|
Misrun
A casting defect is an undesired irregularity in a metal casting process. Some defects can be tolerated while others can be repaired, otherwise they must be eliminated. They are broken down into five main categories: ''gas porosity'', ''shrinkage defects'', ''mould material defects'', ''pouring metal defects'', and ''metallurgical defects''. Terminology The terms "defect" and "" refer to two specific and separate things in castings. Defects are defined as conditions in a casting that must be corrected or removed, or the casting must be rejected. Discontinuities, also known as "imperfections", are defined as "interruptions in the physical continuity of the casting". Therefore, if the casting is less than perfect, but still useful and in tolerance, the imperfections should be deemed "discontinuities". Types There are many types of defects which result from many different causes. Some of the solutions to certain defects can be the cause for another type of defect. The following def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Misrun
A casting defect is an undesired irregularity in a metal casting process. Some defects can be tolerated while others can be repaired, otherwise they must be eliminated. They are broken down into five main categories: ''gas porosity'', ''shrinkage defects'', ''mould material defects'', ''pouring metal defects'', and ''metallurgical defects''. Terminology The terms "defect" and "" refer to two specific and separate things in castings. Defects are defined as conditions in a casting that must be corrected or removed, or the casting must be rejected. Discontinuities, also known as "imperfections", are defined as "interruptions in the physical continuity of the casting". Therefore, if the casting is less than perfect, but still useful and in tolerance, the imperfections should be deemed "discontinuities". Types There are many types of defects which result from many different causes. Some of the solutions to certain defects can be the cause for another type of defect. The following def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Porosity (casting)
A casting defect is an undesired irregularity in a metal casting process. Some defects can be tolerated while others can be repaired, otherwise they must be eliminated. They are broken down into five main categories: ''gas porosity'', ''shrinkage defects'', ''mould material defects'', ''pouring metal defects'', and ''metallurgical defects''. Terminology The terms "defect" and "" refer to two specific and separate things in castings. Defects are defined as conditions in a casting that must be corrected or removed, or the casting must be rejected. Discontinuities, also known as "imperfections", are defined as "interruptions in the physical continuity of the casting". Therefore, if the casting is less than perfect, but still useful and in tolerance, the imperfections should be deemed "discontinuities". Types There are many types of defects which result from many different causes. Some of the solutions to certain defects can be the cause for another type of defect. The following def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrinkage Porosity
A casting defect is an undesired irregularity in a metal casting process. Some defects can be tolerated while others can be repaired, otherwise they must be eliminated. They are broken down into five main categories: ''gas porosity'', ''shrinkage defects'', ''mould material defects'', ''pouring metal defects'', and ''metallurgical defects''. Terminology The terms "defect" and "" refer to two specific and separate things in castings. Defects are defined as conditions in a casting that must be corrected or removed, or the casting must be rejected. Discontinuities, also known as "imperfections", are defined as "interruptions in the physical continuity of the casting". Therefore, if the casting is less than perfect, but still useful and in tolerance, the imperfections should be deemed "discontinuities". Types There are many types of defects which result from many different causes. Some of the solutions to certain defects can be the cause for another type of defect. The following def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pipe Shrinkage
A casting defect is an undesired irregularity in a metal casting process. Some defects can be tolerated while others can be repaired, otherwise they must be eliminated. They are broken down into five main categories: ''gas porosity'', ''shrinkage defects'', ''mould material defects'', ''pouring metal defects'', and ''metallurgical defects''. Terminology The terms "defect" and "" refer to two specific and separate things in castings. Defects are defined as conditions in a casting that must be corrected or removed, or the casting must be rejected. Discontinuities, also known as "imperfections", are defined as "interruptions in the physical continuity of the casting". Therefore, if the casting is less than perfect, but still useful and in tolerance, the imperfections should be deemed "discontinuities". Types There are many types of defects which result from many different causes. Some of the solutions to certain defects can be the cause for another type of defect. The following def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microshrinkage
A casting defect is an undesired irregularity in a metal casting process. Some defects can be tolerated while others can be repaired, otherwise they must be eliminated. They are broken down into five main categories: ''gas porosity'', ''shrinkage defects'', ''mould material defects'', ''pouring metal defects'', and ''metallurgical defects''. Terminology The terms "defect" and "" refer to two specific and separate things in castings. Defects are defined as conditions in a casting that must be corrected or removed, or the casting must be rejected. Discontinuities, also known as "imperfections", are defined as "interruptions in the physical continuity of the casting". Therefore, if the casting is less than perfect, but still useful and in tolerance, the imperfections should be deemed "discontinuities". Types There are many types of defects which result from many different causes. Some of the solutions to certain defects can be the cause for another type of defect. The following def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pipe (casting)
A casting defect is an undesired irregularity in a metal casting process. Some defects can be tolerated while others can be repaired, otherwise they must be eliminated. They are broken down into five main categories: ''gas porosity'', ''shrinkage defects'', ''mould material defects'', ''pouring metal defects'', and ''metallurgical defects''. Terminology The terms "defect" and "" refer to two specific and separate things in castings. Defects are defined as conditions in a casting that must be corrected or removed, or the casting must be rejected. Discontinuities, also known as "imperfections", are defined as "interruptions in the physical continuity of the casting". Therefore, if the casting is less than perfect, but still useful and in tolerance, the imperfections should be deemed "discontinuities". Types There are many types of defects which result from many different causes. Some of the solutions to certain defects can be the cause for another type of defect. The following de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Entrapment
A casting defect is an undesired irregularity in a metal casting process. Some defects can be tolerated while others can be repaired, otherwise they must be eliminated. They are broken down into five main categories: ''gas porosity'', ''shrinkage defects'', ''mould material defects'', ''pouring metal defects'', and ''metallurgical defects''. Terminology The terms "defect" and "" refer to two specific and separate things in castings. Defects are defined as conditions in a casting that must be corrected or removed, or the casting must be rejected. Discontinuities, also known as "imperfections", are defined as "interruptions in the physical continuity of the casting". Therefore, if the casting is less than perfect, but still useful and in tolerance, the imperfections should be deemed "discontinuities". Types There are many types of defects which result from many different causes. Some of the solutions to certain defects can be the cause for another type of defect. The following def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casting (metalworking)
In metalworking and jewelry making, casting is a process in which a liquid metal is delivered into a mold (usually by a crucible) that contains a negative impression (i.e., a three-dimensional negative image) of the intended shape. The metal is poured into the mold through a hollow channel called a sprue. The metal and mold are then cooled, and the metal part (the ''casting'') is extracted. Casting is most often used for making complex shapes that would be difficult or uneconomical to make by other methods. Casting processes have been known for thousands of years, and have been widely used for sculpture (especially in bronze), jewelry in precious metals, and weapons and tools. Highly engineered castings are found in 90 percent of durable goods, including cars, trucks, aerospace, trains, mining and construction equipment, oil wells, appliances, pipes, hydrants, wind turbines, nuclear plants, medical devices, defense products, toys, and more. Traditional techniques include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrinkage (casting)
In metalworking and jewelry making, casting is a process in which a liquid metal is delivered into a mold (usually by a crucible) that contains a negative impression (i.e., a three-dimensional negative image) of the intended shape. The metal is poured into the mold through a hollow channel called a sprue. The metal and mold are then cooled, and the metal part (the ''casting'') is extracted. Casting is most often used for making complex shapes that would be difficult or uneconomical to make by other methods. Casting processes have been known for thousands of years, and have been widely used for sculpture (especially in bronze), jewelry in precious metals, and weapons and tools. Highly engineered castings are found in 90 percent of durable goods, including cars, trucks, aerospace, trains, mining and construction equipment, oil wells, appliances, pipes, hydrants, wind turbines, nuclear plants, medical devices, defense products, toys, and more. Traditional techniques include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosphere is the outer region of a star, which includes the layers above the opaque photosphere; stars of low temperature might have outer atmospheres containing compound molecules. The atmosphere of Earth is composed of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), argon (0.9%), carbon dioxide (0.04%) and trace gases. Most organisms use oxygen for respiration; lightning and bacteria perform nitrogen fixation to produce ammonia that is used to make nucleotides and amino acids; plants, algae, and cyanobacteria use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. The layered composition of the atmosphere minimises the harmful effects of sunlight, ultraviolet radiation, the solar wind, and cosmic rays to protect organisms from genetic damage. The current c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Flushing
In chemistry, sparging, also known as gas flushing in metallurgy, is a technique in which a gas is bubbled through a liquid in order to remove ''other'' dissolved gas(es) and/or dissolved volatile liquid(s) from that liquid. It is a method of degassing. According to Henry's law, the concentration of each gas in a liquid is proportional to the partial pressure of that gas (in the gaseous state) in contact with the liquid. Sparging introduces a gas that has little or no partial pressure of the gas(es) to be removed, and increases the area of the gas-liquid interface, which encourages some of the dissolved gas(es) to diffuse into the sparging gas before the sparging gas escapes from the liquid. Many sparging processes, such as solvent removal, use air as the sparging gas. To remove oxygen, or for sensitive solutions or reactive molten metals, a chemically inert gas such as nitrogen, argon, or helium is used. Liquid chromatography Solvents used in high-performance liquid chromatogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
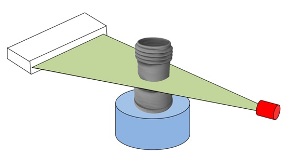
Industrial CT Scanning
Industrial computed tomography (CT) scanning is any computer-aided tomographic process, usually X-ray computed tomography, that uses irradiation to produce three-dimensional internal and external representations of a scanned object. Industrial CT scanning has been used in many areas of industry for internal inspection of components. Some of the key uses for industrial CT scanning have been flaw detection, failure analysis, metrology, assembly analysis and reverse engineering applications. Just as in medical imaging, industrial imaging includes both nontomographic radiography (industrial radiography) and computed tomographic radiography (computed tomography). Types of scanners ''Line beam scanning'' is the traditional process of industrial CT scanning.Hofmann, J., Flisch, A., Obrist, A., Adaptive CT scanning-mesh based optimisation methods for industrial X-ray computer tomography applications. NDT&E International (37), 2004, pp. 271–278. X-rays are produced and the beam is co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |