|
Matrix Diagonal
In linear algebra, a diagonal matrix is a matrix in which the entries outside the main diagonal are all zero; the term usually refers to square matrices. Elements of the main diagonal can either be zero or nonzero. An example of a 2×2 diagonal matrix is \left begin 3 & 0 \\ 0 & 2 \end\right/math>, while an example of a 3×3 diagonal matrix is \left begin 6 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 \end\right/math>. An identity matrix of any size, or any multiple of it (a scalar matrix), is a diagonal matrix. A diagonal matrix is sometimes called a scaling matrix, since matrix multiplication with it results in changing scale (size). Its determinant is the product of its diagonal values. Definition As stated above, a diagonal matrix is a matrix in which all off-diagonal entries are zero. That is, the matrix with ''n'' columns and ''n'' rows is diagonal if \forall i,j \in \, i \ne j \implies d_ = 0. However, the main diagonal entries are unrestricted. The term ''diagonal matrix'' may so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Algebra
Linear algebra is the branch of mathematics concerning linear equations such as: :a_1x_1+\cdots +a_nx_n=b, linear maps such as: :(x_1, \ldots, x_n) \mapsto a_1x_1+\cdots +a_nx_n, and their representations in vector spaces and through matrices. Linear algebra is central to almost all areas of mathematics. For instance, linear algebra is fundamental in modern presentations of geometry, including for defining basic objects such as lines, planes and rotations. Also, functional analysis, a branch of mathematical analysis, may be viewed as the application of linear algebra to spaces of functions. Linear algebra is also used in most sciences and fields of engineering, because it allows modeling many natural phenomena, and computing efficiently with such models. For nonlinear systems, which cannot be modeled with linear algebra, it is often used for dealing with first-order approximations, using the fact that the differential of a multivariate function at a point is the line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commute (mathematics)
In mathematics, a binary operation is commutative if changing the order of the operands does not change the result. It is a fundamental property of many binary operations, and many mathematical proofs depend on it. Most familiar as the name of the property that says something like or , the property can also be used in more advanced settings. The name is needed because there are operations, such as division and subtraction, that do not have it (for example, ); such operations are ''not'' commutative, and so are referred to as ''noncommutative operations''. The idea that simple operations, such as the multiplication and addition of numbers, are commutative was for many years implicitly assumed. Thus, this property was not named until the 19th century, when mathematics started to become formalized. A similar property exists for binary relations; a binary relation is said to be symmetric if the relation applies regardless of the order of its operands; for example, equality is sym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
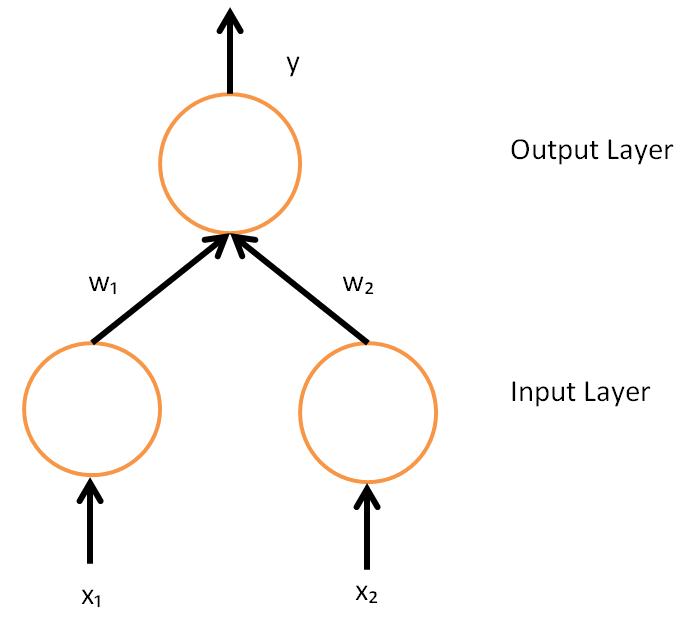
Backpropagation
In machine learning, backpropagation (backprop, BP) is a widely used algorithm for training feedforward artificial neural networks. Generalizations of backpropagation exist for other artificial neural networks (ANNs), and for functions generally. These classes of algorithms are all referred to generically as "backpropagation". In fitting a neural network, backpropagation computes the gradient of the loss function with respect to the weights of the network for a single input–output example, and does so efficiently, unlike a naive direct computation of the gradient with respect to each weight individually. This efficiency makes it feasible to use gradient methods for training multilayer networks, updating weights to minimize loss; gradient descent, or variants such as stochastic gradient descent, are commonly used. The backpropagation algorithm works by computing the gradient of the loss function with respect to each weight by the chain rule, computing the gradient one laye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn', that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence. Machine learning algorithms build a model based on sample data, known as training data, in order to make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed to do so. Machine learning algorithms are used in a wide variety of applications, such as in medicine, email filtering, speech recognition, agriculture, and computer vision, where it is difficult or unfeasible to develop conventional algorithms to perform the needed tasks.Hu, J.; Niu, H.; Carrasco, J.; Lennox, B.; Arvin, F.,Voronoi-Based Multi-Robot Autonomous Exploration in Unknown Environments via Deep Reinforcement Learning IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020. A subset of machine learning is closely related to computational statistics, which focuses on making pred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparse Matrix
In numerical analysis and scientific computing, a sparse matrix or sparse array is a matrix in which most of the elements are zero. There is no strict definition regarding the proportion of zero-value elements for a matrix to qualify as sparse but a common criterion is that the number of non-zero elements is roughly equal to the number of rows or columns. By contrast, if most of the elements are non-zero, the matrix is considered dense. The number of zero-valued elements divided by the total number of elements (e.g., ''m'' × ''n'' for an ''m'' × ''n'' matrix) is sometimes referred to as the sparsity of the matrix. Conceptually, sparsity corresponds to systems with few pairwise interactions. For example, consider a line of balls connected by springs from one to the next: this is a sparse system as only adjacent balls are coupled. By contrast, if the same line of balls were to have springs connecting each ball to all other balls, the system would correspond to a dense matrix. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Module
In mathematics, a free module is a module that has a basis – that is, a generating set consisting of linearly independent elements. Every vector space is a free module, but, if the ring of the coefficients is not a division ring (not a field in the commutative case), then there exist non-free modules. Given any set and ring , there is a free -module with basis , which is called the ''free module on'' or ''module of formal'' -''linear combinations'' of the elements of . A free abelian group is precisely a free module over the ring of integers. Definition For a ring R and an R- module M, the set E\subseteq M is a basis for M if: * E is a generating set for M; that is to say, every element of M is a finite sum of elements of E multiplied by coefficients in R; and * E is linearly independent, that is, for every subset \ of distinct elements of E, r_1 e_1 + r_2 e_2 + \cdots + r_n e_n = 0_M implies that r_1 = r_2 = \cdots = r_n = 0_R (where 0_M is the zero element of M a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Linear Group
In mathematics, the general linear group of degree ''n'' is the set of invertible matrices, together with the operation of ordinary matrix multiplication. This forms a group, because the product of two invertible matrices is again invertible, and the inverse of an invertible matrix is invertible, with identity matrix as the identity element of the group. The group is so named because the columns (and also the rows) of an invertible matrix are linearly independent, hence the vectors/points they define are in general linear position, and matrices in the general linear group take points in general linear position to points in general linear position. To be more precise, it is necessary to specify what kind of objects may appear in the entries of the matrix. For example, the general linear group over R (the set of real numbers) is the group of invertible matrices of real numbers, and is denoted by GL''n''(R) or . More generally, the general linear group of degree ''n'' over an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Center Of A Ring
In algebra, the center of a ring ''R'' is the subring consisting of the elements ''x'' such that ''xy = yx'' for all elements ''y'' in ''R''. It is a commutative ring and is denoted as Z(R); "Z" stands for the German word ''Zentrum'', meaning "center". If ''R'' is a ring, then ''R'' is an associative algebra over its center. Conversely, if ''R'' is an associative algebra over a commutative subring ''S'', then ''S'' is a subring of the center of ''R'', and if ''S'' happens to be the center of ''R'', then the algebra ''R'' is called a central algebra. Examples *The center of a commutative ring ''R'' is ''R'' itself. *The center of a skew-field is a field. *The center of the (full) matrix ring with entries in a commutative ring ''R'' consists of ''R''-scalar multiples of the identity matrix. *Let ''F'' be a field extension of a field ''k'', and ''R'' an algebra over ''k''. Then Z\left(R \otimes_k F\right) = Z(R) \otimes_k F. *The center of the universal enveloping algebra of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algebra (ring Theory)
In mathematics, an algebra over a field (often simply called an algebra) is a vector space equipped with a bilinear product. Thus, an algebra is an algebraic structure consisting of a set together with operations of multiplication and addition and scalar multiplication by elements of a field and satisfying the axioms implied by "vector space" and "bilinear". The multiplication operation in an algebra may or may not be associative, leading to the notions of associative algebras and non-associative algebras. Given an integer ''n'', the ring of real square matrices of order ''n'' is an example of an associative algebra over the field of real numbers under matrix addition and matrix multiplication since matrix multiplication is associative. Three-dimensional Euclidean space with multiplication given by the vector cross product is an example of a nonassociative algebra over the field of real numbers since the vector cross product is nonassociative, satisfying the Jacobi identity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endomorphism Algebra
In mathematics, an endomorphism is a morphism from a mathematical object to itself. An endomorphism that is also an isomorphism is an automorphism. For example, an endomorphism of a vector space is a linear map , and an endomorphism of a group is a group homomorphism . In general, we can talk about endomorphisms in any category. In the category of sets, endomorphisms are functions from a set ''S'' to itself. In any category, the composition of any two endomorphisms of is again an endomorphism of . It follows that the set of all endomorphisms of forms a monoid, the full transformation monoid, and denoted (or to emphasize the category ). Automorphisms An invertible endomorphism of is called an automorphism. The set of all automorphisms is a subset of with a group structure, called the automorphism group of and denoted . In the following diagram, the arrows denote implication: Endomorphism rings Any two endomorphisms of an abelian group, , can be added tog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ring (algebra)
In mathematics, rings are algebraic structures that generalize fields: multiplication need not be commutative and multiplicative inverses need not exist. In other words, a ''ring'' is a set equipped with two binary operations satisfying properties analogous to those of addition and multiplication of integers. Ring elements may be numbers such as integers or complex numbers, but they may also be non-numerical objects such as polynomials, square matrices, functions, and power series. Formally, a ''ring'' is an abelian group whose operation is called ''addition'', with a second binary operation called ''multiplication'' that is associative, is distributive over the addition operation, and has a multiplicative identity element. (Some authors use the term " " with a missing i to refer to the more general structure that omits this last requirement; see .) Whether a ring is commutative (that is, whether the order in which two elements are multiplied might change the resul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Module (ring Theory)
In mathematics, a module is a generalization of the notion of vector space in which the field of scalars is replaced by a ring. The concept of ''module'' generalizes also the notion of abelian group, since the abelian groups are exactly the modules over the ring of integers. Like a vector space, a module is an additive abelian group, and scalar multiplication is distributive over the operation of addition between elements of the ring or module and is compatible with the ring multiplication. Modules are very closely related to the representation theory of groups. They are also one of the central notions of commutative algebra and homological algebra, and are used widely in algebraic geometry and algebraic topology. Introduction and definition Motivation In a vector space, the set of scalars is a field and acts on the vectors by scalar multiplication, subject to certain axioms such as the distributive law. In a module, the scalars need only be a ring, so the mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |