|
Marginal Concepts
In economics, marginal concepts are associated with a ''specific change'' in the quantity used of a good or service, as opposed to some notion of the over-all significance of that class of good or service, or of some total quantity thereof.{{citation needed, date=February 2012 Marginality Constraints are conceptualized as a ''border'' or ''margin''. Wicksteed, Philip Henry; ''The Common Sense of Political Economy'' (1910), Bk I Ch 2 and elsewhere. The location of the margin for any individual corresponds to his or her ''endowment'', broadly conceived to include opportunities. This endowment is determined by many things including physical laws (which constrain how forms of energy and matter may be transformed), accidents of nature (which determine the presence of natural resources), and the outcomes of past decisions made both by others and by the individual himself or herself. A value that holds true given particular constraints is a ''marginal'' value. A change that would b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economics
Economics () is the social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analyzes what's viewed as basic elements in the economy, including individual agents and markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyzes the economy as a system where production, consumption, saving, and investment interact, and factors affecting it: employment of the resources of labour, capital, and land, currency inflation, economic growth, and public policies that have impact on these elements. Other broad distinctions within economics include those between positive economics, describing "what is", and normative economics, advocating "what ought to be"; between economic theory and applied economics; between rational a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opportunity Cost
In microeconomic theory, the opportunity cost of a particular activity is the value or benefit given up by engaging in that activity, relative to engaging in an alternative activity. More effective it means if you chose one activity (for example, an investment) you are giving up the opportunity to do a different option. The optimal activity is the one that, net of its opportunity cost, provides the greater return compared to any other activities, net of their opportunity costs. For example, if you buy a car and use it exclusively to transport yourself, you cannot rent it out, whereas if you rent it out you cannot use it to transport yourself. If your cost of transporting yourself without the car is more than what you get for renting out the car, the optimal choice is to use the car yourself. In basic equation form, opportunity cost can be defined as: "Opportunity Cost = (returns on best Forgone Option) - (returns on Chosen Option)." The opportunity cost of mowing one’s own l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marginalism
Marginalism is a theory of economics that attempts to explain the discrepancy in the value of goods and services by reference to their secondary, or marginal, utility. It states that the reason why the price of diamonds is higher than that of water, for example, owes to the greater additional satisfaction of the diamonds over the water. Thus, while the water has greater total utility, the diamond has greater marginal utility. Although the central concept of marginalism is that of marginal utility, marginalists, following the lead of Alfred Marshall, drew upon the idea of marginal physical productivity in explanation of cost. The neoclassical tradition that emerged from British marginalism abandoned the concept of utility and gave marginal rates of substitution a more fundamental role in analysis. Marginalism is an integral part of mainstream economic theory. Important marginal concepts Marginality For issues of marginality, constraints are conceptualized as a ''border'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marginal Efficiency Of Capital
Marginal may refer to: * ''Marginal'' (album), the third album of the Belgian rock band Dead Man Ray, released in 2001 * ''Marginal'' (manga) * '' El Marginal'', Argentine TV series * Marginal seat or marginal constituency or marginal, in politics See also Economics * Marginalism * Marginal analysis * Marginal concepts *Marginal cost * Marginal demand * Marginal product *Marginal product of labor *Marginal propensity to consume *Marginal rate of substitution * Marginal use *Marginal utility * Marginal rate Other * Margin (other) * Marginalization * Marginal intra-industry trade, where the change in a country's exports are essentially of the same products as its change in imports * Marginal land, land that is of little value because of its unsuitability for growing crops and other uses * Marginal model, in hierarchical linear modeling * Marginal observables, in physics; see Renormalization group * Marginal person, in sociology; see Marginalization * Marginal plant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marginal Tax Rate
In a tax system, the tax rate is the ratio (usually expressed as a percentage) at which a business or person is taxed. There are several methods used to present a tax rate: statutory, average, marginal, and effective. These rates can also be presented using different definitions applied to a tax base: inclusive and exclusive. Statutory A statutory tax rate is the legally imposed rate. An income tax could have multiple statutory rates for different income levels, where a sales tax may have a flat statutory rate. The statutory tax rate is expressed as a percentage and will always be higher than the effective tax rate. Average An average tax rate is the ratio of the total amount of taxes paid to the total tax base (taxable income or spending), expressed as a percentage. * Let t be the total tax liability. * Let i be the total tax base. ::= \frac. In a proportional tax, the tax rate is fixed and the average tax rate equals this tax rate. In case of tax brackets, commonly us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
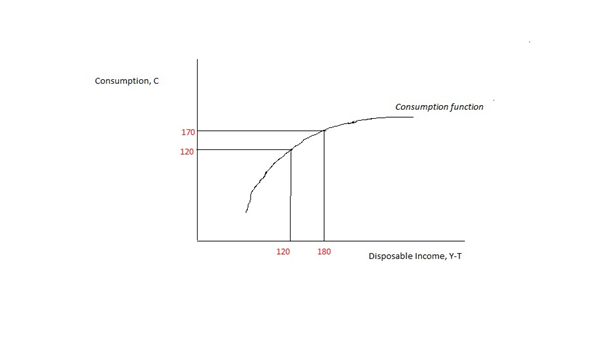
Marginal Propensity To Consume
In economics, the marginal propensity to consume (MPC) is a metric that quantifies induced consumption, the concept that the increase in personal consumer spending ( consumption) occurs with an increase in disposable income (income after taxes and transfers). The proportion of disposable income which individuals spend on consumption is known as propensity to consume. MPC is the proportion of additional income that an individual consumes. For example, if a household earns one extra dollar of disposable income, and the marginal propensity to consume is 0.65, then of that dollar, the household will spend 65 cents and save 35 cents. Obviously, the household cannot spend ''more'' than the extra dollar (without borrowing or using savings). If the extra money accessed by the individual gives more economic confidence, then the MPC of the individual may well exceed 1, as they may borrow or utilise savings. The MPC is higher in the case of poorer people than in rich. According to John Mayn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marginal Propensity To Save
The marginal propensity to save (MPS) is the fraction of an increase in income that is not spent and instead used for saving. It is the slope of the line plotting saving against income. For example, if a household earns one extra dollar, and the marginal propensity to save is 0.35, then of that dollar, the household will spend 65 cents and save 35 cents. Likewise, it is the fractional decrease in saving that results from a decrease in income. The MPS plays a central role in Keynesian economics as it quantifies the saving-income relation, which is the flip side of the consumption-income relation, and according to Keynes it reflects the fundamental psychological law. The marginal propensity to save is also a key variable in determining the value of the multiplier. Calculation MPS can be calculated as the change in savings divided by the change in income. :MPS=\frac Or mathematically, the marginal propensity to save (MPS) function is expressed as the derivative of the savings (S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marginal Revenue Product
Marginal may refer to: * ''Marginal'' (album), the third album of the Belgian rock band Dead Man Ray, released in 2001 * ''Marginal'' (manga) * '' El Marginal'', Argentine TV series * Marginal seat or marginal constituency or marginal, in politics See also Economics * Marginalism * Marginal analysis *Marginal concepts *Marginal cost * Marginal demand *Marginal product *Marginal product of labor *Marginal propensity to consume *Marginal rate of substitution * Marginal use *Marginal utility *Marginal rate Other * Margin (other) * Marginalization * Marginal intra-industry trade, where the change in a country's exports are essentially of the same products as its change in imports * Marginal land, land that is of little value because of its unsuitability for growing crops and other uses * Marginal model, in hierarchical linear modeling * Marginal observables, in physics; see Renormalization group * Marginal person, in sociology; see Marginalization * Marginal plant, see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marginal Rate Of Transformation
Marginal may refer to: * ''Marginal'' (album), the third album of the Belgian rock band Dead Man Ray, released in 2001 * ''Marginal'' (manga) * '' El Marginal'', Argentine TV series * Marginal seat or marginal constituency or marginal, in politics See also Economics * Marginalism * Marginal analysis * Marginal concepts *Marginal cost * Marginal demand * Marginal product * Marginal product of labor *Marginal propensity to consume *Marginal rate of substitution * Marginal use *Marginal utility * Marginal rate Other * Margin (other) * Marginalization * Marginal intra-industry trade, where the change in a country's exports are essentially of the same products as its change in imports * Marginal land, land that is of little value because of its unsuitability for growing crops and other uses * Marginal model, in hierarchical linear modeling * Marginal observables, in physics; see Renormalization group * Marginal person, in sociology; see Marginalization * Marginal plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marginal Product Of Capital
In economics, the marginal product of capital (MPK) is the additional production that a firm experiences when it adds an extra unit of capital. It is a feature of the production function, alongside the labour input. Definition The marginal product of capital (MPK) is the additional output resulting, ceteris paribus ("all things being equal"), from the use of an additional unit of physical capital, such as machines or buildings used by businesses. The marginal product of capital (MPK) is the amount of extra output the firm gets from an extra unit of capital, holding the amount of labor constant: : MP_K = F(K + 1, L) - F(K, L) Thus, the marginal product of capital is the difference between the amount of output produced with K + 1 units of capital and that produced with only K units of capital.N. Gregory Mankiw. (2010). Macroeconomics. United States: Worth Publishers Determining marginal product of capital is essential when a firm is debating on whether or not to invest on the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marginal Product Of Labor
In economics, the marginal product of labor (MPL) is the change in output that results from employing an added unit of labor. It is a feature of the production function, and depends on the amounts of physical capital and labor already in use. Definition The marginal product of a factor of production is generally defined as the change in output resulting from a unit or infinitesimal change in the quantity of that factor used, holding all other input usages in the production process constant. The marginal product of labor is then the change in output (''Y'') per unit change in labor (''L''). In discrete terms the marginal product of labor is: : \frac . In continuous terms, the ''MPL'' is the first derivative of the production function: : \frac .Perloff, J., ''Microeconomics Theory and Applications with Calculus'', Pearson 2008. p. 173. Graphically, the ''MPL'' is the slope of the production function. Examples There is a factory which produces toys. When there are no workers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
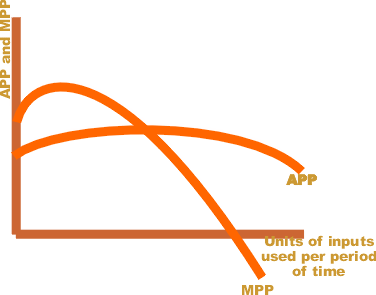
Marginal Product
In economics and in particular neoclassical economics, the marginal product or marginal physical productivity of an input (factor of production) is the change in output resulting from employing one more unit of a particular input (for instance, the change in output when a firm's labor is increased from five to six units), assuming that the quantities of other inputs are kept constant. The marginal product of a given input can be expressed as: :MP = \frac where \Delta X is the change in the firm's use of the input (conventionally a one-unit change) and \Delta Y is the change in quantity of output produced (resulting from the change in the input). Note that the quantity Y of the "product" is typically defined ignoring external costs and benefits. If the output and the input are infinitely divisible, so the marginal "units" are infinitesimal, the marginal product is the mathematical derivative of the production function with respect to that input. Suppose a firm's output ''Y'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |