|
Monorepo
In version-control systems, a monorepo (" mono" meaning 'single' and "repo" being short for ' repository') is a software-development strategy in which the code for a number of projects is stored in the same repository. This practice dates back to at least the early 2000s, when it was commonly called a shared codebase. Google, Meta, Microsoft, Uber, Airbnb, and Twitter all employ very large monorepos with varying strategies to scale build systems and version control software with a large volume of code and daily changes. A related concept is a monolithic application, but whereas a monolith combines its sub-projects into one large project, a monorepo may contain multiple independent projects. Advantages There are a number of potential advantages to a monorepo over individual repositories: ; Ease of code reuse : Similar functionality or communication protocols can be abstracted into shared libraries and directly included by projects, without the need of a dependency package ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bazel (software)
Bazel () is a free and open-source software tool used for the automation of building and testing software. Similar to build tools like Make, Apache Ant, and Apache Maven, Bazel builds software applications from source code using rules. Rules and macros are created in the Starlark language, a dialect of Python. There are built-in rules for building software written in Java, Kotlin, Scala, C, C++, Go, Python, Rust, JavaScript, Objective-C, and bash scripts. Bazel can produce software application packages suitable for deployment for the Android and iOS operating systems. History In 2006, Google started the development of a build tool called ''Blaze''. The motivation was to have a build system that provides both speed and correctness in a large monorepo. Bazel was created as an open-source port of Blaze, using its anagram as a name. Bazel was first released in March 2015 and entered beta by September 2015. Version 1.0 was released in October 2019. Rationale Bazel has b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Buck (software)
Buck is a multi-language build system developed and used by Meta Platforms, Inc. It was designed for building small, reusable modules consisting of code and resources within a monorepo. It supports many programming languages, including C++, Swift, Unix Shell, Java, Kotlin, Python, Lua, OCaml, Rust and Go. It can produce binary outputs for a variety of target platforms including iOS, Android, .NET, and Java virtual machine (VM) runtime systems. Licensing for Buck1 is under Apache License 2.0, while Buck2 is under either MIT or Apache 2.0. Buck requires the explicit declaration of dependencies. Because all dependencies are explicit and Buck has a directed acyclic graph of all source files and build targets, Buck can perform incremental recompilation, only rebuilding targets downstream of files that have changed. Buck computes a key for each target that is a hash of the contents of the files it depends on. It stores a mapping from that key to the build target in a build cache. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
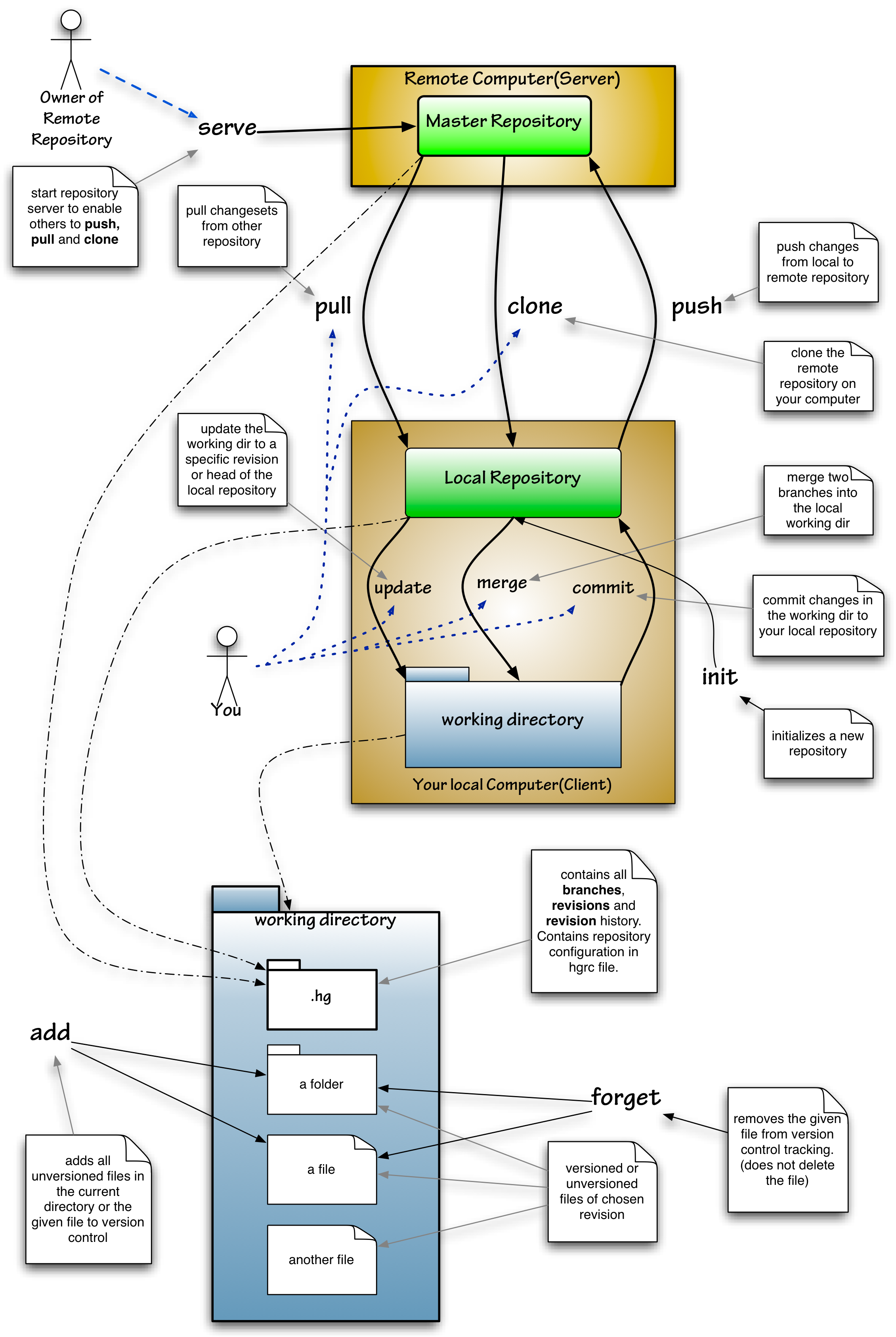
Mercurial
Mercurial is a distributed revision control tool for software developers. It is supported on Microsoft Windows, Linux, and other Unix-like systems, such as FreeBSD and macOS. Mercurial's major design goals include high performance and scalability, decentralization, fully distributed collaborative development, robust handling of both plain text and binary files, and advanced branching and merging capabilities, while remaining conceptually simple. It includes an integrated web-interface. Mercurial has also taken steps to ease the transition for users of other version control systems, particularly Subversion. Mercurial is primarily a command-line driven program, but graphical user interface extensions are available, e.g. TortoiseHg, and several IDEs offer support for version control with Mercurial. All of Mercurial's operations are invoked as arguments to its driver program hg (a reference to Hg – the chemical symbol of the element mercury). Olivia Mackall originated Mercu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Atomic Commit
In the field of computer science, an atomic Commit (data management), commit is an operation that applies a set of distinct changes as a single operation. If the changes are applied, then the atomic commit is said to have succeeded. If there is a failure before the atomic commit can be completed, then all of the changes completed in the atomic commit are reversed. This ensures that the system is always left in a consistent state. The other key property of isolation comes from their nature as atomicity (database systems), atomic operations. Isolation ensures that only one atomic commit is processed at a time. The most common uses of atomic commits are in database systems and Version control, version control systems. The problem with atomic commits is that they require coordination between multiple systems. As computer networks are unreliable services, this means no algorithm can coordinate with all systems as proven in the Two Generals' Problem, Two Generals Problem. As databases bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Code Refactoring
In computer programming and software design, code refactoring is the process of restructuring existing source code—changing the '' factoring''—without changing its external behavior. Refactoring is intended to improve the design, structure, and/or implementation of the software (its '' non-functional'' attributes), while preserving its functionality. Potential advantages of refactoring may include improved code readability and reduced complexity; these can improve the source code's maintainability and create a simpler, cleaner, or more expressive internal architecture or object model to improve extensibility. Another potential goal for refactoring is improved performance; software engineers face an ongoing challenge to write programs that perform faster or use less memory. Typically, refactoring applies a series of standardized basic ''micro-refactorings'', each of which is (usually) a tiny change in a computer program's source code that either preserves the behavior of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The early 1980s and home computers, rise of personal computers through software like Windows, and the company has since expanded to Internet services, cloud computing, video gaming and other fields. Microsoft is the List of the largest software companies, largest software maker, one of the Trillion-dollar company, most valuable public U.S. companies, and one of the List of most valuable brands, most valuable brands globally. Microsoft was founded by Bill Gates and Paul Allen to develop and sell BASIC interpreters for the Altair 8800. It rose to dominate the personal computer operating system market with MS-DOS in the mid-1980s, followed by Windows. During the 41 years from 1980 to 2021 Microsoft released 9 versions of MS-DOS with a median frequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Apache Subversion
Apache Subversion (often abbreviated SVN, after its command name ''svn'') is a version control system distributed as open source under the Apache License. Software developers use Subversion to maintain current and historical versions of files such as source code, web pages, and documentation. Its goal is to be a mostly compatible successor to the widely used Concurrent Versions System (CVS). The open source community has used Subversion widely: for example, in projects such as Apache Software Foundation, FreeBSD, SourceForge, and from 2006 to 2019, GCC. CodePlex was previously a common host for Subversion repositories. Subversion was created by CollabNet Inc. in 2000, and is now a top-level Apache project being built and used by a global community of contributors. History CollabNet founded the Subversion project in 2000 as an effort to write an open-source version-control system which operated much like CVS but which fixed the bugs and supplied some features missing in CVS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Repository (version Control)
In version control systems, a repository is a data structure that stores metadata for a set of files or directory structure. Depending on whether the version control system in use is distributed, like Git or Mercurial, or centralized, like Subversion, CVS, or Perforce, the whole set of information in the repository may be duplicated on every user's system or may be maintained on a single server. Some of the metadata that a repository contains includes, among other things, a historical record of changes in the repository, a set of commit objects, and a set of references to commit objects, called ''heads''. The main purpose of a repository is to store a set of files, as well as the history of changes made to those files. Exactly how each version control system handles storing those changes, however, differs greatly. For instance, Subversion in the past relied on a database instance but has since moved to storing its changes directly on the filesystem. These differences in stor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Directed Acyclic Graph
In mathematics, particularly graph theory, and computer science, a directed acyclic graph (DAG) is a directed graph with no directed cycles. That is, it consists of vertices and edges (also called ''arcs''), with each edge directed from one vertex to another, such that following those directions will never form a closed loop. A directed graph is a DAG if and only if it can be topologically ordered, by arranging the vertices as a linear ordering that is consistent with all edge directions. DAGs have numerous scientific and computational applications, ranging from biology (evolution, family trees, epidemiology) to information science (citation networks) to computation (scheduling). Directed acyclic graphs are also called acyclic directed graphs or acyclic digraphs. Definitions A graph is formed by vertices and by edges connecting pairs of vertices, where the vertices can be any kind of object that is connected in pairs by edges. In the case of a directed graph, each edg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Continuous Testing
Continuous testing is the process of executing automated tests as part of the software delivery pipeline to obtain immediate feedback on the business risks associated with a software release candidate.Part of the Pipeline: Why Continuous Testing Is Essential by Adam Auerbach, TechWell Insights August 2015The Relationship between Risk and Continuous Testing: An Interview with Wayne Ariola by Cameron Philipp-Edmonds, Stickyminds December 2015 Continuous testing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Software Build
A software build is the process of converting source code files into standalone artifact (software development), software artifact(s) that can be run on a computer, or the result of doing so. In software production, builds optimize software for performance and distribution, packaging into formats such as '.''exe'; '.deb'; '.apk. The build process often employs specialized tools such as CMake, Make, or Gradle, and integrates with automation systems including Jenkins (software), Jenkins or Git Actions. Despite advancements, challenges such as dependency conflicts, platform compatibility, and long compile times, remain problems. Software development In software development, building software is an end-to-end process that involves many distinct functions. Some of these functions are described below. Version control The version control function carries out activities such as workspace creation and updating, baselining and reporting. It creates an environment for the build process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Virtual File System For Git
Virtual File System for Git (VFS for Git), developed by Microsoft, is an extension to the Git version control system. Overview VFS for Git is designed to ease the handling of enterprise-scale Git repositories, such as the Microsoft Windows operating system (whose development switched to Git under Microsoft's internal "One Engineering System" initiative). The system exposes a virtual file system that only downloads files to local storage as they are needed. History VFS for Git was originally named Git Virtual File System (GVFS). However due to complaints by the developers of GNOME over confusion with GNOME Virtual File System, Microsoft announced that it would solicit ideas for a new name of the software in June 2018, following its acquisition of GitHub. Its first release under the new name was in August 2018. In November 2017, GitHub announced that it would support VFS for Git. VFS for Git has been superseded by Scalar. Scalar was then integrated into the Microsoft Git pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |