|
Maximum Potential Intensity
The maximum potential intensity of a tropical cyclone is the theoretical limit of the strength of a tropical cyclone. Maximum potential intensity Due to surface friction, the inflow only partially conserves angular momentum. Thus, the sea surface lower boundary acts as both a source (evaporation) and sink (friction) of energy for the system. This fact leads to the existence of a theoretical upper bound on the strongest wind speed that a tropical cyclone can attain. Because evaporation increases linearly with wind speed (just as climbing out of a pool feels much colder on a windy day), there is a positive feedback on energy input into the system known as the Wind-Induced Surface Heat Exchange (WISHE) feedback. This feedback is offset when frictional dissipation, which increases with the cube of the wind speed, becomes sufficiently large. This upper bound is called the "maximum potential intensity", v_p, and is given by :v_p^2 = \frac\frac\Delta k where T_s is the temperature of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its location and strength, a tropical cyclone is referred to by different names, including hurricane (), typhoon (), tropical storm, cyclonic storm, tropical depression, or simply cyclone. A hurricane is a strong tropical cyclone that occurs in the Atlantic Ocean or northeastern Pacific Ocean, and a typhoon occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. In the Indian Ocean, South Pacific, or (rarely) South Atlantic, comparable storms are referred to simply as "tropical cyclones", and such storms in the Indian Ocean can also be called "severe cyclonic storms". "Tropical" refers to the geographical origin of these systems, which form almost exclusively over tropical seas. "Cyclone" refers to their winds moving in a circle, whirling round ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Sounding
Atmospheric sounding or atmospheric profiling is a measurement of vertical distribution of physical properties of the atmospheric column such as pressure, temperature, wind speed and wind direction (thus deriving wind shear), liquid water content, ozone concentration, pollution, and other properties. Such measurements are performed in a variety of ways including remote sensing and in situ observations. The most common in situ sounding is a radiosonde, which usually is a weather balloon, but can also be a rocketsonde. Remote sensing soundings generally use passive infrared and microwave radiometers: * airborne instruments * surface stations * Earth-observing satellite instruments such as AIRS and AMSU * observation of atmospheres on different planets, such as the Mars climate sounder on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Direct methods Sensors that measure atmospheric constituents directly, such as thermometers, barometers, and humidity sensors, can be sent aloft on balloons, roc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Meteorological Society
The American Meteorological Society (AMS) is the premier scientific and professional organization in the United States promoting and disseminating information about the Atmospheric sciences, atmospheric, Oceanography, oceanic, and Hydrology, hydrologic sciences. Its mission is to advance the atmospheric and related sciences, technologies, applications, and services for the benefit of society. Background Founded on December 29, 1919, by Charles Franklin Brooks at a meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science in St. Louis and incorporated on January 21, 1920, the American Meteorological Society has a membership of more than 13,000 weather, water, and climate scientists, professionals, researchers, educators, students, and enthusiasts. AMS offers numerous programs and services in the sphere of water, weather and climate sciences. It publishes eleven atmospheric and related oceanic and hydrologic journals (in print and online), sponsors as many as twelve conf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Climate
The ''Journal of Climate'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal published semi-monthly by the American Meteorological Society. It covers research that advances basic understanding of the dynamics and physics of the climate system on large spatial scales, including variability of the atmosphere, oceans, land surface, and cryosphere; past, present, and projected future changes in the Climate, climate system; and climate simulation and prediction. See also *List of scientific journals in earth and atmospheric sciences A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America * SC Germania List, German rugby unio ... External links * Climatology journals Publications established in 1988 English-language journals American Meteorological Society academic journals {{climate-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
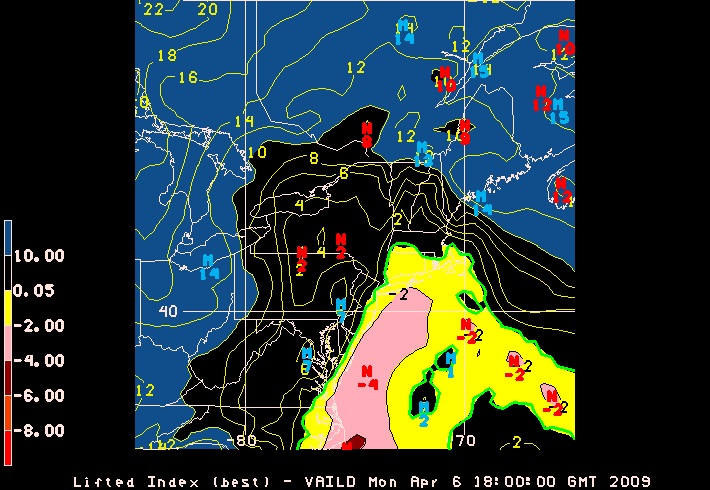
Lifted Index
The lifted index (LI) is the temperature difference between the environment Te(p) and an air parcel lifted adiabatically Tp(p) at a given pressure height in the troposphere (lowest layer where most weather occurs) of the atmosphere, usually 500 hPa ( mb). The temperature is measured in Celsius. When the value is positive, the atmosphere (at the respective height) is stable and when the value is negative, the atmosphere is unstable. Determining LI LI can be computed using computer algorithms but can also be determined graphically. To do this, generally, the parcel is lifted from the portion of the planetary boundary layer (PBL) that lies below the morning inversion. The air here should be about 60 to 65% RH, which is then lifted along the dry adiabat (see also adiabatic process) to the lifting condensation level (LCL), which is the intersection of that curve with the average mixing ratio in the boundary layer. Once the LCL is found, the parcel is lifted along the moist adiab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Thermodynamics
Atmospheric thermodynamics is the study of heat-to-work transformations (and their reverse) that take place in the earth's atmosphere and manifest as weather or climate. Atmospheric thermodynamics use the laws of classical thermodynamics, to describe and explain such phenomena as the properties of moist air, the formation of clouds, atmospheric convection, boundary layer meteorology, and vertical instabilities in the atmosphere. Atmospheric thermodynamic diagrams are used as tools in the forecasting of storm development. Atmospheric thermodynamics forms a basis for cloud microphysics and convection parameterizations used in numerical weather models and is used in many climate considerations, including convective-equilibrium climate models. Overview The atmosphere is an example of a non-equilibrium system. Atmospheric thermodynamics describes the effect of buoyant forces that cause the rise of less dense (warmer) air, the descent of more dense air, and the transformation of water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celsius
The degree Celsius is the unit of temperature on the Celsius scale (originally known as the centigrade scale outside Sweden), one of two temperature scales used in the International System of Units (SI), the other being the Kelvin scale. The degree Celsius (symbol: °C) can refer to a specific temperature on the Celsius scale or a unit to indicate a difference or range between two temperatures. It is named after the Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius (1701–1744), who developed a similar temperature scale in 1742. Before being renamed in 1948 to honour Anders Celsius, the unit was called ''centigrade'', from the Latin ''centum'', which means 100, and ''gradus'', which means steps. Most major countries use this scale; the other major scale, Fahrenheit, is still used in the United States, some island territories, and Liberia. The Kelvin scale is of use in the sciences, with representing absolute zero. Since 1743 the Celsius scale has been based on 0 °C for the freezing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Surface Temperature
Sea surface temperature (SST), or ocean surface temperature, is the ocean temperature close to the surface. The exact meaning of ''surface'' varies according to the measurement method used, but it is between and below the sea surface. Air masses in the Earth's atmosphere are highly modified by sea surface temperatures within a short distance of the shore. Localized areas of heavy snow can form in bands downwind of warm water bodies within an otherwise cold air mass. Warm sea surface temperatures are known to be a cause of tropical cyclogenesis over the Earth's oceans. Tropical cyclones can also cause a cool wake, due to turbulent mixing of the upper of the ocean. SST changes diurnally, like the air above it, but to a lesser degree. There is less SST variation on breezy days than on calm days. In addition, ocean currents such as the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation (AMO), can affect SST's on multi-decadal time scales, a major impact results from the global thermohaline ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metre Per Second
The metre per second is the unit of both speed (a scalar (physics), scalar quantity) and velocity (a Vector (mathematics and physics), vector quantity, which has direction and magnitude) in the International System of Units (SI), equal to the speed of a body covering a distance of one metre in a time of one second. The International System of Units, SI unit symbols are m/s, m·s−1, m s−1, or . Sometimes it is abbreviated as "mps". Conversions is equivalent to: : = 3.6 kilometres per hour, km/h (exactly) : ≈ 3.2808 feet per second (approximately) : ≈ 2.2369 miles per hour (approximately) : ≈ 1.9438 knot (unit), knots (approximately) 1 feet per second, foot per second = (exactly) 1 miles per hour, mile per hour = (exactly) 1 kilometres per hour, km/h = (exactly) Relation to other measures The benz, named in honour of Karl Benz, has been proposed as a name for one metre per second. Although it has seen some support as a practical unit, primarily from German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Season
A season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperate and polar regions, the seasons are marked by changes in the intensity of sunlight that reaches the Earth's surface, variations of which may cause animals to undergo hibernation or to migrate, and plants to be dormant. Various cultures define the number and nature of seasons based on regional variations, and as such there are a number of both modern and historical cultures whose number of seasons varies. The Northern Hemisphere experiences most direct sunlight during May, June, and July, as the hemisphere faces the Sun. The same is true of the Southern Hemisphere in November, December, and January. It is Earth's axial tilt that causes the Sun to be higher in the sky during the summer months, which increases the solar flux. However, due to seas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Spray
Sea spray are aerosol particles formed from the ocean, mostly by ejection into Earth's atmosphere by bursting bubbles at the air-sea interface. Sea spray contains both organic matter and inorganic salts that form sea salt aerosol (SSA). SSA has the ability to form cloud condensation nuclei (CCN) and remove anthropogenic aerosol pollutants from the atmosphere. Coarse sea spray has also been found to inhibit the development of lightning in storm clouds. Sea spray is directly (and indirectly, through SSA) responsible for a significant degree of the heat and moisture fluxes between the atmosphere and the ocean, affecting global climate patterns and tropical storm intensity. Sea spray also influences plant growth and species distribution in coastal ecosystems and increases corrosion of building materials in coastal areas. Generation Formation When wind, whitecaps, and breaking waves mix air into the sea surface, the air regroups to form bubbles, floats to the surface, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convective Available Potential Energy
In meteorology, convective available potential energy (commonly abbreviated as CAPE), is the integrated amount of work that the upward (positive) buoyancy force would perform on a given mass of air (called an air parcel) if it rose vertically through the entire atmosphere. Positive CAPE will cause the air parcel to rise, while negative CAPE will cause the air parcel to sink. Nonzero CAPE is an indicator of atmospheric instability in any given atmospheric sounding, a necessary condition for the development of cumulus and cumulonimbus clouds with attendant severe weather hazards. Mechanics CAPE exists within the conditionally unstable layer of the troposphere, the free convective layer (FCL), where an ascending air parcel is warmer than the ambient air. CAPE is measured in joules per kilogram of air (J/kg). Any value greater than 0 J/kg indicates instability and an increasing possibility of thunderstorms and hail. Generic CAPE is calculated by integrating vertically the loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
