|
Micrometeor
A micrometeoroid is a tiny meteoroid: a small particle of rock in space, usually weighing less than a gram. A micrometeorite is such a particle that survives passage through Earth's atmosphere and reaches Earth's surface. The term "micrometeoroid" was officially deprecated by the IAU in 2017, as redundant to meteoroid. Origins and orbits Micrometeoroids are very small pieces of rock or metal broken off from larger chunks of rock and debris often dating back to the birth of the Solar System. Micrometeoroids are extremely common in space. Tiny particles are a major contributor to space weathering processes. When they hit the surface of the Moon, or any airless body (Mercury, the asteroids, etc.), the resulting melting and vaporization causes darkening and other optical changes in the regolith. Micrometeoroids have less stable orbits than meteoroids, due to their greater surface area to mass ratio. Micrometeoroids that fall to Earth can provide information on millimeter scale h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrometeorite
A micrometeorite is a micrometeoroid that has survived entry through the Earth's atmosphere. Usually found on Earth's surface, micrometeorites differ from meteorites in that they are smaller in size, more abundant, and different in composition. The IAU officially defines meteorites as 30 micrometers to 1 meter; micrometeorites are the small end of the range (~submillimeter). They are a subset of cosmic dust, which also includes the smaller interplanetary dust particles (IDPs). Micrometeorites enter Earth's atmosphere at high velocities (at least 11 km/s) and undergo heating through atmospheric friction and compression. Micrometeorites individually weigh between 10−9 and 10−4 g and collectively comprise most of the extraterrestrial material that has come to the present-day Earth. Fred Lawrence Whipple first coined the term "micro-meteorite" to describe dust-sized objects that fall to the Earth. Sometimes meteoroids and micrometeoroids entering the Earth's atmospher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrometeorite
A micrometeorite is a micrometeoroid that has survived entry through the Earth's atmosphere. Usually found on Earth's surface, micrometeorites differ from meteorites in that they are smaller in size, more abundant, and different in composition. The IAU officially defines meteorites as 30 micrometers to 1 meter; micrometeorites are the small end of the range (~submillimeter). They are a subset of cosmic dust, which also includes the smaller interplanetary dust particles (IDPs). Micrometeorites enter Earth's atmosphere at high velocities (at least 11 km/s) and undergo heating through atmospheric friction and compression. Micrometeorites individually weigh between 10−9 and 10−4 g and collectively comprise most of the extraterrestrial material that has come to the present-day Earth. Fred Lawrence Whipple first coined the term "micro-meteorite" to describe dust-sized objects that fall to the Earth. Sometimes meteoroids and micrometeoroids entering the Earth's atmospher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrometeorites
A micrometeorite is a micrometeoroid that has survived atmospheric entry, entry through the atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere. Usually found on Earth's surface, micrometeorites differ from meteorites in that they are smaller in size, more abundant, and different in composition. The International Astronomical Union, IAU officially defines meteorites as 30 micrometers to 1 meter; micrometeorites are the small end of the range (~submillimeter). They are a subset of cosmic dust, which also includes the smaller interplanetary dust particles (IDPs). Micrometeorites enter Earth's atmosphere at high velocity, velocities (at least 11 km/s) and undergo heating through drag (physics), atmospheric friction and Compression (physics), compression. Micrometeorites individually weigh between 10−9 and 10−4 g and collectively comprise most of the extraterrestrial material that has come to the present-day Earth. Fred Lawrence Whipple first coined the term "micro-meteorite" to des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
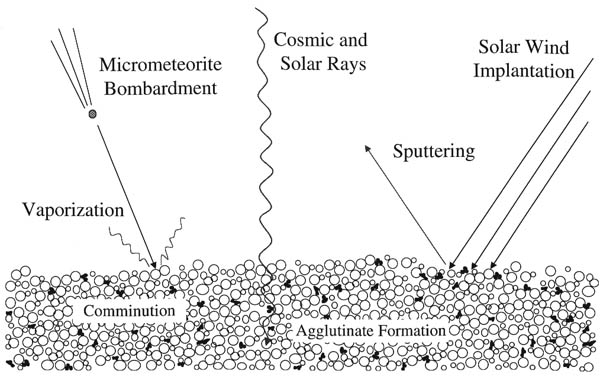
Space Weathering
Space weathering is the type of weathering that occurs to any object exposed to the harsh environment of outer space. Bodies without atmospheres (including the Moon, Mercury, the asteroids, comets, and most of the moons of other planets) take on many weathering processes: * collisions of galactic cosmic rays and solar cosmic rays, * irradiation, implantation, and sputtering from solar wind particles, and * bombardment by different sizes of meteorites and micrometeorites. Space weathering is important because these processes affect the physical and optical properties of the surface of many planetary bodies. Therefore, it is critical to understand the effects of space weathering in order to properly interpret remotely sensed data. History Much of our knowledge of the space weathering process comes from studies of the lunar samples returned by the Apollo program, particularly the lunar soils (or regolith). The constant flux of high energy particles and micrometeorites, along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meteoroid
A meteoroid () is a small rocky or metallic body in outer space. Meteoroids are defined as objects significantly smaller than asteroids, ranging in size from grains to objects up to a meter wide. Objects smaller than this are classified as micrometeoroids or space dust. Most are fragments from comets or asteroids, whereas others are collision impact debris ejected from bodies such as the Moon or Mars. When a meteoroid, comet, or asteroid enters Earth's atmosphere at a speed typically in excess of , aerodynamic heating of that object produces a streak of light, both from the glowing object and the trail of glowing particles that it leaves in its wake. This phenomenon is called a meteor or "shooting star". Meteors typically become visible when they are about 100 km above sea level. A series of many meteors appearing seconds or minutes apart and appearing to originate from the same fixed point in the sky is called a meteor shower. A meteorite is the remains of a meteoroid th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interplanetary Dust Cloud
The interplanetary dust cloud, or zodiacal cloud (as the source of the zodiacal light), consists of cosmic dust (small particles floating in outer space) that pervades the space between planets within planetary systems, such as the Solar System. This system of particles has been studied for many years in order to understand its nature, origin, and relationship to larger bodies. There are several methods to obtain space dust measurement. In the Solar System, the interplanetary dust particles have a role in scattering sunlight and in emitting thermal radiation, which is the most prominent feature of the night sky's radiation, with wavelengths ranging 5–50 μm. The particle sizes of grains characterizing the infrared emission near Earth's orbit typically range 10–100 μm. Microscopic impact craters on lunar rocks returned by the Apollo Program revealed the size distribution of cosmic dust particles bombarding the lunar surface. The ’’Grün’’ distribution of interpl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interplanetary Dust Cloud
The interplanetary dust cloud, or zodiacal cloud (as the source of the zodiacal light), consists of cosmic dust (small particles floating in outer space) that pervades the space between planets within planetary systems, such as the Solar System. This system of particles has been studied for many years in order to understand its nature, origin, and relationship to larger bodies. There are several methods to obtain space dust measurement. In the Solar System, the interplanetary dust particles have a role in scattering sunlight and in emitting thermal radiation, which is the most prominent feature of the night sky's radiation, with wavelengths ranging 5–50 μm. The particle sizes of grains characterizing the infrared emission near Earth's orbit typically range 10–100 μm. Microscopic impact craters on lunar rocks returned by the Apollo Program revealed the size distribution of cosmic dust particles bombarding the lunar surface. The ’’Grün’’ distribution of interpl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regolith
Regolith () is a blanket of unconsolidated, loose, heterogeneous superficial deposits covering solid rock. It includes dust, broken rocks, and other related materials and is present on Earth, the Moon, Mars, some asteroids, and other terrestrial planets and moons. Etymology The term ''regolith'' combines two Greek words: (), 'blanket', and (), 'rock'. The American geologist George P. Merrill first defined the term in 1897, writing: Earth Earth's regolith includes the following subdivisions and components: * soil or pedolith * alluvium and other transported cover, including that transported by aeolian, glacial, marine, and gravity flow processes. * "saprolith'", generally divided into the ** ''upper saprolite'': completely oxidised bedrock ** ''lower saprolite'': chemically reduced partially weathered rocks ** ''saprock'': fractured bedrock with weathering restricted to fracture margins * volcanic ash and lava flows that are interbedded with unconsolidated material * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meteorites
A meteorite is a solid piece of debris from an object, such as a comet, asteroid, or meteoroid, that originates in outer space and survives its passage through the atmosphere to reach the surface of a planet or moon. When the original object enters the atmosphere, various factors such as friction, pressure, and chemical interactions with the atmospheric gases cause it to heat up and radiate energy. It then becomes a meteor and forms a fireball, also known as a shooting star; astronomers call the brightest examples " bolides". Once it settles on the larger body's surface, the meteor becomes a meteorite. Meteorites vary greatly in size. For geologists, a bolide is a meteorite large enough to create an impact crater. Meteorites that are recovered after being observed as they transit the atmosphere and impact the Earth are called meteorite falls. All others are known as meteorite finds. Meteorites have traditionally been divided into three broad categories: stony meteorites that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury (planet)
Mercury is the smallest planet in the Solar System and the closest to the Sun. Its orbit around the Sun takes 87.97 Earth days, the shortest of all the Sun's planets. It is named after the Roman god ' ( Mercury), god of commerce, messenger of the gods, and mediator between gods and mortals, corresponding to the Greek god Hermes (). Like Venus, Mercury orbits the Sun within Earth's orbit as an inferior planet, and its apparent distance from the Sun as viewed from Earth never exceeds 28°. This proximity to the Sun means the planet can only be seen near the western horizon after sunset or the eastern horizon before sunrise, usually in twilight. At this time, it may appear as a bright star-like object, but is more difficult to observe than Venus. From Earth, the planet telescopically displays the complete range of phases, similar to Venus and the Moon, which recurs over its synodic period of approximately 116 days. The synodic proximity of Mercury to Earth makes Mercury most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of Australia). The Moon is a planetary-mass object with a differentiated rocky body, making it a satellite planet under the geophysical definitions of the term and larger than all known dwarf planets of the Solar System. It lacks any significant atmosphere, hydrosphere, or magnetic field. Its surface gravity is about one-sixth of Earth's at , with Jupiter's moon Io being the only satellite in the Solar System known to have a higher surface gravity and density. The Moon orbits Earth at an average distance of , or about 30 times Earth's diameter. Its gravitational influence is the main driver of Earth's tides and very slowly lengthens Earth's day. The Moon's orbit around Earth has a sidereal period of 27.3 days. During each synodic period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Nebula
The formation of the Solar System began about 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed. This model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, chemistry, geology, physics, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations. The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |