|
Mitchella Repens
''Mitchella repens'' (partridge berry, or squaw vine (no longer used)) is the best known plant in the genus '' Mitchella''. It is a creeping prostrate herbaceous woody shrub occurring in North America belonging to the madder family (Rubiaceae). Naming ''Mitchella repens'' is one of the many species first described by Carl Linnaeus. Its species name is the Latin adjective ''repens'', which means "creeping". Common names for ''Mitchella repens'' include partridge berry (or partridgeberry), squaw berry (no longer used), two-eyed berry, running fox, and Noon kie oo nah yeah (in the Mohawk language). Description The partridge berry is an evergreen plant growing as a non-climbing vine, no taller than 6 cm tall with creeping stems 15 to 30 cm long. The evergreen, dark green, shiny leaves are ovate to cordate in shape. The leaves have a pale yellow midrib. The petioles are short, and the leaves are paired oppositely on the stems. Adventitious roots may grow at the nodes; and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was born in Råshult, the countryside of Småland, in southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he continued to collect an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovary (plants)
In the flowering plants, an ovary is a part of the female reproductive organ of the flower or gynoecium. Specifically, it is the part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. The pistil may be made up of one carpel or of several fused carpels (e.g. dicarpel or tricarpel), and therefore the ovary can contain part of one carpel or parts of several fused carpels. Above the ovary is the style and the stigma, which is where the pollen lands and germinates to grow down through the style to the ovary, and, for each individual pollen grain, to fertilize one individual ovule. Some wind pollinated flowers have much reduced and modified ovaries. Fruits A fruit is the mature, ripened ovary of a flower following double fertilization in an angiosperm. Because gymnosperms do not have an ovary but reproduce through double fertilization of unprotected ovules, they produce naked seeds that do not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berries
A berry is a small, pulpy, and often edible fruit. Typically, berries are juicy, rounded, brightly colored, sweet, sour or tart, and do not have a stone or pit, although many pips or seeds may be present. Common examples are strawberries, raspberries, blueberries, blackberries, red currants, white currants and blackcurrants. In Britain, soft fruit is a horticultural term for such fruits. In common usage, the term "berry" differs from the scientific or botanical definition of a fruit produced from the ovary of a single flower in which the outer layer of the ovary wall develops into an edible fleshy portion (pericarp). The botanical definition includes many fruits that are not commonly known or referred to as berries, such as grapes, tomatoes, cucumbers, eggplants, bananas, and chili peppers. Fruits commonly considered berries but excluded by the botanical definition include strawberries, raspberries, and blackberries, which are aggregate fruits and mulberries, which are mul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitchelleae
Mitchelleae is a tribe of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae and contains 14 species in 2 genera. Its representatives are found from eastern China to temperate eastern Asia, and from eastern Canada to Guatemala. Genera Currently accepted names * ''Damnacanthus'' C.F.Gaertn. (12 sp) * '' Mitchella'' L. (2 sp) Synonyms * ''Baumannia'' DC. = ''Damnacanthus'' * ''Chamaedaphne'' Mitch. = '' Mitchella'' * ''Disperma'' J.F.Gmel. = '' Mitchella'' * ''Geoherpum'' Willd. = '' Mitchella'' * ''Perdicesca'' Prov. = '' Mitchella'' * ''Tetraplasia'' Rehder = ''Damnacanthus ''Damnacanthus'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. The genus is found from Assam to temperate eastern Asia. Species * '' Damnacanthus angustifolius'' Hayata * '' Damnacanthus biflorus'' (Rehder) Masam. * '' Damnacanthus gig ...'' References Rubioideae tribes {{Rubioideae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaccinium Vitis-idaea
''Vaccinium vitis-idaea'', the lingonberry, partridgeberry, mountain cranberry or cowberry, is a small evergreen shrub in the heath family Ericaceae, that bears edible fruit. It is native to boreal forest and Arctic tundra throughout the Northern Hemisphere, from Europe and Asia to North America. Lingonberries are picked in the wild and used to accompany a variety of dishes in Northern Baltoscandia, Russia, Canada and Alaska. Commercial cultivation is undertaken in the U.S. Pacific Northwest and in many other regions of the world. Names ''Vaccinium vitis-idaea'' is most commonly known in English as 'lingonberry' or 'cowberry'.Gray's Manual of Botany: Asa GrayInteractive Flora of Northwest Europe''Vaccinium vitis-idaea''/ref> The name 'lingonberry' originates from the Swedish name for the species, and is derived from the Norse , or heather. The genus name ''Vaccinium'' is a classical Latin name for a plant, possibly the bilberry or hyacinth, and may be derived from the Latin , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrarium
A terrarium (plural: terraria or terrariums) is usually a sealable glass container containing soil and plants that can be opened for maintenance to access the plants inside; however, terraria can also be open to the atmosphere. Terraria are often kept as ornamental items. A closed terrarium's transparent walls allow heat and light to enter, creating a unique environment for plant growth. Heat entering the sealed container allows the creation of a small water cycle due to evaporating moisture from the soil and plants. The water vapor then condenses onto the walls of the container, eventually falling back onto the plants and soil below. Light passing through the transparent walls, allowing photosynthesis, with the constant water supply provide an ideal environment for plants. Open terraria are not sealed and are better suited to plants requiring a more arid environment. History The first terrarium was developed by botanist Nathaniel Bagshaw Ward in 1842. Ward had an interest in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by Honduras; to the southeast by El Salvador and to the south by the Pacific Ocean. With an estimated population of around million, Guatemala is the most populous country in Central America and the 11th most populous country in the Americas. It is a representative democracy with its capital and largest city being Nueva Guatemala de la Asunción, also known as Guatemala City, the most populous city in Central America. The territory of modern Guatemala hosted the core of the Maya civilization, which extended across Mesoamerica. In the 16th century, most of this area was conquered by the Spanish and claimed as part of the viceroyalty of New Spain. Guatemala attained independence in 1821 from Spain and Mexico. In 1823, it became part of the Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White-tailed Deer
The white-tailed deer (''Odocoileus virginianus''), also known as the whitetail or Virginia deer, is a medium-sized deer native to North America, Central America, and South America as far south as Peru and Bolivia. It has also been introduced to New Zealand, all the Greater Antilles in the Caribbean (Cuba, Jamaica Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of His ..., Hispaniola, and Puerto Rico), and some countries in Europe, such as the Czech Republic, Finland, France, Germany, Romania and Serbia. In the Americas, it is the most widely distributed wild ungulate. In North America, the species is widely distributed east of the Rocky Mountains as well as in southwestern Arizona and most of Mexico, except Baja California peninsula, Lower California. It is mostly displaced by the black ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skunk
Skunks are mammals in the family Mephitidae. They are known for their ability to spray a liquid with a strong, unpleasant scent from their anal glands. Different species of skunk vary in appearance from black-and-white to brown, cream or ginger colored, but all have warning coloration. While related to polecats and other members of the weasel family, skunks have as their closest relatives the Old World stink badgers. Taxonomy In alphabetical order, the living species of skunks are: * Family Mephitidae ** Genus: ''Conepatus'' *** ''Conepatus chinga'' – Molina's hog-nosed skunk *** ''Conepatus humboldtii'' – Humboldt's hog-nosed skunk *** ''Conepatus leuconotus'' – American hog-nosed skunk *** ''Conepatus semistriatus'' – striped hog-nosed skunk ** Genus: '' Mephitis'' *** ''Mephitis macroura'' – hooded skunk *** ''Mephitis mephitis'' – striped skunk ** Genus: ''Spilogale'' *** ''Spilogale angustifrons'' – southern spotted s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
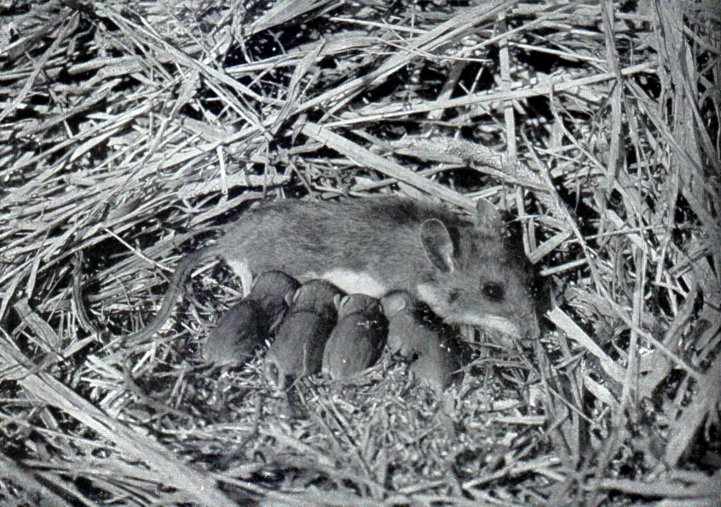
White-footed Mice
The white-footed mouse (''Peromyscus leucopus'') is a rodent native to North America from Ontario, Quebec, Labrador, and the Maritime Provinces (excluding the island of Newfoundland) to the southwestern United States and Mexico. In the Maritimes, its only location is a disjunct population in southern Nova Scotia. It is also known as the woodmouse, particularly in Texas. Description Adults are in length, not counting the tail, which can add another . A young adult weighs . While their maximum lifespan is 96 months, the mean life expectancy for the species is 45.5 months for females and 47.5 for males. In northern climates, the average life expectancy is 12–24 months. The species is similar to ''Peromyscus maniculatus''. White-footed Mouse, Quetico.jpg, In Quetico Provincial Park, Ontario File:Rhus typhina-Peromyscus leucopus-female.jpg, Female on a staghorn sumac Behavior and diet White-footed mice are omnivorous, and eat seeds and insects. They are timid and generally avoid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
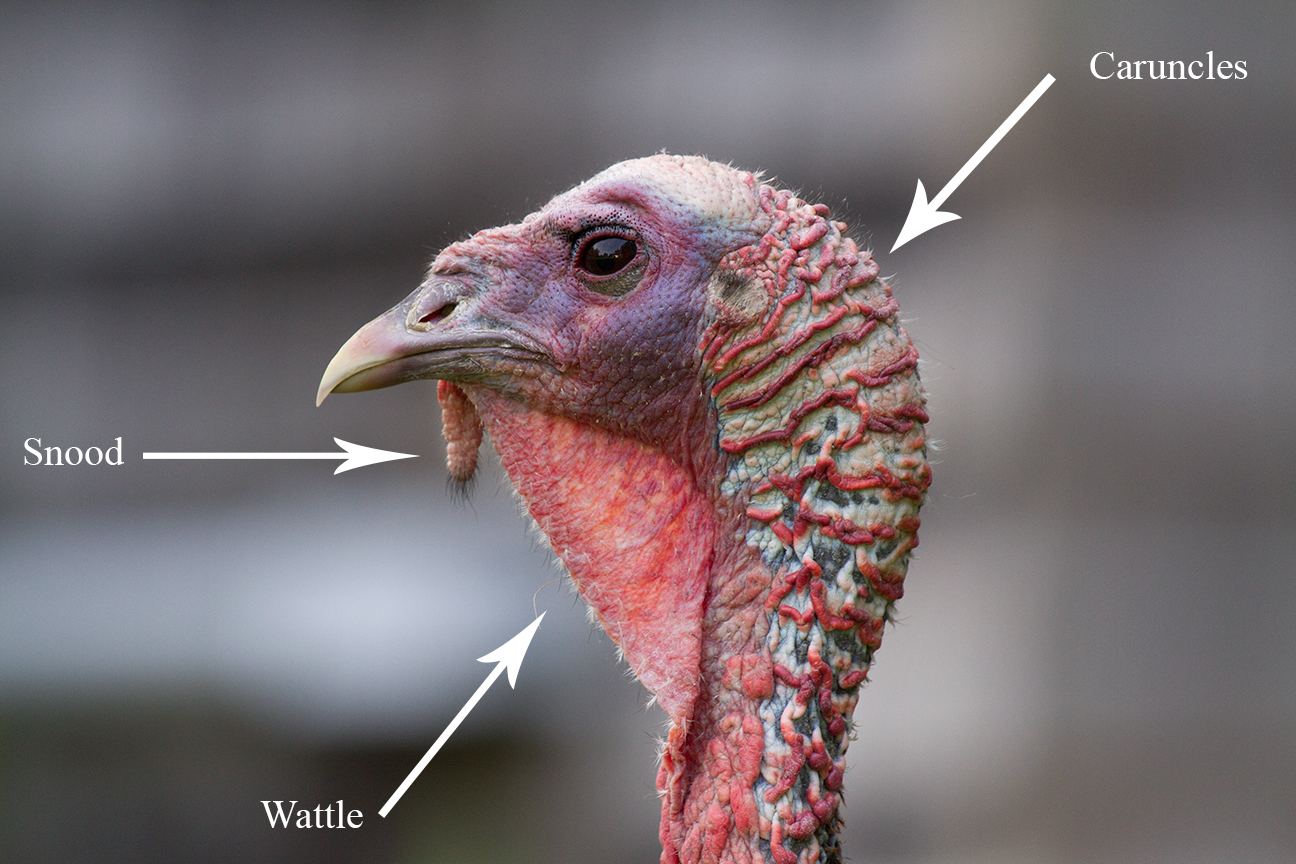
Wild Turkey
The wild turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo'') is an Upland game bird, upland ground bird native to North America, one of two extant species of Turkey (bird), turkey and the heaviest member of the order Galliformes. It is the ancestor to the domestic turkey, which was originally derived from a southern Mexican subspecies of wild turkey (not the related ocellated turkey). Description Adult wild turkeys have long reddish-yellow to grayish-green legs. The body feathers are generally blackish and dark, sometimes grey brown overall with a coppery sheen that becomes more complex in adult males. Adult males, called toms or gobblers, have a large, featherless, reddish head, red throat, and red Wattle (anatomy), wattles on the throat and neck. The head has fleshy growths called Caruncle (bird anatomy) , caruncles. Juvenile males are called jakes; the difference between an adult male and a juvenile is that the jake has a very short beard and his tail fan has longer feathers in the middle. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Bobwhite
The northern bobwhite (''Colinus virginianus''), also known as the Virginia quail or (in its home range) bobwhite quail, is a ground-dwelling bird native to Canada, the United States, Mexico, and Cuba, with introduced populations elsewhere in the Caribbean, Europe, and Asia. It is a member of the group of species known as New World quail (Odontophoridae). They were initially placed with the Old World quail in the pheasant family (Phasianidae), but are not particularly closely related. The name "bobwhite" is an onomatopoeic derivation from its characteristic whistling call. Despite its secretive nature, the northern bobwhite is one of the most familiar quails in eastern North America, because it is frequently the only quail in its range. Habitat degradation has likely contributed to the northern bobwhite population in eastern North America declining by roughly 85% from 1966 to 2014. This population decline is apparently range-wide and continuing. There are 23 subspecies of norther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_(255_30)_Tulip;_cross-section.jpg)
.jpg)