science and commerce. Systems of measurement in use include the International System of Units or (the modern form of the metric system), the British imperial system, and the United States customary system. History The French Revolution gave rise to the metric system, and this has spread around the world, replacing most customary units of measure. In most systems, length (distance), mass, and time are ''base quantities''. Later science developments showed that an electromagnetic quantity such as electric charge or electric current could be added to extend the set of base quantities. Gaussian units have only length, mass, and time as base quantities, with no separate electromagnetic dimension. Other quantities, such as Power (physics), power and speed, are derived from the base set: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motion Controller
In video games and entertainment systems, a motion controller is a type of game controller that uses accelerometers or other sensors to track motion and provide input. History Motion controllers using accelerometers are used as controllers for video games, which was made more popular since 2006 by the Wii Remote controller for Nintendo's Wii console, which uses accelerometers to detect its approximate orientation and acceleration, and serves an image sensor, so it can be used as a pointing device. It was followed by other similar devices, including the ASUS Eee Stick, Sony PlayStation Move (which also uses magnetometers to track the Earth's magnetic field and computer vision via the PlayStation Eye to aid in position tracking), Joy-Con, and HP Swing. The PlayStation 3's first controller, the Sixaxis, included motion sensing at the notable loss of haptic feedback (vibration) due to interference concerns; these features were both included on the later DualShock 3. Other systems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpeg)