|
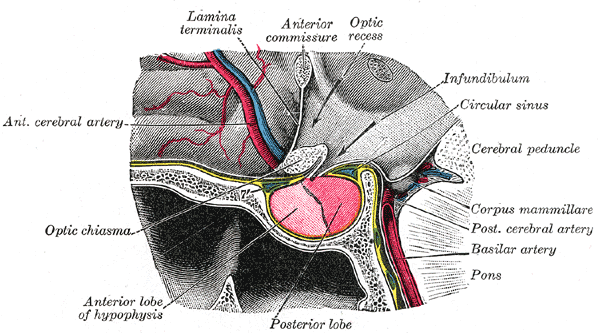
Massa Intermedia
The interthalamic adhesion (also known as the intermediate mass or middle commissure) is a flattened band of tissue that connects both parts of the thalamus at their medial surfaces. The medial surfaces form the upper part of the lateral wall to the third ventricle. In humans, it is only about one centimeter long – though in females, it is about 50% larger on average. Sometimes, it is in two parts – and 20% of the time, it is absent. In other mammals, it is larger. In 1889, a Portuguese anatomist by the name of Macedo examined 215 brains, showing that male humans are approximately twice as likely to lack an interthalamic adhesion as are female humans. He also reported its absence, still reported today in about 20% of humans. Its absence is seen to be of no consequence. The interthalamic adhesion contains nerve cells and nerve fibers; a few of the latter may cross the middle line, but most of them pass toward the middle line and then curve laterally on the same side. It is sti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronal Section
The coronal plane (also known as the frontal plane) is an anatomical plane that divides the body into Anatomical terms of location#Dorsal and ventral, dorsal and ventral sections. It is perpendicular to the sagittal plane, sagittal and transverse plane, transverse planes. Details The coronal plane is an example of a Anatomical terms of location#General usage, longitudinal plane. For a human, the mid-coronal plane would transect a standing body into two halves (front and back, or anterior and posterior) in an imaginary line that cuts through both shoulders. The description of the coronal plane applies to most animals as well as humans even though humans walk upright and the various planes are usually shown in the vertical orientation. The sternal plane (''planum sternale'') is a coronal plane which transects the front of the Human sternum, sternum. Etymology The term is derived from Latin ''corona'' ('garland, crown'), from Ancient Greek κορώνη (''korōnē'', 'garland, wrea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Ventricle
The third ventricle is one of the four connected ventricles of the ventricular system within the mammalian brain. It is a slit-like cavity formed in the diencephalon between the two thalami, in the midline between the right and left lateral ventricles, and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Running through the third ventricle is the interthalamic adhesion, which contains thalamic neurons and fibers that may connect the two thalami. Structure The third ventricle is a narrow, laterally flattened, vaguely rectangular region, filled with cerebrospinal fluid, and lined by ependyma. It is connected at the superior anterior corner to the lateral ventricles, by the interventricular foramina, and becomes the cerebral aqueduct (''aqueduct of Sylvius'') at the posterior caudal corner. Since the interventricular foramina are on the lateral edge, the corner of the third ventricle itself forms a bulb, known as the ''anterior recess'' (it is also known as the ''bulb of the ventricl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalamus
The thalamus (from Greek θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter located in the dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of the forebrain). Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all directions, allowing hub-like exchanges of information. It has several functions, such as the relaying of sensory signals, including motor signals to the cerebral cortex and the regulation of consciousness, sleep, and alertness. Anatomically, it is a paramedian symmetrical structure of two halves (left and right), within the vertebrate brain, situated between the cerebral cortex and the midbrain. It forms during embryonic development as the main product of the diencephalon, as first recognized by the Swiss embryologist and anatomist Wilhelm His Sr. in 1893. Anatomy The thalamus is a paired structure of gray matter located in the forebrain which is superior to the midbrain, near the center of the brain, with nerve fibers projecting out to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. Non-animals like plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Neurons are typically classified into three types based on their function. Sensory neurons respond to stimuli such as touch, sound, or light that affect the cells of the sensory organs, and they send signals to the spinal cord or brain. Motor neurons receive signals from the brain and spinal cord to control everything from muscle contractions to glandular output. Interneurons connect neurons to other neurons within the same region of the brain or spinal cord. When multiple neurons are connected together, they form what is called a neural circuit. A typical neuron consists of a cell body (soma), dendrites, and a single axon. The soma is a compact structure, and the axon and dend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action potentials away from the nerve cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles, and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the axons are called afferent nerve fibers and the electrical impulse travels along these from the periphery to the cell body and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction can be the cause of many inherited and acquired neurological disorders that affect both the peripheral and central neurons. Nerve fibers are classed into three typesgroup A nerve fibers, group B nerve fibers, and group C nerve fibers. Groups A and B are myelinated, and group C are unmyelinated. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commissure
A commissure () is the location at which two objects abut or are joined. The term is used especially in the fields of anatomy and biology. * The most common usage of the term refers to the brain's commissures, of which there are five. Such a commissure is a bundle of commissural fibers as a tract that crosses the midline at its level of origin or entry (as opposed to a decussation of fibers that cross obliquely). The five are the anterior commissure, posterior commissure, corpus callosum, commissure of fornix (hippocampal commissure), and habenular commissure. They consist of fibre tracts that connect the two cerebral hemispheres and span the longitudinal fissure. In the spinal cord there are the anterior white commissure, and the gray commissure. ''Commissural neurons'' refer to neuronal cells that grow their axons across the midline of the nervous system within the brain and the spinal cord. * ''Commissure'' also often refers to cardiac anatomy of heart valves. In the heart, a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnold–Chiari Malformation
Chiari malformation (CM) is a structural defect in the cerebellum, characterized by a downward displacement of one or both cerebellar tonsils through the foramen magnum (the opening at the base of the skull). CMs can cause headaches, difficulty swallowing, vomiting, dizziness, neck pain, unsteady gait, poor hand coordination, numbness and tingling of the hands and feet, and speech problems. Less often, people may experience ringing or buzzing in the ears, weakness, slow heart rhythm, or fast heart rhythm, curvature of the spine (scoliosis) related to spinal cord impairment, abnormal breathing, such as central sleep apnea, characterized by periods of breathing cessation during sleep, and, in severe cases, paralysis. This can sometimes lead to non-communicating hydrocephalus as a result of obstruction of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) outflow. The cerebrospinal fluid outflow is caused by phase difference in outflow and influx of blood in the vasculature of the brain. The malformation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States and one of the most prestigious and highly ranked universities in the world. The university is composed of ten academic faculties plus Harvard Radcliffe Institute. The Faculty of Arts and Sciences offers study in a wide range of undergraduate and graduate academic disciplines, and other faculties offer only graduate degrees, including professional degrees. Harvard has three main campuses: the Cambridge campus centered on Harvard Yard; an adjoining campus immediately across Charles River in the Allston neighborhood of Boston; and the medical campus in Boston's Longwood Medical Area. Harvard's endowment is valued at $50.9 billion, making it the wealthiest academic institution in the world. Endowment inco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |