|
Mothers Against Decapentaplegic Homolog 9
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 9 also known as SMAD9, SMAD8, and MADH6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SMAD9'' gene. SMAD9, as its name describes, is a homolog of the Drosophila gene: "Mothers against decapentaplegic". It belongs to the SMAD family of proteins, which belong to the TGFβ superfamily of modulators. Like many other TGFβ family members, SMAD9 is involved in cell signalling. When a bone morphogenetic protein binds to a receptor ( BMP type 1 receptor kinase) it causes SMAD9 to interact with SMAD anchor for receptor activation (SARA).The binding of ligands causes the phosphorylation of the SMAD9 protein and the dissociation from SARA and the association with SMAD4. It is subsequently transferred to the nucleus where it forms complexes with other proteins and acts as a transcription factor. SMAD9 is a receptor regulated SMAD ( R-SMAD) and is activated by bone morphogenetic protein type 1 receptor kinase. There are two isoforms of the protein. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription Factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The function of TFs is to regulate—turn on and off—genes in order to make sure that they are expressed in the desired cells at the right time and in the right amount throughout the life of the cell and the organism. Groups of TFs function in a coordinated fashion to direct cell division, cell growth, and cell death throughout life; cell migration and organization (body plan) during embryonic development; and intermittently in response to signals from outside the cell, such as a hormone. There are up to 1600 TFs in the human genome. Transcription factors are members of the proteome as well as regulome. TFs work alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (as an activator), or blocking (as a repressor) the recruitment of RNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MH2 Domain
MH or mH may refer to: Businesses and organizations * Malaysia Airlines, by IATA airline designator * Menntaskólinn við Hamrahlíð, a gymnasium in Reykjavík, Iceland * Miami Heat, an NBA basketball team Places * Mahalle, (abbreviated mh. on maps) a Turkish residential district * Maharashtra, a state of western India (ISO 3166-2 code MH) * Marshall Islands (ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 country code and postal symbol MH) * County Meath, Ireland (code MH) * Montserrat (FIPS PUB 10-4 territory code MH) People Politics * Mohammad Hatta, 1st Vice President of Indonesia, 3rd Prime Minister of Indonesia, 4th Minister of Defense of Indonesia and 4th Foreign Minister of Indonesia Musicians * Michael Hutchence, frontman and lead singer of Australian rock band INXS Technologists * Michael Hood, internet researcher Science and technology * .mh, the Internet country code top-level domain for Marshall Islands * Malignant hyperthermia, in medicine *Masked hypertension, the phenomenon where a patie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Developmental Genes And Proteins
Development of the human body is the process of growth to maturity. The process begins with fertilization, where an egg released from the ovary of a female is penetrated by a sperm cell from a male. The resulting zygote develops through mitosis and cell differentiation, and the resulting embryo then implants in the uterus, where the embryo continues development through a fetal stage until birth. Further growth and development continues after birth, and includes both physical and psychological development, influenced by genetic, hormonal, environmental and other factors. This continues throughout life: through childhood and adolescence into adulthood. Before birth Development before birth, or prenatal development () is the process in which a zygote, and later an embryo and then a fetus develops during gestation. Prenatal development starts with fertilization and the formation of the zygote, the first stage in embryonic development which continues in fetal development until b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mothers Against Drunk Driving
Mothers Against Drunk Driving (MADD) is a non-profit organization in the United States, Canada and Brazil that seeks to stop drunk driving, support those affected by drunk driving, prevent underage drinking, and strive for stricter impaired driving policy, whether that impairment is caused by alcohol or any other drug. The Irving, Texas–based organization was founded on September 5, 1980, in California by Candace Lightner after her 13-year-old daughter, Cari, was killed by a drunk driver. There is at least one MADD office in every state of the United States and at least one in each province of Canada. These offices offer victim services and many resources involving alcohol safety. MADD has claimed that drunk driving has been reduced by half since its founding. Positions According to MADD's website, "The mission of Mothers Against Drunk Driving is to end drunk driving, help fight drugged driving, support the victims of these violent crimes and prevent underage drinking." General ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
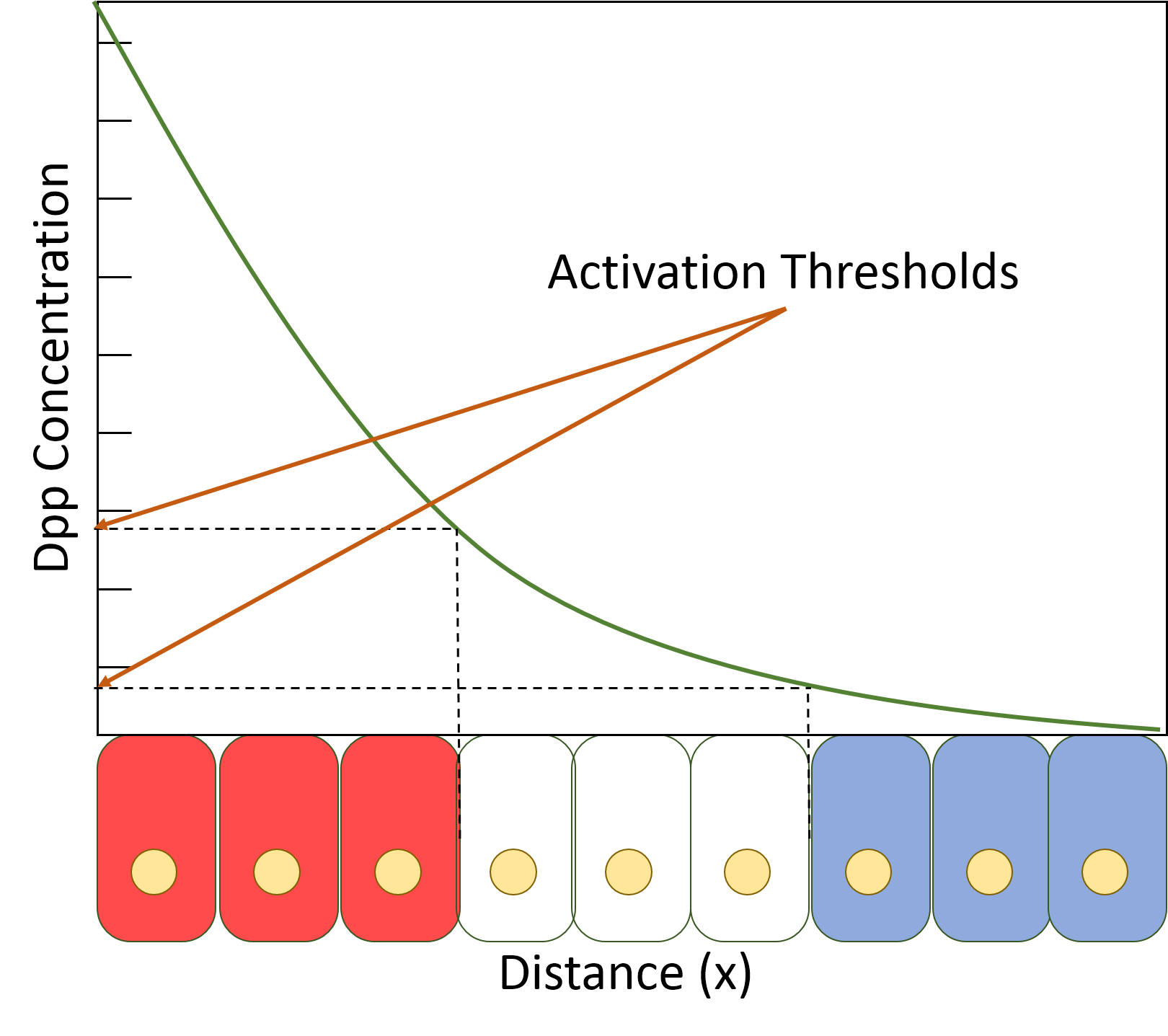
Decapentaplegic
Decapentaplegic (Dpp) is a key morphogen involved in the development of the fruit fly ''Drosophila melanogaster'' and is the first validated secreted morphogen. It is known to be necessary for the correct patterning and development of the early ''Drosophila'' embryo and the fifteen imaginal discs, which are tissues that will become limbs and other organs and structures in the adult fly. It has also been suggested that Dpp plays a role in regulating the growth and size of tissues. Flies with mutations in decapentaplegic fail to form these structures correctly, hence the name (''decapenta''-, fifteen, -''plegic'', paralysis). Dpp is the Drosophila homolog of the vertebrate bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), which are members of the TGF-β superfamily, a class of proteins that are often associated with their own specific signaling pathway. Studies of Dpp in Drosophila have led to greater understanding of the function and importance of their homologs in vertebrates like humans. Func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caenorhabditis Elegans
''Caenorhabditis elegans'' () is a free-living transparent nematode about 1 mm in length that lives in temperate soil environments. It is the type species of its genus. The name is a blend of the Greek ''caeno-'' (recent), ''rhabditis'' (rod-like) and Latin ''elegans'' (elegant). In 1900, Maupas initially named it '' Rhabditides elegans.'' Osche placed it in the subgenus ''Caenorhabditis'' in 1952, and in 1955, Dougherty raised ''Caenorhabditis'' to the status of genus. ''C. elegans'' is an unsegmented pseudocoelomate and lacks respiratory or circulatory systems. Most of these nematodes are hermaphrodites and a few are males. Males have specialised tails for mating that include spicules. In 1963, Sydney Brenner proposed research into ''C. elegans,'' primarily in the area of neuronal development. In 1974, he began research into the molecular and developmental biology of ''C. elegans'', which has since been extensively used as a model organism. It was the first multicellu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoforms
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene or gene family and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some isoforms have unique functions. A set of protein isoforms may be formed from alternative splicings, variable promoter usage, or other post-transcriptional modifications of a single gene; post-translational modifications are generally not considered. (For that, see Proteoforms.) Through RNA splicing mechanisms, mRNA has the ability to select different protein-coding segments ( exons) of a gene, or even different parts of exons from RNA to form different mRNA sequences. Each unique sequence produces a specific form of a protein. The discovery of isoforms could explain the discrepancy between the small number of protein coding regions genes revealed by the human genome project and the large diversity of proteins seen in an organism: different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R-SMAD
R-SMADs are receptor-regulated SMADs. SMADs are transcription factors that transduce extracellular TGF-β superfamily ligand signaling from cell membrane bound TGF-β receptors into the nucleus where they activate transcription TGF-β target genes. R-SMADS are directly phosphorylated on their c-terminus by type 1 TGF-β receptors through their intracellular kinase domain, leading to r-SMAD activation. R-SMADS include SMAD2 and SMAD3 from the TGF-β/Activin/Nodal branch, and SMAD1, SMAD5 and SMAD8 from the BMP/GDP branch of TGF-β signaling. In response to signals by the TGF-β superfamily of ligands these proteins associate with receptor kinases and are phosphorylated at an SSXS motif at their extreme C-terminus. These proteins then typically bind to the common mediator Smad or co-SMAD SMAD4. Smad complexes then accumulate in the cell nucleus where they regulate transcription of specific target genes: * SMAD2 and SMAD3 are activated in response to TGF-β/ Activin or Nodal sign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Nucleus
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have no nuclei, and a few others including osteoclasts have many. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm; and the nuclear matrix, a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support. The cell nucleus contains nearly all of the cell's genome. Nuclear DNA is often organized into multiple chromosomes – long stands of DNA dotted with various proteins, such as histones, that protect and organize the DNA. The genes within these chromosomes are structured in such a way to promote cell function. The nucleus maintains the integrity of genes and controls the activities of the cell by regulating gene expres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drosophila Melanogaster
''Drosophila melanogaster'' is a species of fly (the taxonomic order Diptera) in the family Drosophilidae. The species is often referred to as the fruit fly or lesser fruit fly, or less commonly the "vinegar fly" or "pomace fly". Starting with Charles W. Woodworth's 1901 proposal of the use of this species as a model organism, ''D. melanogaster'' continues to be widely used for biological research in genetics, physiology, microbial pathogenesis, and life history evolution. As of 2017, five Nobel Prizes have been awarded to drosophilists for their work using the insect. ''D. melanogaster'' is typically used in research owing to its rapid life cycle, relatively simple genetics with only four pairs of chromosomes, and large number of offspring per generation. It was originally an African species, with all non-African lineages having a common origin. Its geographic range includes all continents, including islands. ''D. melanogaster'' is a common pest in homes, restaurants, and othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |