|
Meatus
In anatomy, a meatus (, ),''OED'' 2nd edition, 1989, as . plural "meatus" or "meatuses", is a natural body opening or canal. Meatus may refer to: * the , the opening of the * The , a canal in the |
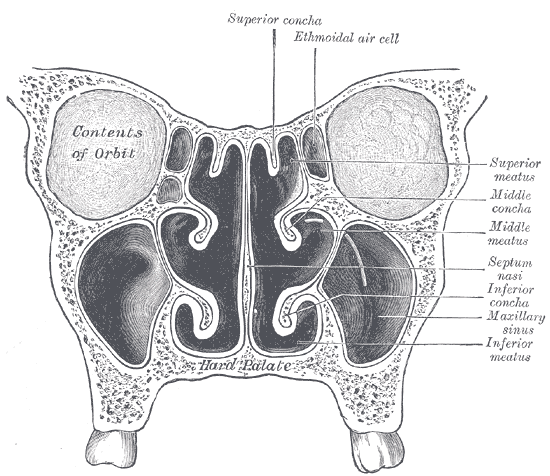
Nasal Meatus
In anatomy, the term nasal meatus can refer to any of the three meatuses (passages) through the skulls nasal cavity: the superior meatus (''meatus nasi superior''), middle meatus (''meatus nasi medius''), and inferior meatus (''meatus nasi inferior''). The nasal meatuses are located beneath each of the corresponding nasal conchae. In the case where a fourth, supreme nasal concha is present, there is a fourth supreme nasal meatus. Structure The superior meatus is the smallest of the three. It is a narrow cavity located obliquely below the superior concha. This meatus is short, lies above and extends from the middle part of the middle concha below. From behind, the sphenopalatine foramen opens into the cavity of the superior meatus and the meatus communicates with the posterior ethmoidal cells. Above and at the back of the superior concha is the sphenoethmoidal recess which the sphenoidal sinus opens into. The superior meatus occupies the middle third of the nasal cavity’s lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Meatus
In anatomy, the term nasal meatus can refer to any of the three meatuses (passages) through the skulls nasal cavity: the superior meatus (''meatus nasi superior''), middle meatus (''meatus nasi medius''), and inferior meatus (''meatus nasi inferior''). The nasal meatuses are located beneath each of the corresponding nasal conchae. In the case where a fourth, supreme nasal concha is present, there is a fourth supreme nasal meatus. Structure The superior meatus is the smallest of the three. It is a narrow cavity located obliquely below the superior concha. This meatus is short, lies above and extends from the middle part of the middle concha below. From behind, the sphenopalatine foramen opens into the cavity of the superior meatus and the meatus communicates with the posterior ethmoidal cells. Above and at the back of the superior concha is the sphenoethmoidal recess which the sphenoidal sinus opens into. The superior meatus occupies the middle third of the nasal cavity’s l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Meatus
In anatomy, the term nasal meatus can refer to any of the three meatuses (passages) through the skulls nasal cavity: the superior meatus (''meatus nasi superior''), middle meatus (''meatus nasi medius''), and inferior meatus (''meatus nasi inferior''). The nasal meatuses are located beneath each of the corresponding nasal conchae. In the case where a fourth, supreme nasal concha is present, there is a fourth supreme nasal meatus. Structure The superior meatus is the smallest of the three. It is a narrow cavity located obliquely below the superior concha. This meatus is short, lies above and extends from the middle part of the middle concha below. From behind, the sphenopalatine foramen opens into the cavity of the superior meatus and the meatus communicates with the posterior ethmoidal cells. Above and at the back of the superior concha is the sphenoethmoidal recess which the sphenoidal sinus opens into. The superior meatus occupies the middle third of the nasal cavity’s l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Meatus
In anatomy, the term nasal meatus can refer to any of the three meatuses (passages) through the skulls nasal cavity: the superior meatus (''meatus nasi superior''), middle meatus (''meatus nasi medius''), and inferior meatus (''meatus nasi inferior''). The nasal meatuses are located beneath each of the corresponding nasal conchae. In the case where a fourth, supreme nasal concha is present, there is a fourth supreme nasal meatus. Structure The superior meatus is the smallest of the three. It is a narrow cavity located obliquely below the superior concha. This meatus is short, lies above and extends from the middle part of the middle concha below. From behind, the sphenopalatine foramen opens into the cavity of the superior meatus and the meatus communicates with the posterior ethmoidal cells. Above and at the back of the superior concha is the sphenoethmoidal recess which the sphenoidal sinus opens into. The superior meatus occupies the middle third of the nasal cavity’s l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
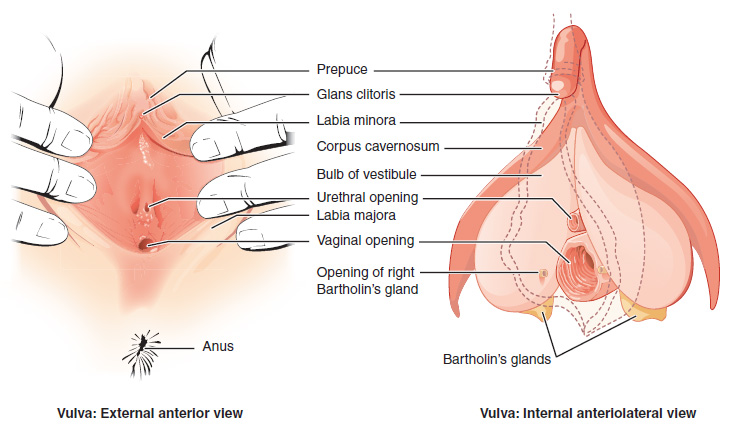
Urinary Meatus
The urinary meatus, (, ) also known as the external urethral orifice, is the opening of the urethra. It is the point where urine exits the urethra in both sexes and where semen exits the urethra in males. The meatus has varying degrees of sensitivity to touch. The meatus is located on the glans of the penis or in the vulval vestibule. In human males The male external urethral orifice is the external opening or urinary meatus, normally located at the tip of the glans penis, at its junction with the frenular delta. It presents as a vertical slit, possibly bounded on either side by two small labia-like projections, and continues longitudinally along the front aspect of the glans, which facilitates the flow of urine micturition. In some cases, the opening may be more rounded. This can occur naturally or may also occur as a side effect of excessive skin removal during circumcision. The meatus is a sensitive part of the male reproductive system. In human females The female external ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Auditory Meatus
The internal auditory meatus (also meatus acusticus internus, internal acoustic meatus, internal auditory canal, or internal acoustic canal) is a canal within the petrous part of the temporal bone of the skull between the posterior cranial fossa and the inner ear. Structure The opening to the meatus is called the porus acusticus internus or internal acoustic opening. It is located inside the posterior cranial fossa of the skull, near the center of the posterior surface of the petrous part of the temporal bone. The size varies considerably. Its outer margins are smooth and rounded. The canal which comprises the internal auditory meatus is short (about 1 cm) and runs laterally into the bone. The lateral (outer) aspect of the canal is known as the fundus. The fundus is subdivided by two thin crests of bone to form three separate canals, through which course the facial and vestibulocochlear nerve branches. The falciform crest first divides the meatus into superior and inferior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urethra
The urethra (from Greek οὐρήθρα – ''ourḗthrā'') is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. In human females and other primates, the urethra connects to the urinary meatus above the vagina, whereas in marsupials, the female's urethra empties into the urogenital sinus. Females use their urethra only for urinating, but males use their urethra for both urination and ejaculation. The external urethral sphincter is a striated muscle that allows voluntary control over urination. The internal sphincter, formed by the involuntary smooth muscles lining the bladder neck and urethra, receives its nerve supply by the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system. The internal sphincter is present both in males and females. Structure The urethra is a fibrous and muscular tube which connects the urinary bladder to the external urethral meatus. Its length differs between the sexes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meatal Stenosis
Urethral meatal stenosis is a narrowing (stenosis) of the opening of the urethra at the external urinary meatus, meatus , thus constricting the opening through which urine leaves the body from the urinary bladder. Symptoms and signs * Abnormal strength and direction of urinary stream * Visible narrow opening at the meatus in boys * Irritation, scarring or swelling of the meatus in boys * Discomfort with urination (dysuria and frequency) * Urinary incontinence, Incontinence (day or night) * Bleeding (hematuria) at end of urination * Urinary tract infections - increased susceptibility due to stricture Causes The protection provided by the foreskin for the glans penis and urinary meatus, meatus has been recognized since 1915. In the absence of the foreskin the meatus is exposed to mechanical and chemical irritation from ammoniacal diaper (nappy) that produces blister formation and ulceration of the urethral opening, which eventually gives rise to meatal stenosis (a narrowing of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vulva
The vulva (plural: vulvas or vulvae; derived from Latin for wrapper or covering) consists of the external sex organ, female sex organs. The vulva includes the mons pubis (or mons veneris), labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, bulb of vestibule, vestibular bulbs, vulval vestibule, urinary meatus, the Vagina#Vaginal opening and hymen, vaginal opening, hymen, and Bartholin's gland, Bartholin's and Skene's gland, Skene's vestibular glands. The urinary meatus is also included as it opens into the vulval vestibule. Other features of the vulva include the pudendal cleft, sebaceous glands, the urogenital triangle (anterior part of the perineum), and pubic hair. The vulva includes the entrance to the vagina, which leads to the uterus, and provides a double layer of protection for this by the folds of the outer and inner labia. Pelvic floor muscles support the structures of the vulva. Other muscles of the urogenital triangle also give support. Blood supply to the vulva comes from the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glans Penis
In male human anatomy, the glans penis, commonly referred to as the glans, is the bulbous structure at the distal end of the human penis that is the human male's most sensitive erogenous zone and their primary anatomical source of sexual pleasure. It is anatomically homologous to the clitoral glans. The glans penis is part of the male reproductive organs in humans and other mammals where it may appear smooth, spiny, elongated or divided. It is externally lined with mucosal tissue, which creates a smooth texture and glossy appearance. In humans, the glans is a continuation of the corpus spongiosum of the penis. At the summit appears the urinary meatus and at the base forms the corona glandis. An elastic band of tissue, known as the frenulum, runs on its ventral surface. In men who are not circumcised, it is completely or partially covered by the foreskin. In adults, the foreskin can generally be retracted over and past the glans manually or sometimes automatically during an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporal Bone
The temporal bones are situated at the sides and base of the skull, and lateral to the temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex. The temporal bones are overlaid by the sides of the head known as the temples, and house the structures of the ears. The lower seven cranial nerves and the major vessels to and from the brain traverse the temporal bone. Structure The temporal bone consists of four parts— the squamous, mastoid, petrous and tympanic parts. The squamous part is the largest and most superiorly positioned relative to the rest of the bone. The zygomatic process is a long, arched process projecting from the lower region of the squamous part and it articulates with the zygomatic bone. Posteroinferior to the squamous is the mastoid part. Fused with the squamous and mastoid parts and between the sphenoid and occipital bones lies the petrous part, which is shaped like a pyramid. The tympanic part is relatively small and lies inferior to the squamous part, anterior to the mast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ear Canal
The ear canal (external acoustic meatus, external auditory meatus, EAM) is a pathway running from the outer ear to the middle ear. The adult human ear canal extends from the pinna to the eardrum and is about in length and in diameter. Structure The human ear canal is divided into two parts. The elastic cartilage part forms the outer third of the canal; its anterior and lower wall are cartilaginous, whereas its superior and back wall are fibrous. The cartilage is the continuation of the cartilage framework of pinna. The cartilaginous portion of the ear canal contains small hairs and specialized sweat glands, called apocrine glands, which produce cerumen ( ear wax). The bony part forms the inner two thirds. The bony part is much shorter in children and is only a ring (''annulus tympanicus'') in the newborn. The layer of epithelium encompassing the bony portion of the ear canal is much thinner and therefore, more sensitive in comparison to the cartilaginous portion. Size and sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |