|
Monsoons
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscillation of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) between its limits to the north and south of the equator. Usually, the term monsoon is used to refer to the rainy phase of a seasonally changing pattern, although technically there is also a dry phase. The term is also sometimes used to describe locally heavy but short-term rains. The major monsoon systems of the world consist of the West African, Asia–Australian, the North American, and South American monsoons. The term was first used in English in British India and neighboring countries to refer to the big seasonal winds blowing from the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea in the southwest bringing heavy rainfall to the area. Etymology The etymology of the word monsoon is not wholl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monsoon Clouds Near Nagercoil
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscillation of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) between its limits to the north and south of the equator. Usually, the term monsoon is used to refer to the rainy phase of a seasonally changing pattern, although technically there is also a dry phase. The term is also sometimes used to describe locally heavy but short-term rains. The major monsoon systems of the world consist of the West African, Asia–Australian, the North American, and South American monsoons. The term was first used in English in British India and neighboring countries to refer to the big seasonal winds blowing from the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea in the southwest bringing heavy rainfall to the area. Etymology The etymology of the word monsoon is not wholly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monsoon Clouds Arriving At Port Blair, Andaman
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscillation of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) between its limits to the north and south of the equator. Usually, the term monsoon is used to refer to the rainy phase of a seasonally changing pattern, although technically there is also a dry phase. The term is also sometimes used to describe locally heavy but short-term rains. The major monsoon systems of the world consist of the West African, Asia–Australian, the North American, and South American monsoons. The term was first used in English in British India and neighboring countries to refer to the big seasonal winds blowing from the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea in the southwest bringing heavy rainfall to the area. Etymology The etymology of the word monsoon is not wholly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monsoon Clouds Lucknow
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscillation of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) between its limits to the north and south of the equator. Usually, the term monsoon is used to refer to the rainy phase of a seasonally changing pattern, although technically there is also a dry phase. The term is also sometimes used to describe locally heavy but short-term rains. The major monsoon systems of the world consist of the West African, Asia–Australian, the North American, and South American monsoons. The term was first used in English in British India and neighboring countries to refer to the big seasonal winds blowing from the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea in the southwest bringing heavy rainfall to the area. Etymology The etymology of the word monsoon is not wholly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau (, also known as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau or the Qing–Zang Plateau () or as the Himalayan Plateau in India, is a vast elevated plateau located at the intersection of Central, South and East Asia covering most of the Tibet Autonomous Region, most of Qinghai, western half of Sichuan, Southern Gansu provinces in Western China, southern Xinjiang, Bhutan, the Indian regions of Ladakh and Lahaul and Spiti (Himachal Pradesh) as well as Gilgit-Baltistan in Pakistan, northwestern Nepal, eastern Tajikistan and southern Kyrgyzstan. It stretches approximately north to south and east to west. It is the world's highest and largest plateau above sea level, with an area of (about five times the size of Metropolitan France). With an average elevation exceeding and being surrounded by imposing mountain ranges that harbor the world's two highest summits, Mount Everest and K2, the Tibetan Plateau is often referred to as "the Roof of the World". The Tibetan Platea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
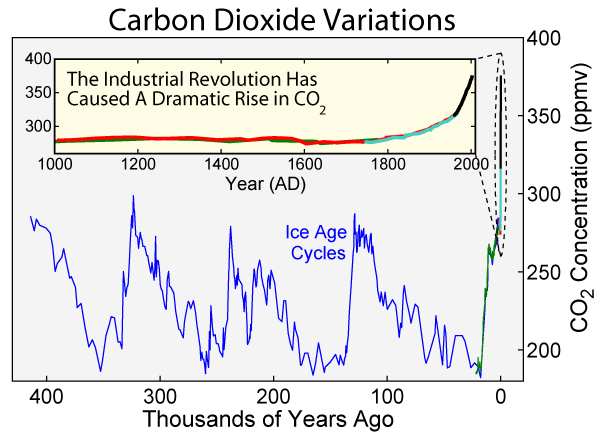
Climate Change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global average temperature is more rapid than previous changes, and is primarily caused by humans burning fossil fuels. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices increase greenhouse gases, notably carbon dioxide and methane. Greenhouse gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight. Larger amounts of these gases trap more heat in Earth's lower atmosphere, causing global warming. Due to climate change, deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Increased warming in the Arctic has contributed to melting permafrost, glacial retreat and sea ice loss. Higher temperatures are also causin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North American Monsoon
The North American monsoon, variously known as the Southwest monsoon, the Mexican monsoon, the New Mexican monsoon, or the Arizona monsoon is a pattern of pronounced increase in thunderstorms and rainfall over large areas of the southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico, typically occurring between June and mid-September. During the monsoon, thunderstorms are fueled by daytime heating and build up during the late afternoon and early evening. Typically, these storms dissipate by late night, and the next day starts out fair, with the cycle repeating daily. The monsoon typically loses its energy by mid-September when much drier conditions are reestablished over the region. Geographically, the North American monsoon precipitation region is centered over the Sierra Madre Occidental in the Mexican states of Sinaloa, Durango, Sonora Sonora (), officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Sonora ( en, Free and Sovereign State of Sonora), is one of the 31 states which, along with Mex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainfall
Rain is water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water for hydroelectric power plants, crop irrigation, and suitable conditions for many types of ecosystems. The major cause of rain production is moisture moving along three-dimensional zones of temperature and moisture contrasts known as weather fronts. If enough moisture and upward motion is present, precipitation falls from convective clouds (those with strong upward vertical motion) such as cumulonimbus (thunder clouds) which can organize into narrow rainbands. In mountainous areas, heavy precipitation is possible where upslope flow is maximized within windward sides of the terrain at elevation which forces moist air to condense and fall out as rainfall along the sides of mountains. On the leeward side of mountains, desert climates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eemian
The Eemian (also called the last interglacial, Sangamonian Stage, Ipswichian, Mikulin, Kaydaky, penultimate,NOAA - Penultimate Interglacial Period http://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/global-warming/penultimate-interglacial-period Valdivia or Riss-Würm) was the interglacial period which began about 130,000 years ago at the end of the Penultimate Glacial Period and ended about 115,000 years ago at the beginning of the Last Glacial Period. It corresponds to Marine Isotope Stage 5e. Although sometimes referred to as the "last interglacial" (in the "most recent previous" sense of "last"), it was the second-to-latest interglacial period of the current Ice Age, the most recent being the Holocene which extends to the present day (having followed the last glacial period). The prevailing Eemian climate was, on average, around 1 to 2 degrees Celsius (1.8 to 3.6 Fahrenheit) warmer than that of the Holocene. During the Eemian, the proportion of in the atmosphere was about 280 parts per million. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the '' Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing a faunal interchange between the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology
''Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology'' ("''Palaeo3''") is a peer-reviewed scientific journal publishing multidisciplinary studies and comprehensive reviews in the field of palaeoenvironmental geology. The journal is edited by T. J. Algeo, H. Falcon-Lang, P. Hesse, I. Montanez, J. Pike and S. Xie. It was established in 1965 and is currently published by Elsevier. Indexing and abstracting ''Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology'' is indexed and abstracted in the following databases: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', ''Advance in Space Research'' has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 3.318. References External links * Biology journals Elsevier academic journals English-language journals Publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by the shores of South China (hence the name), in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Philippines (mainly Luzon, Mindoro and Palawan), and in the south by Borneo, eastern Sumatra and the Bangka Belitung Islands, encompassing an area of around . It communicates with the East China Sea via the Taiwan Strait, the Philippine Sea via the Luzon Strait, the Sulu Sea via the straits around Palawan (e.g. the Mindoro and Balabac Straits), the Strait of Malacca via the Singapore Strait, and the Java Sea via the Karimata and Bangka Straits. The Gulf of Thailand and the Gulf of Tonkin are also part of the South China Sea. The shallow waters south of the Riau Islands are also known as the Natuna Sea. The South China Sea is a region of tremendous economic and geostrategic importance. One-third of the world's maritime shipping p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
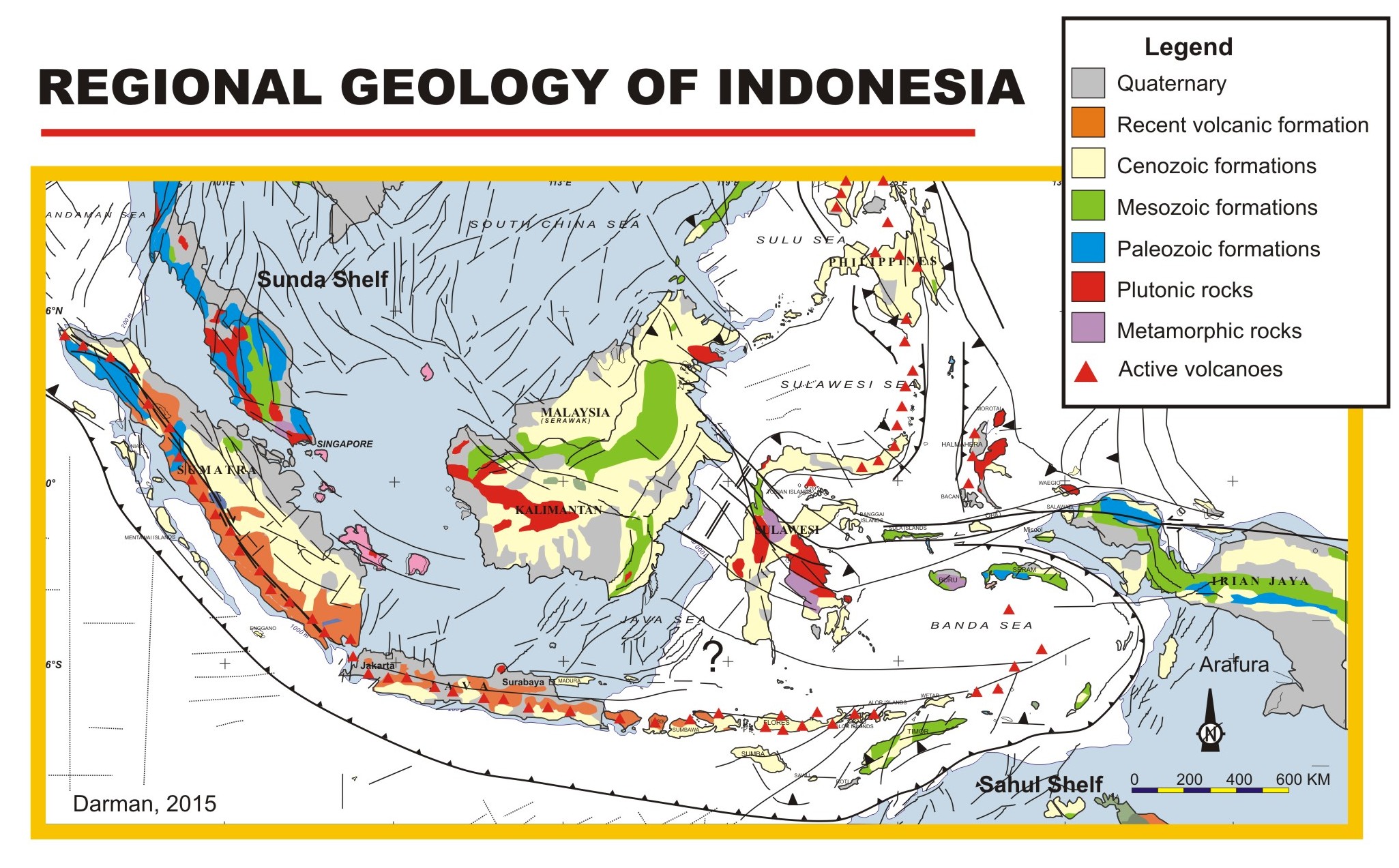
Geology Of Indonesia
This is a brief summary of the geology of Indonesia. Indonesia is located between two major tectonic plates, the Australian Plate and the Eurasian Plate. Tectonics The tectonics of Indonesia are very complex, as it is a meeting point of several tectonic plates. Indonesia is located between two continental plates: the Australian Plate ( Sahul Shelf) and the Eurasian Plate (Sunda Shelf); and between two oceanic plates: the Pacific Plate and the Philippine Sea Plate. The subduction of the Indian Plate beneath the Eurasian Plate formed the volcanic arc in western Indonesia, one of the most seismically active areas on the planet with a long history of powerful eruptions and earthquakes. This chain of active volcanoes formed Sumatra, Java, Bali, and the Lesser Sunda Islands, most of which, particularly Java and Bali, emerged within the last 2–3 million years. The Pacific and Australian plate movements controlled the tectonics of the eastern portion of Indonesia. Structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |