|
Methylmalonyl-CoA
Methylmalonyl-CoA is the thioester consisting of coenzyme A linked to methylmalonic acid. It is an important intermediate in the biosynthesis of succinyl-CoA, which plays an essential role in the tricarboxylic acid cycle (aka the Citric Acid Cycle, or Krebs Cycle). The compound is sometimes referred to as "methylmalyl-CoA". Biosynthesis and metabolism Methylmalonyl-CoA results from the metabolism of fatty acid with an odd number of carbons or from cholesterol side-chains, forming Propionyl-CoA. Propionyl-CoA and bicarbonate are converted to Methylmalonyl-CoA by the enzyme propionyl-CoA Carboxylase. It then is converted into succinyl-CoA by methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (MUT). This reaction is a reversible isomerization. In this way, the compound enters the Citric Acid Cycle. The following diagram demonstrates the aforementioned reaction: Propionyl CoA + Bicarbonate → Methylmalonyl CoA → Succinyl CoA Vitamin B12 Vitamin B12 plays an integral role in this reaction. Coenzyme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
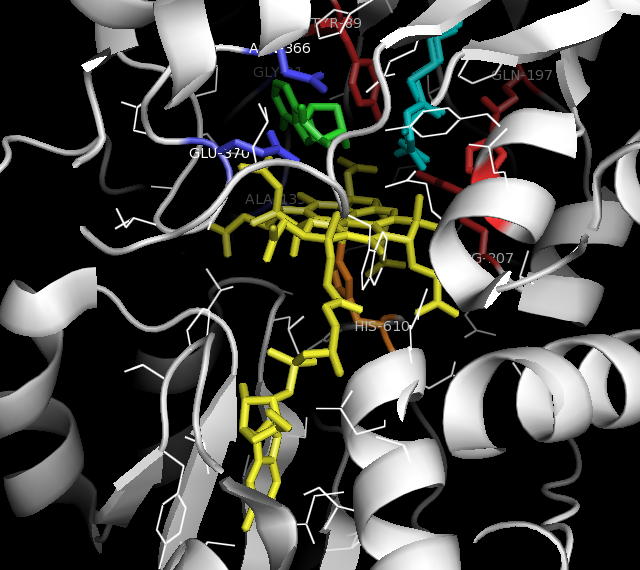
Methylmalonyl-CoA Mutase
Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (, MCM), mitochondrial, also known as methylmalonyl-CoA isomerase, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MUT'' gene. This vitamin B12-dependent enzyme catalyzes the isomerization of methylmalonyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA in humans. Mutations in ''MUT'' gene may lead to various types of methylmalonic aciduria. MCM was first identified in rat liver and sheep kidney in 1955. In its latent form, it is 750 amino acids in length. Upon entry to the mitochondria, the 32 amino acid mitochondrial leader sequence at the N-terminus of the protein is cleaved, forming the fully processed monomer. The monomers then associate into homodimers, and bind AdoCbl (one for each monomer active site) to form the final, active holoenzyme form. Structure Gene The ''MUT'' gene lies on the chromosome location of 6p12.3 and consists of 13 exons, spanning over 35kb. Protein The mature enzyme is a homodimer with the N-terminal CoA binding domain and the C- terminal cobalam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propionyl-CoA
Propionyl-CoA is a coenzyme A derivative of propionic acid. It is composed of a 24 total carbon chain (without the coenzyme, it is a 3 carbon structure) and its production and metabolic fate depend on which organism it is present in. Several different pathways can lead to its production, such as through the catabolism of specific amino acids or the oxidation of odd-chain fatty acids. It later can be broken down by propionyl-CoA carboxylase or through the methylcitrate cycle. In different organisms, however, propionyl-CoA can be sequestered into controlled regions, to alleviate its potential toxicity through accumulation. Genetic deficiencies regarding the production and breakdown of propionyl-CoA also have great clinical and human significance. Production There are several different pathways through which propionyl-CoA can be produced: * Propionyl-CoA, a three-carbon structure, is considered to be a minor species of propionic acid. Therefore, odd-number chains of fatty acids are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin involved in metabolism. It is one of eight B vitamins. It is required by animals, which use it as a cofactor in DNA synthesis, in both fatty acid and amino acid metabolism. It is important in the normal functioning of the nervous system via its role in the synthesis of myelin, and in the circulatory system in the maturation of red blood cells in the bone marrow. Plants do not need cobalamin and carry out the reactions with enzymes that are not dependent on it. Vitamin B12 is the most chemically complex of all vitamins, and for humans, the only vitamin that must be sourced from animal-derived foods or from supplements. Only some archaea and bacteria can synthesize vitamin B12. Most people in developed countries get enough B12 from the consumption of meat or foods with animal sources. Foods containing vitamin B12 include meat, clams, liver, fish, poultry, eggs, and dairy products. Many breakfast cereals are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propionyl-CoA Carboxylase
Propionyl-CoA carboxylase (, PCC) catalyses the carboxylation reaction of propionyl-CoA in the mitochondrial matrix. PCC has been classified both as a ligase and a lyase. The enzyme is biotin-dependent. The product of the reaction is (S)-methylmalonyl CoA. : ATP + propionyl-CoA + HCO3− ADP + phosphate + (S)-methylmalonyl-CoA (S)-Methylmalonyl-CoA cannot be directly utilized by animals. It is acted upon by a racemase, yielding (R)-methylmalonyl-CoA, which is then converted into succinyl-CoA by methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (one of the few metabolic enzymes which requires vitamin B12 as a cofactor). Succinyl-CoA, a Krebs cycle intermediate, is further metabolized into fumarate, then malate, and then oxaloacetate. Oxaloacetate may be transported into the cytosol to form phosphoenol pyruvate and other gluconeogenic intermediates. Propionyl-CoA is therefore an important precursor to glucose. Propionyl-CoA is the end product of odd-chain fatty acid metabolism, including most methylated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicarbonate
In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogencarbonate) is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid. It is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula . Bicarbonate serves a crucial biochemical role in the physiological pH buffering system. The term "bicarbonate" was coined in 1814 by the English chemist William Hyde Wollaston. The name lives on as a trivial name. Chemical properties The bicarbonate ion (hydrogencarbonate ion) is an anion with the empirical formula and a molecular mass of 61.01 daltons; it consists of one central carbon atom surrounded by three oxygen atoms in a trigonal planar arrangement, with a hydrogen atom attached to one of the oxygens. It is isoelectronic with nitric acid . The bicarbonate ion carries a negative one formal charge and is an amphiprotic species which has both acidic and basic properties. It is both the conjugate base of carbonic acid ; and the conjugate acid of , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radical Reaction
In chemistry, a radical, also known as a free radical, is an atom, molecule, or ion that has at least one unpaired electron, unpaired valence electron. With some exceptions, these unpaired electrons make radicals highly chemical reaction, chemically reactive. Many radicals spontaneously dimer (chemistry), dimerize. Most organic radicals have short lifetimes. A notable example of a radical is the hydroxyl radical (HO·), a molecule that has one unpaired electron on the oxygen atom. Two other examples are triplet oxygen and methylene radical, triplet carbene (꞉) which have two unpaired electrons. Radicals may be generated in a number of ways, but typical methods involve redox reactions. Ionizing radiation, heat, electrical discharges, and electrolysis are known to produce radicals. Radicals are intermediates in many chemical reactions, more so than is apparent from the balanced equations. Radicals are important in combustion, atmospheric chemistry, polymerization, Plasma (ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cofactor (biochemistry)
A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound or metallic ion that is required for an enzyme's role as a catalyst (a catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction). Cofactors can be considered "helper molecules" that assist in biochemical transformations. The rates at which these happen are characterized in an area of study called enzyme kinetics. Cofactors typically differ from ligands in that they often derive their function by remaining bound. Cofactors can be divided into two types: inorganic ions and complex organic molecules called coenzymes. Coenzymes are mostly derived from vitamins and other organic essential nutrients in small amounts. (Note that some scientists limit the use of the term "cofactor" for inorganic substances; both types are included here.) Coenzymes are further divided into two types. The first is called a "prosthetic group", which consists of a coenzyme that is tightly (or even covalently) and permanently bound to a protein. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organometallic Chemistry
Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and selenium, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide (metal carbonyls), cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term " metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal phosphine complexes are repres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosylcobalamin
Adenosylcobalamin (AdoCbl), also known as coenzyme B12, cobamamide, and dibencozide, is, along with methylcobalamin (MeCbl), one of the biologically active forms of vitamin B12. Adenosylcobalamin participates as a cofactor in radical-mediated 1,2-carbon skeleton rearrangements. These processes require the formation of the deoxyadenosyl radical through homolytic dissociation of the carbon-cobalt bond. This bond is exceptionally weak, with a bond dissociation energy of 31 kcal/mol, which is further lowered in the chemical environment of an enzyme active site. An enzyme that uses adenosylcobalamin as a cofactor is methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (MCM). Further experimentation has also determined adenosylcobalamin's role in regulating expression of some bacterial genes. By binding to CarH, AdoCbl can modulate carotenoid genes, which confer warm colors onto various plants. Carotenoid transcription is activated by sunlight, due to the response from AdoCbl. There are other photoreceptors acros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isomerization
In chemistry, isomerization or isomerisation is the process in which a molecule, polyatomic ion or molecular fragment is transformed into an isomer with a different chemical structure. Enolization is an example of isomerization, as is tautomerization. When the isomerization occurs intramolecularly it may be called a rearrangement reaction. When the activation energy for the isomerization reaction is sufficiently small, both isomers will exist in a temperature-dependent equilibrium with each other. Many values of the standard free energy difference, \Delta G^\circ, have been calculated, with good agreement between observed and calculated data. Examples and applications Alkanes Skeletal isomerization occurs in the cracking process, used in the petrochemical industry. As well as reducing the average chain length, straight-chain hydrocarbons are converted to branched isomers in the process, as illustrated the following reaction of ''n''-butane to ''i''-butane. :\overset -> \o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reversible Reaction
A reversible reaction is a reaction in which the conversion of reactants to products and the conversion of products to reactants occur simultaneously. : \mathit aA + \mathit bB \mathit cC + \mathit dD A and B can react to form C and D or, in the reverse reaction, C and D can react to form A and B. This is distinct from a reversible process in thermodynamics. Weak acids and bases undergo reversible reactions. For example, carbonic acid: : H2CO3 (l) + H2O(l) ⇌ HCO3−(aq) + H3O+(aq). The concentrations of reactants and products in an equilibrium mixture are determined by the analytical concentrations of the reagents (A and B or C and D) and the equilibrium constant, ''K''. The magnitude of the equilibrium constant depends on the Gibbs free energy change for the reaction. So, when the free energy change is large (more than about 30 kJ mol−1), the equilibrium constant is large (log K > 3) and the concentrations of the reactants at equilibrium are very small. Such a reac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |