|
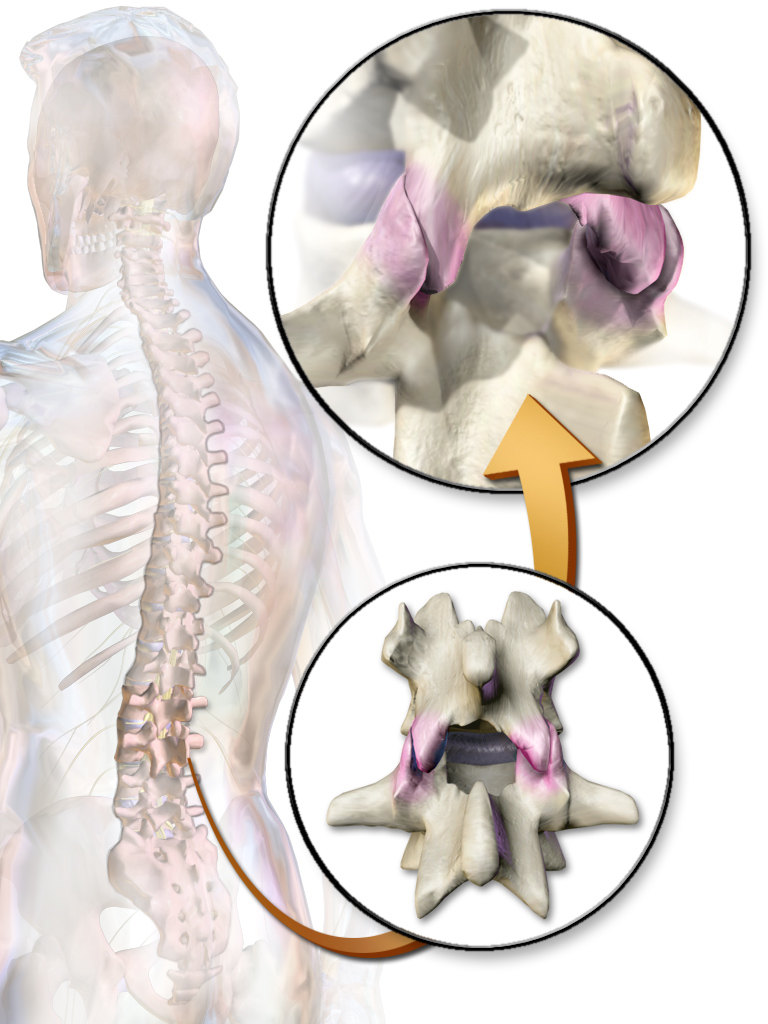
Meningeal Branches Of Spinal Nerve
The meningeal branches of the spinal nerves (also known as recurrent meningeal nerves, sinuvertebral nerves, or recurrent nerves of Luschka) are a number of small nerves that branch from the segmental spinal nerve near the origin of the anterior and posterior rami, but before the rami communicans; rami communicantes are branches which communicate between the spinal nerves and the sympathetic trunk. They then re-enter the intervertebral foramen, and innervate the facet joints, the anulus fibrosus of the intervertebral disc, and the ligaments and periosteum of the spinal canal, carrying pain sensation. The nucleus pulposus An intervertebral disc (or intervertebral fibrocartilage) lies between adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column. Each disc forms a fibrocartilaginous joint (a symphysis), to allow slight movement of the vertebrae, to act as a ligament to hold t ... of the intervertebral disk has no pain innervation. References * Drake RL, Vogl W, Mitchell AWM. ''Gray's Ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anulus Fibrosus Disci Intervertebralis
An intervertebral disc (or intervertebral fibrocartilage) lies between adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column. Each disc forms a fibrocartilaginous joint (a symphysis), to allow slight movement of the vertebrae, to act as a ligament to hold the vertebrae together, and to function as a shock absorber for the spine. Structure Intervertebral discs consist of an outer fibrous ring, the anulus fibrosus disci intervertebralis, which surrounds an inner gel-like center, the nucleus pulposus. The ''anulus fibrosus'' consists of several layers (laminae) of fibrocartilage made up of both type I and type II collagen. Type I is concentrated toward the edge of the ring, where it provides greater strength. The stiff laminae can withstand compressive forces. The fibrous intervertebral disc contains the ''nucleus pulposus'' and this helps to distribute pressure evenly across the disc. This prevents the development of stress concentrations which could cause damage to the underlying vertebrae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Nerve
A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into the corresponding cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal regions of the spine. There are eight pairs of cervical nerves, twelve pairs of thoracic nerves, five pairs of lumbar nerves, five pairs of sacral nerves, and one pair of coccygeal nerves. The spinal nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system. Structure Each spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, formed from the combination of nerve fibers from its dorsal and ventral roots. The dorsal root is the afferent sensory root and carries sensory information to the brain. The ventral root is the efferent motor root and carries motor information from the brain. The spinal nerve emerges from the spinal column through an opening (intervertebral foramen) between adjacent vertebrae. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rami Communicans
Ramus communicans (plural rami communicantes) is the Latin term used for a nerve which connects two other nerves, and can be translated as "communicating branch". Structure When used without further definition, it almost always refers to a communicating branch between a spinal nerve and the sympathetic trunk. More specifically, it usually refers to one of the following : * Gray ramus communicans * White ramus communicans The grey and white rami communicantes are responsible for conveying autonomic signals, specifically for the sympathetic nervous system. Their difference in coloration is caused by differences in myelination of the nerve fibres contained within, i.e. there are more myelinated than unmyelinated fibres in the white rami communicantes while the converse is true for the grey rami communicantes. Gray ramus communicans The grey rami communicantes exist at every level of the spinal cord and are responsible for carrying postganglionic nerve fibres from the paravertebr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intervertebral Foramen
The intervertebral foramen (also called neural foramen, and often abbreviated as IV foramen or IVF) is a foramen between two spinal vertebrae. Cervical, thoracic, and lumbar vertebrae all have intervertebral foramina. The foramina, or openings, are present between every pair of vertebrae in these areas. A number of structures pass through the foramen. These are the root of each spinal nerve, the spinal artery of the segmental artery, communicating veins between the internal and external plexuses, recurrent meningeal (sinu-vertebral) nerves, and transforaminal ligaments. When the spinal vertebrae are articulated with each other, the bodies form a strong pillar that supports the head and trunk, and the vertebral foramen constitutes a canal for the protection of the medulla spinalis (spinal cord). The size of the foramina is variable due to placement, pathology, spinal loading, and posture. Foramina can be occluded by arthritic degenerative changes and space-occupying lesions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygapophysial Joint
The facet joints (or zygapophysial joints, zygapophyseal, apophyseal, or Z-joints) are a set of synovial joint, synovial, plane joints between the articular processes of two adjacent vertebrae. There are two facet joints in each functional spinal unit, spinal motion segment and each facet joint is innervated by the Meningeal branches of spinal nerve, recurrent meningeal nerves. Innervation Innervation to the facet joints vary between segments of the spinal, but they are generally innervated by medial branch nerves that come off the dorsal rami. It is thought that these nerves are for primary sensory input, though there is some evidence that they have some motor input local musculature. Within the cervical spine, most joints are innervated by the medial branch nerve (a branch of the dorsal rami) from the same levels. In other words, the facet joint between C4 and C5 vertebral segments is innervated by the C4 and C5 medial branch nerves. However, there are two exceptions: # The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intervertebral Disk
An intervertebral disc (or intervertebral fibrocartilage) lies between adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column. Each disc forms a fibrocartilaginous joint (a symphysis), to allow slight movement of the vertebrae, to act as a ligament to hold the vertebrae together, and to function as a shock absorber for the spine. Structure Intervertebral discs consist of an outer fibrous ring, the anulus fibrosus disci intervertebralis, which surrounds an inner gel-like center, the nucleus pulposus. The ''anulus fibrosus'' consists of several layers (laminae) of fibrocartilage made up of both type I collagen, type I and type II collagen. Type I is concentrated toward the edge of the ring, where it provides greater strength. The stiff laminae can withstand compressive forces. The fibrous intervertebral disc contains the ''nucleus pulposus'' and this helps to distribute pressure evenly across the disc. This prevents the development of stress concentrations which could cause damage to the under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Canal
The spinal canal (or vertebral canal or spinal cavity) is the canal that contains the spinal cord within the vertebral column. The spinal canal is formed by the vertebrae through which the spinal cord passes. It is a process of the dorsal body cavity. This canal is enclosed within the foramen of the vertebrae. In the intervertebral spaces, the canal is protected by the ligamentum flavum posteriorly and the posterior longitudinal ligament anteriorly. Structure The outermost layer of the meninges, the dura mater, is closely associated with the arachnoid mater which in turn is loosely connected to the innermost layer, the pia mater. The meninges divide the spinal canal into the epidural space and the subarachnoid space. The pia mater is closely attached to the spinal cord. A subdural space is generally only present due to trauma and/or pathological situations. The subarachnoid space is filled with cerebrospinal fluid and contains the vessels that supply the spinal cord, namely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleus Pulposus
An intervertebral disc (or intervertebral fibrocartilage) lies between adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column. Each disc forms a fibrocartilaginous joint (a symphysis), to allow slight movement of the vertebrae, to act as a ligament to hold the vertebrae together, and to function as a shock absorber for the spine. Structure Intervertebral discs consist of an outer fibrous ring, the anulus fibrosus disci intervertebralis, which surrounds an inner gel-like center, the nucleus pulposus. The ''anulus fibrosus'' consists of several layers (laminae) of fibrocartilage made up of both type I and type II collagen. Type I is concentrated toward the edge of the ring, where it provides greater strength. The stiff laminae can withstand compressive forces. The fibrous intervertebral disc contains the ''nucleus pulposus'' and this helps to distribute pressure evenly across the disc. This prevents the development of stress concentrations which could cause damage to the underlying vertebrae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |