|
Molecular Logic Gates
A molecular logic gate is a molecule that performs a logical operation based on one or more physical or chemical inputs and a single output. The field has advanced from simple logic systems based on a single chemical or physical input to molecules capable of combinatorial and sequential operations such as arithmetic operations (i.e. moleculators and memory storage algorithms). For logic gates with a single input, there are four possible output patterns. When the input is 0, the output can be either a 0 or 1. When the input is 1, the output can again be 0 or 1. The four output bit patterns that can arise corresponds to a specific logic type: PASS 0, YES, NOT and PASS 1. PASS 0 always outputs 0, whatever the input. PASS 1 always outputs 1, whatever the input. YES outputs a 1 when the input is 1 and NOT is the inverse YES – it outputs a 0 when the input is 1. An example of a YES logic gate is the molecular structure shown below. A "1" output is given only when sodium ions are presen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A YES Molecular Logic Gate
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''a'' (pronounced ), plural ''aes''. It is similar in shape to the Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version can be written in two forms: the double-storey a and single-storey ɑ. The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type. In English grammar, " a", and its variant " an", are indefinite articles. History The earliest certain ancestor of "A" is aleph (also written 'aleph), the first letter of the Phoenician alphabet, which consisted entirely of consonants (for that reason, it is also called an abjad to distinguish it f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescence
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, than the absorbed radiation. A perceptible example of fluorescence occurs when the absorbed radiation is in the ultraviolet region of the electromagnetic spectrum (invisible to the human eye), while the emitted light is in the visible region; this gives the fluorescent substance a distinct color that can only be seen when the substance has been exposed to UV light. Fluorescent materials cease to glow nearly immediately when the radiation source stops, unlike phosphorescent materials, which continue to emit light for some time after. Fluorescence has many practical applications, including mineralogy, gemology, medicine, chemical sensors (fluorescence spectroscopy), fluorescent labelling, dyes, biological detectors, cosmic-ray detection, vacu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Self-assembly
In chemistry and materials science, molecular self-assembly is the process by which molecules adopt a defined arrangement without guidance or management from an outside source. There are two types of self-assembly: intramolecular and intermolecular. Commonly, the term ''molecular self-assembly'' refers to the former, while the latter is more commonly called ''folding''. Supramolecular systems Molecular self-assembly is a key concept in supramolecular chemistry. This is because assembly of molecules in such systems is directed through non-covalent interactions (e.g., hydrogen bonding, metal coordination, hydrophobic forces, van der Waals forces, pi-stacking interactions, and/or electrostatic) as well as electromagnetic interactions. Common examples include the formation of colloids, biomolecular condensates, micelles, vesicles, liquid crystal phases, and Langmuir monolayers by surfactant molecules. Further examples of supramolecular assemblies demonstrate that a variety of d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naphthalene
Naphthalene is an organic compound with formula . It is the simplest polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, and is a white crystalline solid with a characteristic odor that is detectable at concentrations as low as 0.08 ppm by mass. As an aromatic hydrocarbon, naphthalene's structure consists of a fused pair of benzene rings. It is best known as the main ingredient of traditional mothballs. History In the early 1820s, two separate reports described a white solid with a pungent odor derived from the distillation of coal tar. In 1821, John Kidd cited these two disclosures and then described many of this substance's properties and the means of its production. He proposed the name ''naphthaline'', as it had been derived from a kind of naphtha (a broad term encompassing any volatile, flammable liquid hydrocarbon mixture, including coal tar). Naphthalene's chemical formula was determined by Michael Faraday in 1826. The structure of two fused benzene rings was proposed by Emil Erlenmeye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrene
Pyrene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) consisting of four fused benzene rings, resulting in a flat aromatic system. The chemical formula is . This yellow solid is the smallest peri-fused PAH (one where the rings are fused through more than one face). Pyrene forms during incomplete combustion of organic compounds. Occurrence and properties Pyrene was first isolated from coal tar, where it occurs up to 2% by weight. As a peri-fused PAH, pyrene is much more resonance-stabilized than its five-member-ring containing isomer fluoranthene. Therefore, it is produced in a wide range of combustion conditions. For example, automobiles produce about 1 μg/km.Senkan, Selim and Castaldi, Marco (2003) "Combustion" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Reactions Oxidation with chromate affords perinaphthenone and then naphthalene-1,4,5,8-tetracarboxylic acid. Pyrene undergoes a series of hydrogenation reactions and is susceptible to halogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudorotaxane
In chemistry, a rotaxane () is a mechanically interlocked molecular architecture consisting of a dumbbell-shaped molecule which is threaded through a macrocycle (see graphical representation). The two components of a rotaxane are kinetically trapped since the ends of the dumbbell (often called ''stoppers'') are larger than the internal diameter of the ring and prevent dissociation (unthreading) of the components since this would require significant distortion of the covalent bonds. Much of the research concerning rotaxanes and other mechanically interlocked molecular architectures, such as catenanes, has been focused on their efficient synthesis or their utilization as artificial molecular machines. However, examples of rotaxane substructure have been found in naturally occurring peptides, including: cystine knot peptides, cyclotides or lasso-peptides such as microcin J25. Synthesis The earliest reported synthesis of a rotaxane in 1967 relied on the statistical probabil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
INHIBIT Molecular Logic Gate By Gunnlaugsson
Inhibitor or inhibition may refer to: In biology * Enzyme inhibitor, a substance that binds to an enzyme and decreases the enzyme's activity * Reuptake inhibitor, a substance that increases neurotransmission by blocking the reuptake of a neurotransmitter * Lateral inhibition, a neural mechanism that increases contrast between active and (neighbouring) inactive neurons * Inhibitory postsynaptic potential, a synaptic potential that decreases the firing of a neuron In chemistry * Corrosion inhibitor, a substance that decreases the rate of metal oxidation * Reaction inhibitor, a substance that prevents or decreases the rate of a chemical reaction * Polymerisation inhibitor, a substance that inhibits unwanted polymerisation of monomers In psychology * Cognitive inhibition, the mind's ability to tune out irrelevant stimuli ** Inhibitory control, a cognitive process that permits an individual to inhibit their impulses * Inhibition of return, a feature of attention * Inhibition theor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorescence
Phosphorescence is a type of photoluminescence related to fluorescence. When exposed to light (radiation) of a shorter wavelength, a phosphorescent substance will glow, absorbing the light and reemitting it at a longer wavelength. Unlike fluorescence, a phosphorescent material does not immediately reemit the radiation it absorbs. Instead, a phosphorescent material absorbs some of the radiation energy and reemits it for a much longer time after the radiation source is removed. In a general sense, there is no distinct boundary between the emission times of fluorescence and phosphorescence (i.e.: if a substance glows under a black light it is generally considered fluorescent, and if it glows in the dark it is often simply called phosphorescent). In a modern, scientific sense, the phenomena can usually be classified by the three different mechanisms that produce the light, and the typical timescales during which those mechanisms emit light. Whereas fluorescent materials stop emit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
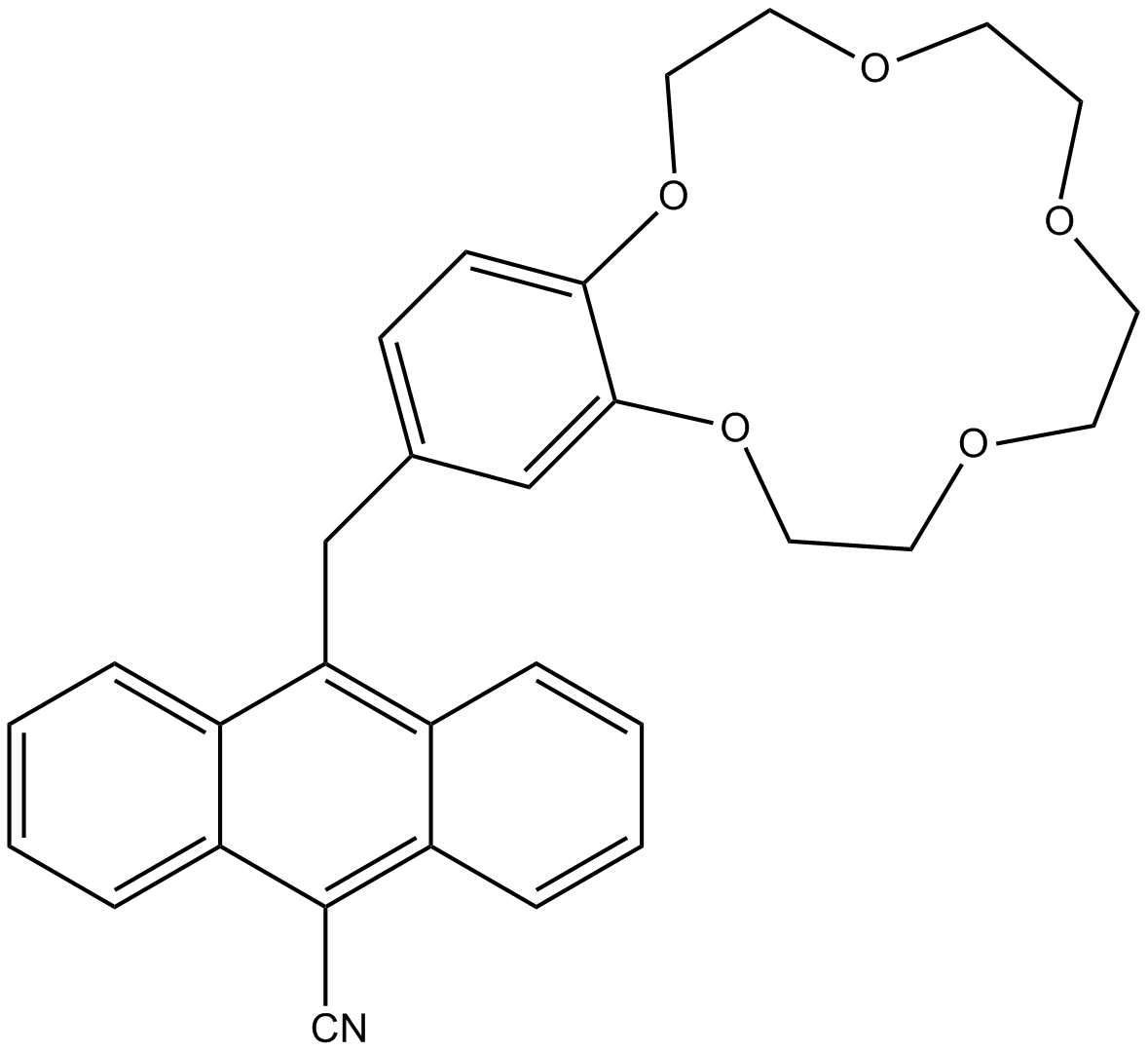
Crown Ether
In organic chemistry, crown ethers are cyclic chemical compounds that consist of a ring containing several ether groups (). The most common crown ethers are cyclic oligomers of ethylene oxide, the repeating unit being ethyleneoxy, i.e., . Important members of this series are the tetramer (''n'' = 4), the pentamer (''n'' = 5), and the hexamer (''n'' = 6). The term "crown" refers to the resemblance between the structure of a crown ether bound to a cation, and a crown sitting on a person's head. The first number in a crown ether's name refers to the number of atoms in the cycle, and the second number refers to the number of those atoms that are oxygen. Crown ethers are much broader than the oligomers of ethylene oxide; an important group are derived from catechol. Crown ethers strongly bind certain cations, forming complexes. The oxygen atoms are well situated to coordinate with a cation located at the interior of the ring, whereas the exterior of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |