|
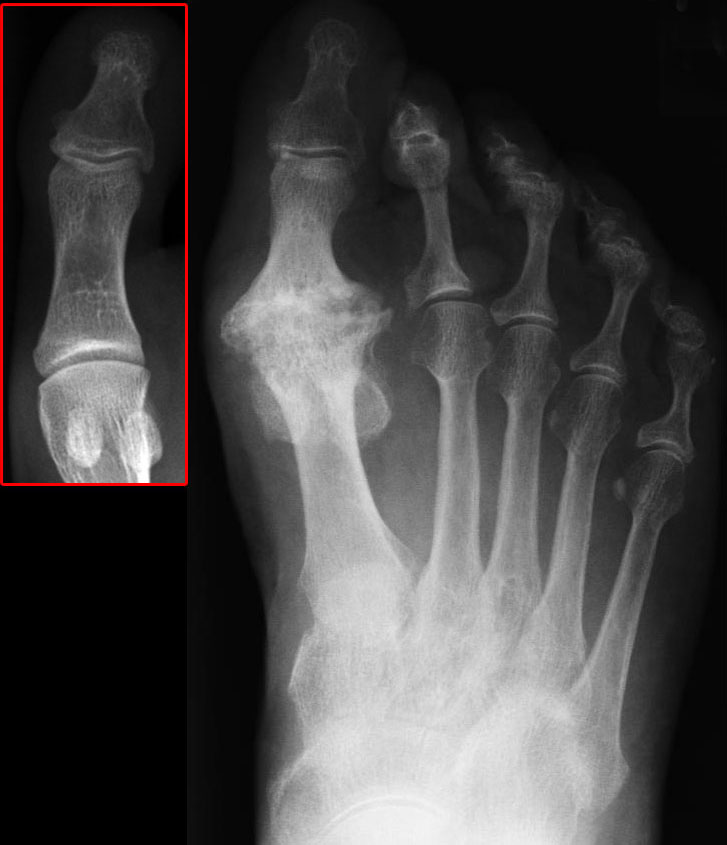
March Fracture
March fracture, is the fracture of the distal third of one of the metatarsals occurring because of recurrent stress. It is more common in soldiers, but also occurs in hikers, organists, and people whose duties entail much standing (such as hospital doctors). March fractures most commonly occur in the second metatarsal, second and third metatarsal bones of the foot.Hamilton Bailey's Demonstrations of Physical Signs in Clinical Surgery It is a common cause of foot pain, especially when people suddenly increase their activities. Signs and symptoms The onset is not dramatic. When the boot or shoes are taken off, there is a cramp-like pain in the affected forefoot, and moderate local edema appears on the dorsal aspect. On moving each toe in turn, that of the involved metatarsal causes pain, and when the bone is palpated from the Dorsum (biology), dorsal surface, a point of tenderness (medicine), tenderness is found directly over the lesion. Radiography at this stage is negative, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metatarsal
The metatarsal bones, or metatarsus, are a group of five long bones in the foot, located between the tarsal bones of the hind- and mid-foot and the phalanges of the toes. Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are numbered from the medial side (the side of the great toe): the first, second, third, fourth, and fifth metatarsal (often depicted with Roman numerals). The metatarsals are analogous to the metacarpal bones of the hand. The lengths of the metatarsal bones in humans are, in descending order, second, third, fourth, fifth, and first. Structure The five metatarsals are dorsal convex long bones consisting of a shaft or body, a base (proximally), and a head (distally).Platzer 2004, p. 220 The body is prismoid in form, tapers gradually from the tarsal to the phalangeal extremity, and is curved longitudinally, so as to be concave below, slightly convex above. The base or posterior extremity is wedge-shaped, articulating proximally with the tarsal bones, and by it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA, or DEXA) is a means of measuring bone mineral density (BMD) using Spectral imaging (radiography), spectral imaging. Two X-ray beams, with different energy levels, are aimed at the patient's bones. When soft tissue absorption is subtracted out, the bone density, bone mineral density (BMD) can be determined from the absorption of each beam by bone. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry is the most widely used and most thoroughly studied bone density measurement technology. The DXA scan is typically used to diagnose and follow osteoporosis, as contrasted to the nuclear bone scan, which is sensitive to certain metabolic diseases of bones in which bones are attempting to heal from infections, fractures, or tumors. It is also sometimes used to assess body composition. Physics Soft tissue and bone have different Attenuation, attenuation coefficients to X-rays. A single X-ray beam passing through the body will be attenuated by both soft tissue and bone, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pes Cavus
Pes cavus, also known as high arch, is a human foot type in which the sole of the foot is distinctly hollow when bearing weight. That is, there is a fixed plantar flexion of the foot. A high arch is the opposite of a flat foot and is somewhat less common. Signs and symptoms Pain and disability As with certain cases of flat feet, high arches may be painful due to metatarsal compression; however, high arches— particularly if they are flexible or properly cared-for—may be an asymptomatic condition. People with pes cavus sometimes—though not always—have difficulty finding shoes that fit and may require support in their shoes. Children with high arches who have difficulty walking may wear specially-designed insoles, which are available in various sizes and can be made to order. Individuals with pes cavus frequently report foot pain, which can lead to a significant limitation in function. The range of complaints reported in the literature include metatarsalgia, pain under th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
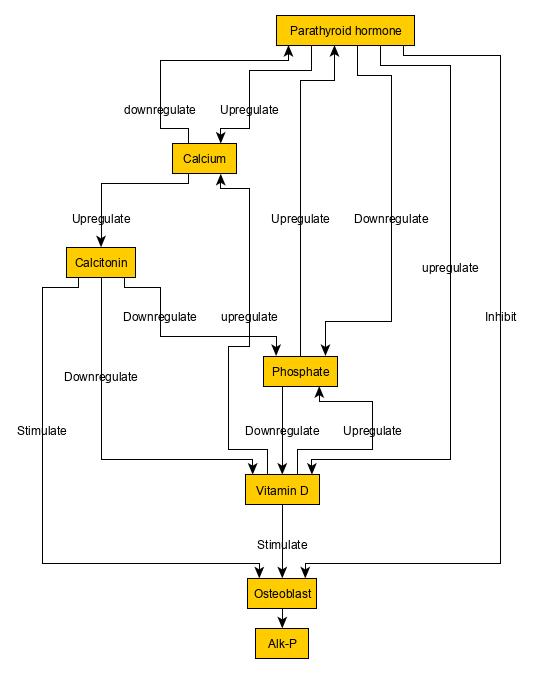
Osteomalacia
Osteomalacia is a disease characterized by the softening of the bones caused by impaired bone metabolism primarily due to inadequate levels of available phosphate, calcium, and vitamin D, or because of resorption of calcium. The impairment of bone metabolism causes inadequate bone mineralization. Osteomalacia in children is known as rickets, and because of this, use of the term "osteomalacia" is often restricted to the milder, adult form of the disease. Signs and symptoms can include diffuse body pains, muscle weakness, and fragility of the bones. In addition to low systemic levels of circulating mineral ions (for example, caused by vitamin D deficiency or renal phosphate wasting) that result in decreased bone and tooth mineralization, accumulation of mineralization-inhibiting proteins and peptides (such as osteopontin and ASARM peptides), and small inhibitory molecules (such as pyrophosphate), can occur in the extracellular matrix of bones and teeth, contributing locally to cause m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to bone fragility, and consequent increase in fracture risk. It is the most common reason for a broken bone among the elderly. Bones that commonly break include the vertebrae in the spine, the bones of the forearm, and the hip. Until a broken bone occurs there are typically no symptoms. Bones may weaken to such a degree that a break may occur with minor stress or spontaneously. After the broken bone heals, the person may have chronic pain and a decreased ability to carry out normal activities. Osteoporosis may be due to lower-than-normal maximum bone mass and greater-than-normal bone loss. Bone loss increases after the menopause due to lower levels of estrogen, and after ' andropause' due to lower levels of testosterone. Osteoporosis may also occur due to a number of diseases or treatments, including alcoholism, anorexia, hyperthyroidism, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lisfranc Joint
The tarsometatarsal joints (Lisfranc joints) are arthrodial joints in the foot. The tarsometatarsal joints involve the first, second and third cuneiform bones, the cuboid bone and the metatarsal bones. The eponym of Lisfranc joint is 18th-19th century surgeon and gynecologist, Jacques Lisfranc de St. Martin. Structure Bones The bones entering into their formation are the first, second, and third cuneiforms, and the cuboid bone, which articulate with the bases of the metatarsal bones. The first metatarsal bone articulates with the first cuneiform; the second is deeply wedged in between the first and third cuneiforms articulating by its base with the second cuneiform; the third articulates with the third cuneiform; the fourth, with the cuboid and third cuneiform; and the fifth, with the cuboid. The bones are connected by dorsal, plantar, and interosseous ligaments. Dorsal ligaments The dorsal ligaments are strong, flat bands. The first metatarsal is joined to the first cuneif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphysis
The diaphysis is the main or midsection (shaft) of a long bone. It is made up of cortical bone and usually contains bone marrow and adipose tissue (fat). It is a middle tubular part composed of compact bone which surrounds a central marrow cavity which contains red or yellow marrow. In diaphysis, primary ossification occurs. Ewing sarcoma tends to occur at the diaphysis.Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Board Review, Cuccurullo Additional images Illu long bone.jpg File:EpiMetaDiaphyse.jpg, Long bone See also *Epiphysis *Metaphysis The metaphysis is the neck portion of a long bone between the epiphysis and the diaphysis. It contains the growth plate, the part of the bone that grows during childhood, and as it grows it ossifies near the diaphysis and the epiphyses. The metap ... References Skeletal system Long bones {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stress Fractures
A stress fracture is a fatigue-induced bone fracture caused by repeated stress over time. Instead of resulting from a single severe impact, stress fractures are the result of accumulated injury from repeated submaximal loading, such as running or jumping. Because of this mechanism, stress fractures are common overuse injuries in athletes. Stress fractures can be described as small cracks in the bone, or hairline fractures. Stress fractures of the foot are sometimes called "march fractures" because of the injury's prevalence among heavily marching soldiers. Stress fractures most frequently occur in weight-bearing bones of the lower extremities, such as the tibia and fibula (bones of the lower leg), metatarsal and navicular bones (bones of the foot). Less common are stress fractures to the femur, pelvis, and sacrum. Treatment usually consists of rest followed by a gradual return to exercise over a period of months. Signs and symptoms Stress fractures are typically discovered after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plantar Fascia
The plantar fascia is the thick connective tissue (aponeurosis) which supports the arch on the bottom (plantar side) of the foot. It runs from the tuberosity of the calcaneus (heel bone) forward to the heads of the metatarsal bones (the bone between each toe and the bones of the mid-foot). Structure The plantar fascia is a broad structure that spans between the medial calcaneal tubercle and the proximal phalanges of the toes. Recent studies suggest that the plantar fascia is actually an aponeurosis rather than true fascia. The Dorland’s Medical Dictionary defines an aponeurosis as: (i) a white, flattened or ribbon-like tendinous expansion, serving mainly to connect a muscle with the parts that it moves, (ii) a term formerly applied to certain fasciae. Further, it defines the plantar aponeurosis as bands of fibrous connective tissue radiating toward the bases of the toes from the medial process of the tuber calcanei (posterior half of the calcaneus). The plantar fascia is m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
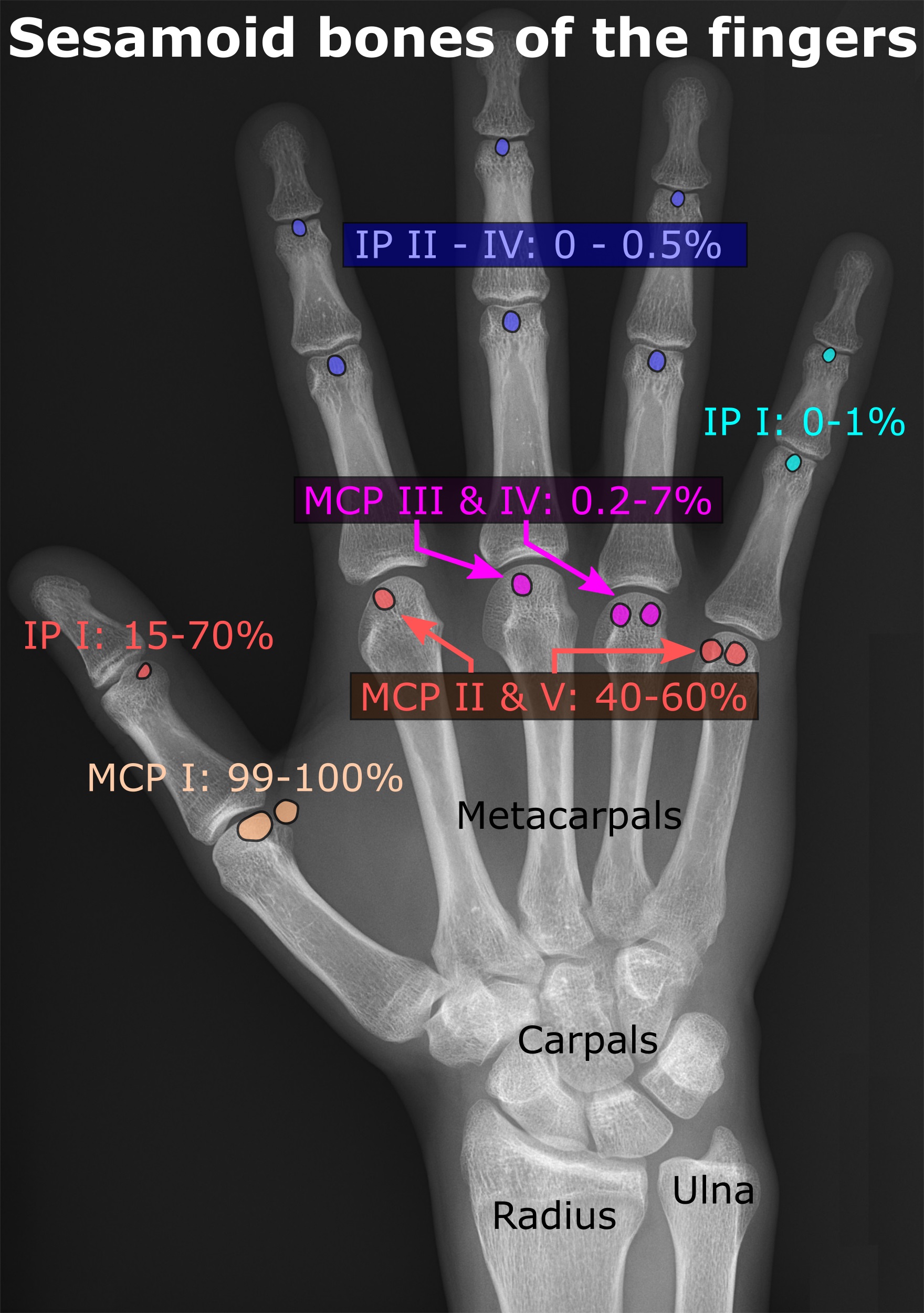
Sesamoid
In anatomy, a sesamoid bone () is a bone embedded within a tendon or a muscle. Its name is derived from the Arabic word for 'sesame seed', indicating the small size of most sesamoids. Often, these bones form in response to strain, or can be present as a normal variant. The patella is the largest sesamoid bone in the body. Sesamoids act like pulleys, providing a smooth surface for tendons to slide over, increasing the tendon's ability to transmit muscular forces. Structure Sesamoid bones can be found on joints throughout the body, including: * In the knee—the patella (within the quadriceps tendon). This is the largest sesamoid bone. * In the hand—two sesamoid bones are commonly found in the distal portions of the first metacarpal bone (within the tendons of adductor pollicis and flexor pollicis brevis). There is also commonly a sesamoid bone in distal portions of the second metacarpal bone. * In the wrist—The pisiform of the wrist is a sesamoid bone (within the tendon o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jones Fracture
A Jones fracture is a Fracture (bone), broken bone in a specific part of the fifth metatarsal of the foot between the epiphysis, base and diaphysis, middle part that is known for its high rate of delayed healing or nonunion. It results in pain near the midportion of the foot on the outside. There may also be bruising and difficulty walking. Onset is generally sudden. The fracture typically occurs when the plantar flexion, toes are pointed and the foot adduction, bends inwards. This movement may occur when changing direction while the heel is off the ground such in dancing, tennis, or basketball. Diagnosis is generally suspected based on symptoms and confirmed with radiography, X-rays. Initial treatment is typically in a orthopedic cast, cast, without any walking on it, for at least six weeks. If, after this period of time, healing has not occurred, a further six weeks of casting may be recommended. Due to poor blood supply in this area, the break sometimes does not heal and sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hallux Rigidus
Hallux rigidus or stiff big toe is Osteoarthritis, degenerative arthritis and stiffness due to Osteophyte, bone spurs that affects the metatarsophalangeal joints (MTP) at the base of the hallux (big toe). Hallux flexus was initially described by Davies-Colley in 1887 as a plantar flexed posture of phalanx relative to the metatarsal head. About the same time, Cotterill first used the term ''hallux rigidus''. Signs and symptoms * Pain and stiffness in the joint at the base of the big toe during use (walking, standing, bending, etc.) * Difficulty with certain activities (running, squatting) * Swelling and inflammation around the joint Although the condition is degenerative, it can occur in patients who are relatively young, particularly active sports people who have at some time suffered Injury, trauma to the joint (turf toe). A notable example is NBA star Shaquille O'Neal who returned to basketball after surgery. Causes This condition, which occurs in adolescents and adults, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |