|
Mental Foramen
The mental foramen is one of two foramina (openings) located on the anterior surface of the mandible. It is part of the mandibular canal. It transmits the terminal branches of the inferior alveolar nerve and the mental vessels. Structure The mental foramen is located on the anterior surface of the mandible. It is directly below the commisure of the lips, and the tendon of depressor labii inferioris muscle. It is at the end of the mandibular canal, which begins at the mandibular foramen on the posterior surface of the mandible. It transmits the terminal branches of the inferior alveolar nerve (the mental nerve), the mental artery, and the mental vein. Variation The mental foramen descends slightly in toothless individuals. The mental foramen is in line with the longitudinal axis of the 2nd premolar in 63% of people. It generally lies at the level of the vestibular fornix and about a finger's breadth above the inferior border of the mandible. In the general population, 17% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower tooth, teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone of the skull (discounting the ossicles of the middle ear). It is connected to the temporal bones by the temporomandibular joints. The bone is formed prenatal development, in the fetus from a fusion of the left and right mandibular prominences, and the point where these sides join, the mandibular symphysis, is still visible as a faint ridge in the midline. Like other symphyses in the body, this is a midline articulation where the bones are joined by fibrocartilage, but this articulation fuses together in early childhood.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, p. 59 The word "mandible" derives from the Latin word ''mandibula'', "jawbone" (literally "one used for chewing"), from ''wikt:mandere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower tooth, teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone of the skull (discounting the ossicles of the middle ear). It is connected to the temporal bones by the temporomandibular joints. The bone is formed prenatal development, in the fetus from a fusion of the left and right mandibular prominences, and the point where these sides join, the mandibular symphysis, is still visible as a faint ridge in the midline. Like other symphyses in the body, this is a midline articulation where the bones are joined by fibrocartilage, but this articulation fuses together in early childhood.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, p. 59 The word "mandible" derives from the Latin word ''mandibula'', "jawbone" (literally "one used for chewing"), from ''wikt:mandere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
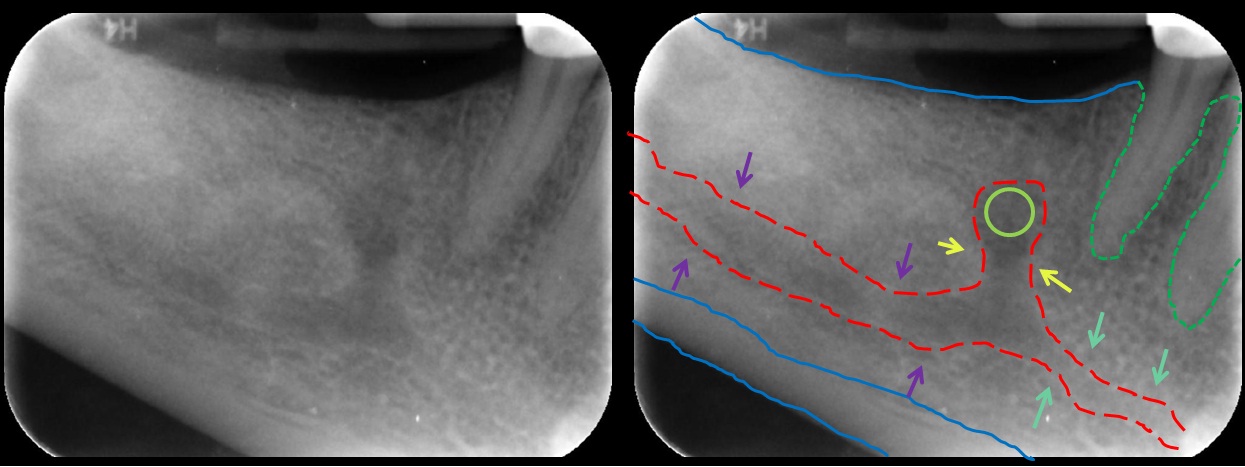
Mandibular Incisive Canal Highlighted
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower tooth, teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone of the skull (discounting the ossicles of the middle ear). It is connected to the temporal bones by the temporomandibular joints. The bone is formed prenatal development, in the fetus from a fusion of the left and right mandibular prominences, and the point where these sides join, the mandibular symphysis, is still visible as a faint ridge in the midline. Like other symphyses in the body, this is a midline articulation where the bones are joined by fibrocartilage, but this articulation fuses together in early childhood.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, p. 59 The word "mandible" derives from the Latin word ''mandibula'', "jawbone" (literally "one used for chewing"), from ''wikt:mandere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foramina
In anatomy and osteology, a foramen (; in Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary '. plural foramina, or foramens ) is an open hole that is present in extant or extinct s. Foramina inside the of typically allow , |
Mandibular Canal
In human anatomy, the mandibular canal is a canal within the mandible that contains the inferior alveolar nerve, inferior alveolar artery, and inferior alveolar vein. It runs obliquely downward and forward in the ramus, and then horizontally forward in the body, where it is placed under the alveoli and communicates with them by small openings. On arriving at the incisor teeth, it turns back to communicate with the mental foramen, giving off a small canal known as the mandibular incisive canal, which run to the cavities containing the incisor teeth. It carries branches of the inferior alveolar nerve and artery. It is continuous with the mental foramen (which opens onto front of mandible) and mandibular foramen (on medial aspect of ramus). Variations The mandibular canal is fairly close to the apices of the second molar in 50% of the radiographs. In 40%, canal is away from the root apices, and in only 10% of the radiographs the root apices appeared to penetrate the canal. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Alveolar Nerve
The inferior alveolar nerve (IAN) (also the inferior dental nerve) is a branch of the mandibular nerve, which is itself the third branch of the trigeminal nerve. The inferior alveolar nerves supply sensation to the lower teeth. Structure The inferior alveolar nerve is a branch of the mandibular nerve. After branching from the mandibular nerve, the inferior alveolar nerve travels behind the lateral pterygoid muscle. It gives off a branch, the mylohyoid nerve, and then enters the mandibular foramen. While in the mandibular canal within the mandible, it supplies the lower teeth (molars and second premolar) with sensory branches that form into the inferior dental plexus and give off small gingival and dental nerves to the teeth. Anteriorly, the nerve gives off the mental nerve at about the level of the mandibular 2nd premolars, which exits the mandible via the mental foramen and supplies sensory branches to the chin and lower lip. The inferior alveolar nerve continues anteriorl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depressor Labii Inferioris Muscle
The depressor labii inferioris (or quadratus labii inferioris) is a facial muscle. It helps to lower the bottom lip. Structure The depressor labii inferioris muscle arises from the lateral surface of the mandible. This is below the mental foramen, and the origin may be around 3 cm wide. It inserts on the skin of the lower lip, blending in with the orbicularis oris muscle around 2 cm wide. At its origin, depressor labii is continuous with the fibers of the platysma muscle. Some yellow fat is intermingled with the fibers. Nerve supply The depressor labii inferioris muscle is supplied by the marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve. Function The depressor labii inferioris muscle helps to depress and everts the lower lip. It is the most important of the muscles of the lower lip for this function. It is an antagonist of the orbicularis oris muscle. It is needed to expose the mandibular (lower) teeth during smiling. Clinical significance Resection The depressor labii ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saunders (imprint)
Saunders is an American academic publisher based in the United States. It is currently an imprint of Elsevier. Formerly independent, the W. B. Saunders company was acquired by CBS in 1968, who added it to their publishing division Holt, Rinehart & Winston. When CBS left the publishing field in 1986, it sold the academic publishing units to Harcourt Brace Jovanovich. Harcourt was acquired by Reed Elsevier in 2001. . . Retrieved May 2, 2015. W. B. Saunders published the Kinsey Reports and |
Mandibular Foramen
The mandibular foramen is an opening on the internal surface of the ramus of the mandible. It allows for divisions of the mandibular nerve and blood vessels to pass through. Structure The mandibular foramen is an opening on the internal surface of the ramus of the mandible. It allows for divisions of the mandibular nerve and blood vessels to pass through. Variation There are two distinct anatomies to its rim. * In the common form the rim is “V” shaped, with a groove separating the anterior and posterior parts. * In the horizontal-oval form there is no groove, and the rim is horizontally oriented and oval in shape, the anterior and posterior parts connected. Rarely, a bifid inferior alveolar nerve may be present, in which case a second mandibular foramen, more inferiorly placed, exists and can be detected by noting a doubled mandibular canal on a radiograph. Function The mandibular nerve is one of three branches of the trigeminal nerve, and the only one having motor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mental Nerve
The mental nerve is a sensory nerve of the face. It is a branch of the posterior trunk of the inferior alveolar nerve, itself a branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3), itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V). It provides sensation to the front of the chin and the lower lip, as well as the gums of the anterior mandibular (lower) teeth. It can be blocked with local anaesthesia for procedures on the chin, lower lip, and mucous membrane of the inner cheek. Problems with the nerve cause chin numbness. Structure The mental nerve is a branch of the posterior trunk of the inferior alveolar nerve. This is a branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3), itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V). It emerges from the mental foramen in the mandible. It divides into three branches beneath the depressor anguli oris muscle. One branch descends to the skin of the chin. Two branches ascend to the skin and mucous membrane of the lower lip. These branches communicate freely with the facial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mental Artery
The inferior alveolar artery (inferior dental artery) is an artery of the face. It is a branch of the first portion of the maxillary artery. Structure It descends with the inferior alveolar nerve to the mandibular foramen on the medial surface of the ramus of the mandible. It runs along the mandibular canal in the substance of the bone, accompanied by the nerve, and opposite the first premolar tooth divides into two branches, incisor and mental. Incisor branch The ''incisor branch'' is continued forward beneath the incisor teeth as far as the middle line, where it anastomoses with the artery of the opposite side The inferior alveolar artery and its incisor branch during their course through the substance of the bone give off a few twigs which are lost in the cancellous tissue, and a series of branches which correspond in number to the roots of the teeth: these enter the minute apertures at the extremities of the roots, and supply the pulp of the teeth. Mental branch The ''m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edentulism
Toothlessness, or edentulism, is the condition of having no teeth. In organisms that naturally have teeth, it is the result of tooth loss. Organisms that never possessed teeth can also be described as edentulous. Examples are the members of the former zoological classification order of '' Edentata'', which included anteaters and sloths, as they possess no anterior teeth and no or poorly developed posterior teeth. In naturally dentate species, edentulism is more than just the simple presence or absence of teeth. It is biochemically complex because the teeth, jaws, and oral mucosa are dynamic (changing over time). Processes such as bone remodeling (loss and gain of bone tissue) in the jaws and inflammation of soft tissue in response to the oral microbiota are clinically important for edentulous people. For example, bone resorption in the jaw is frequently how the teeth were able to detach in the first place; the jaw in an edentulous area undergoes further resorption even aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |