|
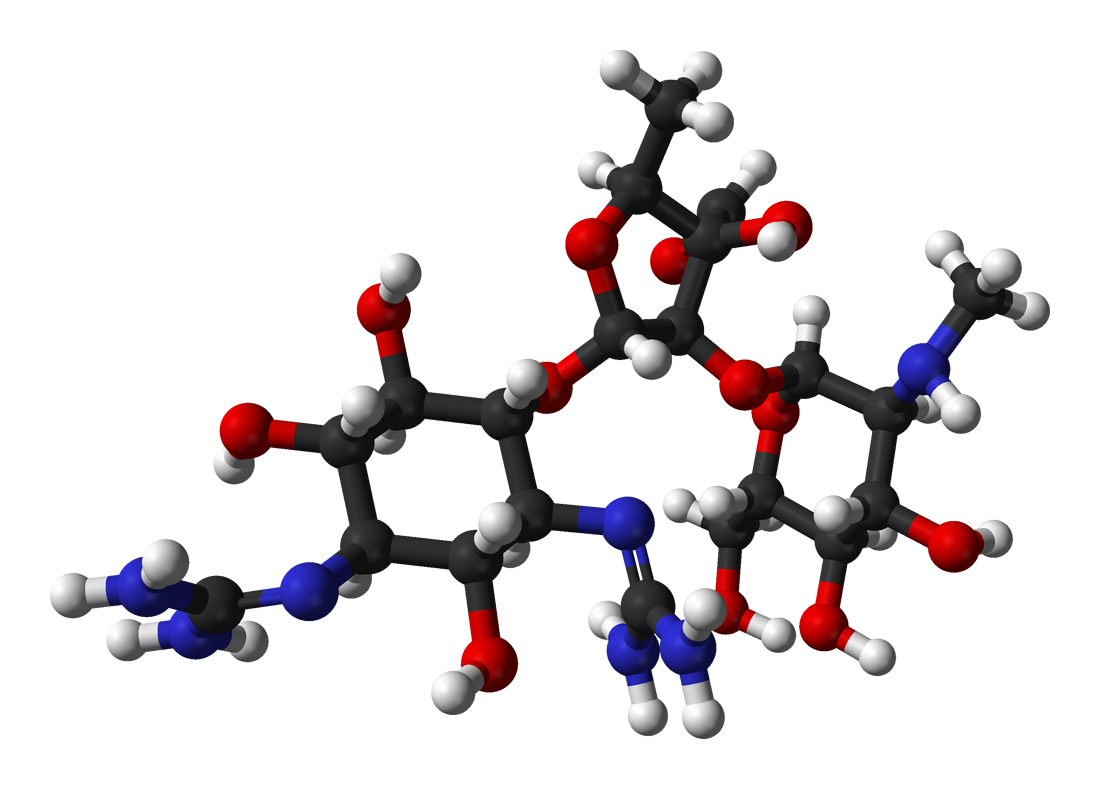
Mimosine
Mimosine or leucenol is a toxic non-protein amino acid chemically similar to tyrosine. It occurs in some ''Mimosa'' spp. (including '' M. pudica'') and all members of the closely related genus ''Leucaena''. This compound, also known as leucenol, was first isolated from the seeds of ''Leucaena glauca'' Benth., and was later investigated by Adams and coworkers. Properties Mimosine melts with decomposition. The hydrochloride salt melts at 174.5‚Äď175.0 ¬įC with decomposition; the hydrobromide decomposes at 179.5 ¬įC, and the hydroiodide decomposes at 183‚Äď183.5 ¬įC. Mimosine only forms monobasic acids, but the methyl ester forms a dihydrochloride, C7H9O2N2(COOMe)‚ÄĘ2 HCl‚ÄʬŠH2O, mp. 175‚Äď6 ¬įC. Biological effects Mimosine arrests dividing cells in the late G1 phase by inhibiting DNA replication initiation. In ruminants, mimosine is degraded to 3,4- and 2,3-dihydroxypyridone (3,4- and 2,3-DHP). Although toxicosis has occurred in Australia, Papua New Guinea, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-proteinogenic Amino Acids
In biochemistry, non-coded or non-proteinogenic amino acids are distinct from the 22 proteinogenic amino acids (21 in eukaryotesplus formylmethionine in eukaryotes with prokaryote organelles like mitochondria) which are naturally encoded in the genome of organisms for the assembly of proteins. However, over 140 non-proteinogenic amino acids occur naturally in proteins and thousands more may occur in nature or be synthesized in the laboratory. Chemically synthesized amino acids can be called unnatural amino acids. Unnatural amino acids can be synthetically prepared from their native analogs via modifications such as amine alkylation, side chain substitution, structural bond extension cyclization, and isosteric replacements within the amino acid backbone. Many non-proteinogenic amino acids are important: * intermediates in biosynthesis, * in post-translational formation of proteins, * in a physiological role (e.g. components of bacterial cell walls, neurotransmitters and toxins), * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explains, the English spellings of both Myanmar and Burma assume a non-rhotic variety of English, in which the letter r before a consonant or finally serves merely to indicate a long vowel: ąmj√¶nm…Ďňź, ňąb…úňźm…ô So the pronunciation of the last syllable of Myanmar as …Ďňźror of Burma as …úňźrm…ôby some speakers in the UK and most speakers in North America is in fact a spelling pronunciation based on a misunderstanding of non-rhotic spelling conventions. The final ''r'' in ''Myanmar'' was not intended for pronunciation and is there to ensure that the final a is pronounced with the broad ''ah'' () in "father". If the Burmese name my, ŠÄôŠÄľŠÄĒŠÄļŠÄôŠÄ¨, label=none were spelled "Myanma" in English, this would be pronounced at the end by all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hordenine
Hordenine is an alkaloid of the phenethylamine class that occurs naturally in a variety of plants, taking its name from one of the most common, barley (''Hordeum'' species). Chemically, hordenine is the ''N''-methyl derivative (chemistry), derivative of N-Methyltyramine, ''N''-methyltyramine, and the ''N'',''N''-dimethyl derivative of the well-known biogenic amine tyramine, from which it is biosynthetically derived and with which it shares some pharmacological properties (see below). , hordenine is widely sold as an ingredient of nutritional supplements, with the claims that it is a stimulant of the central nervous system, and has the ability to promote weight loss by enhancing metabolism. In experimental animals, given sufficiently large doses parenterally (by injection), hordenine does produce an increase in blood pressure, as well as other disturbances of the cardiovascular, respiratory, and nervous systems. These effects are generally not reproduced by oral administration of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leucaena Leucocephala
''Leucaena leucocephala'' is a small fast-growing Mimosoideae, mimosoid tree native to southern Mexico and northern Central America (Belize and Guatemala) and is now naturalized throughout the tropics including parts of Asia. Common names include jumbay, pearl wattle (called so because of its yellowish white hue), white leadtree, river tamarind, ipil-ipil,tan tan, and white popinac.Ipil-ipil, ''Leucaena glauca'' BPI.da.gov.ph ''Leucaena leucocephala'' is used for a variety of purposes, such as fencing, soil fertility, firewood, Fiber crop, fiber, and livestock fodder. Use by humans During the 1970s and 1980s, it was promoted as a "miracle tree" for its multiple uses. It has also been described as a "conflict tree" because it is used for forage production ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonium
The ammonium cation is a positively-charged polyatomic ion with the chemical formula or . It is formed by the protonation of ammonia (). Ammonium is also a general name for positively charged or protonated substituted amines and quaternary ammonium cations (), where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups (indicated by R). Acid‚Äďbase properties The ammonium ion is generated when ammonia, a weak base, reacts with Br√łnsted acids (proton donors): :H+ + NH3 -> H4 The ammonium ion is mildly acidic, reacting with Br√łnsted bases to return to the uncharged ammonia molecule: : H4 + B- -> HB + NH3 Thus, treatment of concentrated solutions of ammonium salts with strong base gives ammonia. When ammonia is dissolved in water, a tiny amount of it converts to ammonium ions: :H2O + NH3 OH- + H4 The degree to which ammonia forms the ammonium ion depends on the pH of the solution. If the pH is low, the equilibrium shifts to the right: more ammonia molecules are co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyruvate
Pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH) is the simplest of the alpha-keto acids, with a carboxylic acid and a ketone functional group. Pyruvate, the conjugate base, CH3COCOO‚ąí, is an intermediate in several metabolic pathways throughout the cell. Pyruvic acid can be made from glucose through glycolysis, converted back to carbohydrates (such as glucose) via gluconeogenesis, or to fatty acids through a reaction with acetyl-CoA. It can also be used to construct the amino acid alanine and can be converted into ethanol or lactic acid via fermentation. Pyruvic acid supplies energy to cells through the citric acid cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle) when oxygen is present (aerobic respiration), and alternatively ferments to produce lactate when oxygen is lacking. Chemistry In 1834, Th√©ophile-Jules Pelouze distilled tartaric acid and isolated glutaric acid and another unknown organic acid. J√∂ns Jacob Berzelius characterized this other acid the following year and named pyruvic acid because it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyridoxal Phosphate
Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, P5P), the active form of vitamin B6, is a coenzyme in a variety of enzymatic reactions. The International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology has catalogued more than 140 PLP-dependent activities, corresponding to ~4% of all classified activities. The versatility of PLP arises from its ability to covalently bind the substrate, and then to act as an electrophilic catalyst, thereby stabilizing different types of carbanionic reaction intermediates. Role as a coenzyme PLP acts as a coenzyme in all transamination reactions, and in certain decarboxylation, deamination, and racemization reactions of amino acids. The aldehyde group of PLP forms a Schiff-base linkage (internal aldimine) with the őĶ-amino group of a specific lysine group of the aminotransferase enzyme. The őĪ-amino group of the amino acid substrate displaces the őĶ-amino group of the active-site lysine residue in a process known as transaldimination. The resulting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mimosinase
In enzymology, a mimosinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :(S)-2-amino-3-(3-hydroxy-4-oxo-4H-pyridin-1-yl)propanoate + H2O \rightleftharpoons 3-hydroxy-4H-pyrid-4-one + L-serine Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are (S)-2-amino-3-(3-hydroxy-4-oxo-4H-pyridin-1-yl)propanoate and H2O, whereas its two products are 3-hydroxy-4H-pyrid-4-one and L-serine. This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolases, those acting on carbon-nitrogen bonds other than peptide bonds, specifically in linear amides. The systematic name A systematic name is a name given in a systematic way to one unique group, organism, object or chemical substance, out of a specific population or collection. Systematic names are usually part of a nomenclature. A semisystematic name or semitrivial ... of this enzyme class is mimosine amidohydrolase. References * EC 3.5.1 Enzymes of unknown structure {{3.5-enzyme-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizobia
Rhizobia are diazotrophic bacteria that fix nitrogen after becoming established inside the root nodules of legumes (Fabaceae). To express genes for nitrogen fixation, rhizobia require a plant host; they cannot independently fix nitrogen. In general, they are gram negative, motile, non-sporulating rods. Rhizobia are a "group of soil bacteria that infect the roots of legumes to form root nodules". Rhizobia are found in the soil and after infection, produce nodules in the legume where they fix nitrogen gas (N2) from the atmosphere turning it into a more readily useful form of nitrogen. From here, the nitrogen is exported from the nodules and used for growth in the legume. Once the legume dies, the nodule breaks down and releases the rhizobia back into the soil where they can live individually or reinfect a new legume host. History The first known species of rhizobia, '' Rhizobium leguminosarum'', was identified in 1889, and all further species were initially placed in the ''Rhiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klebsiella Pneumoniae
''Klebsiella pneumoniae'' is a Gram-negative, non-motile, encapsulated, lactose-fermenting, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium. It appears as a mucoid lactose fermenter on MacConkey agar. Although found in the normal flora of the mouth, skin, and intestines, it can cause destructive changes to human and animal lungs if aspirated, specifically to the alveoli resulting in bloody, brownish or yellow colored jelly like sputum. In the clinical setting, it is the most significant member of the genus ''Klebsiella'' of the Enterobacteriaceae. ''K. oxytoca'' and ''K. rhinoscleromatis'' have also been demonstrated in human clinical specimens. In recent years, ''Klebsiella'' species have become important pathogens in nosocomial infections. It naturally occurs in the soil, and about 30% of strains can fix nitrogen in anaerobic conditions. As a free-living diazotroph, its nitrogen-fixation system has been much-studied, and is of agricultural interest, as ''K. pneumoniae'' has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbe
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ŠĹÄŌĀő≥őĪőĹőĻŌÉőľŌĆŌā, ''organism√≥s'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in older texts. The informal synonym ''microbe'' () comes from őľőĻőļŌĀŌĆŌā, mikr√≥s, "small" and ő≤őĮőŅŌā, b√≠os, "life". is an organism of microscopic size, which may exist in its single-celled form or as a colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen microbial life was suspected from ancient times, such as in Jain scriptures from sixth century BC India. The scientific study of microorganisms began with their observation under the microscope in the 1670s by Anton van Leeuwenhoek. In the 1850s, Louis Pasteur found that microorganisms caused food spoilage, debunking the theory of spontaneous generation. In the 1880s, Robert Koch discovered that microorganisms caused the diseases tuberculosis, cholera, diphtheria, and anthrax. Because mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
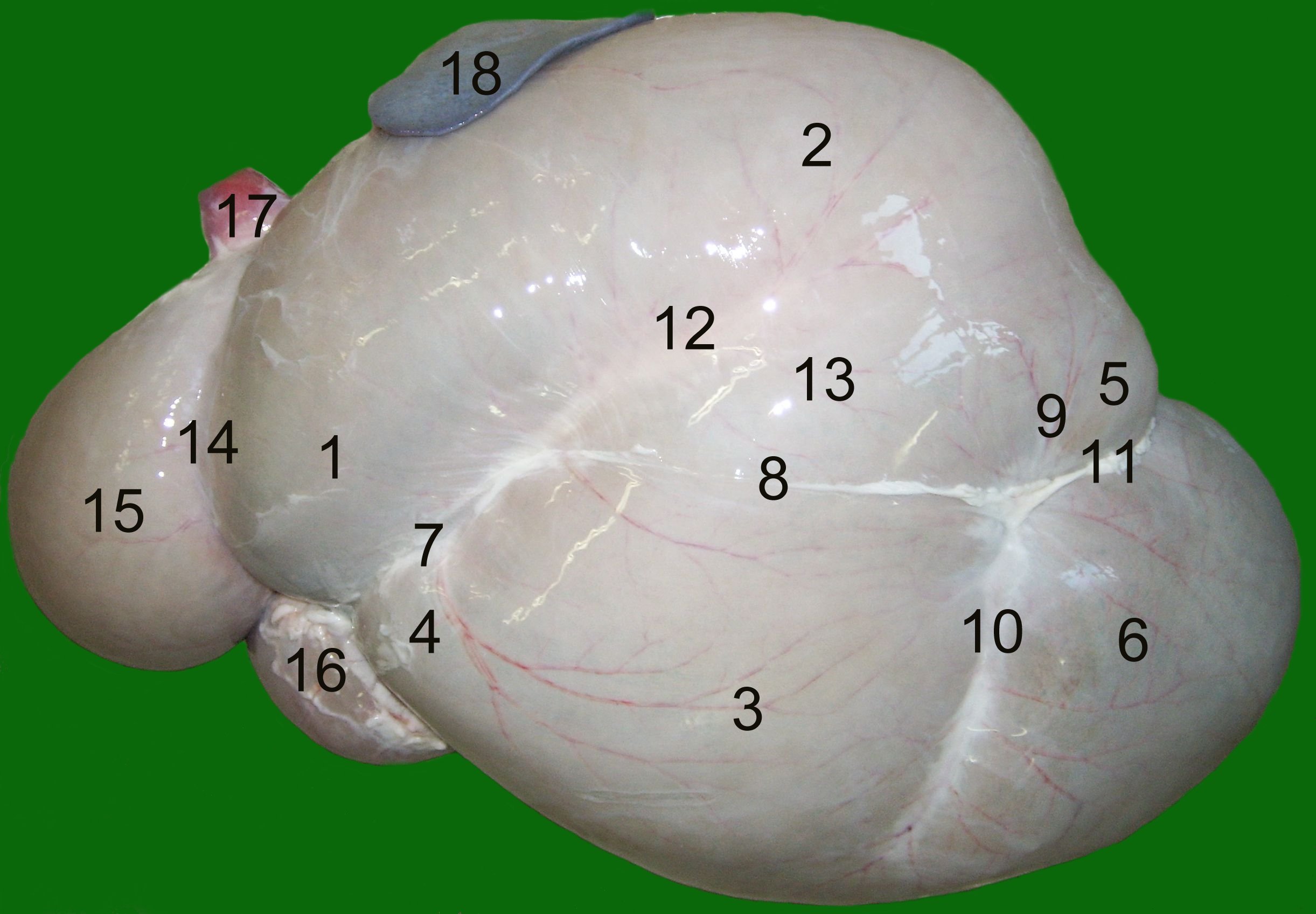
Rumen
The rumen, also known as a paunch, is the largest stomach compartment in ruminants and the larger part of the reticulorumen, which is the first chamber in the alimentary canal of ruminant animals. The rumen's microbial favoring environment allows it to serve as the primary site for microbial fermentation of ingested feed. The smaller part of the reticulorumen is the reticulum, which is fully continuous with the rumen, but differs from it with regard to the texture of its lining. Brief anatomy The rumen is composed of several muscular sacs, the cranial sac, ventral sac, ventral blindsac, and reticulum. The lining of the rumen wall is covered in small fingerlike projections called papillae, which are flattened, approximately 5mm in length and 3mm wide in cattle. The reticulum is lined with ridges that form a hexagonal honeycomb pattern. The ridges are approximately 0.1‚Äď0.2mm wide and are raised 5mm above the reticulum wall. The hexagons in the reticulum are approximately 2‚ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |