|
Mycophenolic Acid
Mycophenolic acid (MPA) is an immunosuppressant medication used to prevent rejection following organ transplantation and to treat autoimmune conditions such as Crohn's disease and lupus. Specifically it is used following kidney, heart, and liver transplantation. It can be given by mouth or by injection into a vein. It comes as mycophenolate sodium and mycophenolate mofetil. Common side effects include nausea, infections, and diarrhea. Other serious side effects include an increased risk of cancer, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, anemia, and gastrointestinal bleeding. Use during pregnancy may harm the baby. It works by blocking inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH), which is needed by lymphocytes to make guanosine. Mycophenolic acid was initially discovered by Italian Bartolomeo Gosio in 1893. It was rediscovered in 1945 and 1968. It was approved for medical use in the United States in 1995 following the discovery of its immunosuppressive properties in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
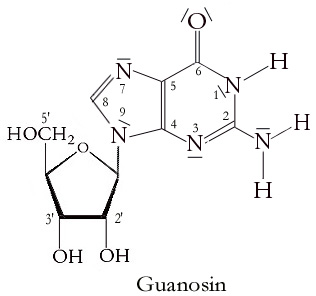
Guanosine
Guanosine (symbol G or Guo) is a purine nucleoside comprising guanine attached to a ribose (ribofuranose) ring via a β-N9-glycosidic bond. Guanosine can be phosphorylated to become guanosine monophosphate (GMP), cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), guanosine diphosphate (GDP), and guanosine triphosphate (GTP). These forms play important roles in various biochemical processes such as synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins, photosynthesis, muscle contraction, and intracellular signal transduction (cGMP). When guanine is attached by its N9 nitrogen to the C1 carbon of a deoxyribose ring it is known as deoxyguanosine. Physical and chemical properties Guanosine is a white, crystalline powder with no odor and mild saline taste. It is very soluble in acetic acid, slightly soluble in water, insoluble in ethanol, diethyl ether, benzene and chloroform. Functions Guanosine is required for an RNA splicing reaction in mRNA, when a "self-splicing" intron removes itself from the mRNA messag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lupus Nephritis
Lupus nephritis is an inflammation of the kidneys caused by systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), an autoimmune disease. It is a type of glomerulonephritis in which the glomeruli become inflamed. Since it is a result of SLE, this type of glomerulonephritis is said to be ''secondary'', and has a different pattern and outcome from conditions with a ''primary'' cause originating in the kidney. The diagnosis of lupus nephritis depends on blood tests, urinalysis, X-rays, ultrasound scans of the kidneys, and a kidney biopsy. On urinalysis, a nephritic picture is found and red blood cell casts, red blood cells and proteinuria is found. Classification The World Health Organization has divided lupus nephritis into five stages based on the biopsy. This classification was defined in 1982 and revised in 1995. Class IV disease ( Diffuse proliferative nephritis) is both the most severe, and the most common subtype. Class VI (advanced sclerosing lupus nephritis) is a final class which is included ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retroperitoneal Fibrosis
Retroperitoneal fibrosis or Ormond's disease is a disease featuring the proliferation of fibrous tissue in the retroperitoneum, the compartment of the body containing the kidneys, aorta, renal tract, and various other structures. It may present with lower back pain, kidney failure, hypertension, deep vein thrombosis, and other obstructive symptoms. It is named after John Kelso Ormond, who rediscovered the condition in 1948. Causes The association of idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis with various immune-related conditions and response to immunosuppression led to a search for an autoimmune cause of idiopathic RPF. Many of these previously idiopathic cases can now be attributed to IgG4-related disease, an autoimmune disorder proposed in 2003. Otherwise, one-third of cases are secondary to malignancy, medication (methysergide, hydralazine, beta blockers), prior radiotherapy, or certain infections. Other associations include: * connective tissue disease * Riedel's thyroiditis * sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by raised areas of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small, localized patches to complete body coverage. Injury to the skin can trigger psoriatic skin changes at that spot, which is known as the Koebner phenomenon. The five main types of psoriasis are plaque, guttate, inverse, pustular, and erythrodermic. Plaque psoriasis, also known as psoriasis vulgaris, makes up about 90% of cases. It typically presents as red patches with white scales on top. Areas of the body most commonly affected are the back of the forearms, shins, navel area, and scalp. Guttate psoriasis has drop-shaped lesions. Pustular psoriasis presents as small, noninfectious, pus-filled blisters. Inverse psoriasis forms red patches in skin folds. Erythrodermic psoriasis occurs when the rash becomes very widespread, and can develop from any of the other types. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasculitides
Vasculitis is a group of disorders that destroy blood vessels by inflammation. Both arteries and veins are affected. Lymphangitis (inflammation of lymphatic vessels) is sometimes considered a type of vasculitis. Vasculitis is primarily caused by leukocyte migration and resultant damage. Although both occur in vasculitis, inflammation of veins (phlebitis) or arteries (arteritis) on their own are separate entities. Signs and symptoms Possible signs and symptoms include: * General symptoms: Fever, unintentional weight loss * Skin: Palpable purpura, livedo reticularis * Muscles and joints: Muscle pain or inflammation, joint pain or joint swelling * Nervous system: Mononeuritis multiplex, headache, stroke, tinnitus, reduced visual acuity, acute visual loss * Heart and arteries: Heart attack, high blood pressure, gangrene * Respiratory tract: Nosebleeds, bloody cough, lung infiltrates * GI tract: Abdominal pain, bloody stool, perforations (hole in the GI tract) * Kidneys: Inflammat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pemphigus Vulgaris
Pemphigus vulgaris is a rare chronic blistering skin disease and the most common form of pemphigus. Pemphigus was derived from the Greek word ''pemphix'', meaning blister. It is classified as a type II hypersensitivity reaction in which antibodies are formed against desmosomes, components of the skin that function to keep certain layers of skin bound to each other. As desmosomes are attacked, the layers of skin separate and the clinical picture resembles a blister. These blisters are due to acantholysis, or breaking apart of intercellular connections through an autoantibody-mediated response. Over time the condition inevitably progresses without treatment: lesions increase in size and distribution throughout the body, behaving physiologically like a severe burn. Before the advent of modern treatments, mortality for the disease was close to 90%. Today, the mortality rate with treatment is between 5-15% due to the introduction of corticosteroids as primary treatment. Nevertheless, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Behçet's Disease
Behçet's disease (BD) is a type of inflammatory disorder which affects multiple parts of the body. The most common symptoms include painful sores on the mucous membranes of the mouth and other parts of the body, inflammation of parts of the eye, and arthritis. The sores can last from a few days, up to a week or more. Less commonly there may be inflammation of the brain or spinal cord, blood clots, aneurysms, or blindness. Often, the symptoms come and go. The cause is unknown. It is believed to be partly genetic. Behçet's is not contagious. Diagnosis is based on at least three episodes of mouth sores in a year together with at least two of the following: genital sores, eye inflammation, skin sores, a positive skin prick test. There is no cure. Treatments may include immunosuppressive medication such as corticosteroids and lifestyle changes. Lidocaine mouthwash may help with the pain. Colchicine may decrease the frequency of attacks. While rare in the United States an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoimmune Diseases
An autoimmune disease is a condition arising from an abnormal immune response to a functioning body part. At least 80 types of autoimmune diseases have been identified, with some evidence suggesting that there may be more than 100 types. Nearly any body part can be involved. Common symptoms can be diverse and transient, ranging from mild to severe, and generally include low grade fever and feeling tired. The cause is unknown. Some autoimmune diseases such as lupus run in families, and certain cases may be triggered by infections or other environmental factors. Some common diseases that are generally considered autoimmune include celiac disease, diabetes mellitus type 1, graves' disease, inflammatory bowel disease, multiple sclerosis, alopecia areata, addison’s disease, pernicious anemia, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and systemic lupus erythematosus. The diagnosis can be difficult to determine. Treatment depends on the type and severity of the condition. Nonsteroidal ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lung Transplantation
Lung transplantation, or pulmonary transplantation, is a surgical procedure in which one or both lungs are replaced by lungs from a donor. Donor lungs can be retrieved from a living or deceased donor. A living donor can only donate one lung lobe. With some lung diseases, a recipient may only need to receive a single lung. With other lung diseases such as cystic fibrosis, it is imperative that a recipient receive two lungs. While lung transplants carry certain associated risks, they can also extend life expectancy and enhance the quality of life for those with end stage pulmonary disease. Qualifying conditions Lung transplantation is the therapeutic measure of last resort for patients with end-stage lung disease who have exhausted all other available treatments without improvement. A variety of conditions may make such surgery necessary. As of 2005, the most common reasons for lung transplantation in the United States were: * 27% chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Transplantation
A heart transplant, or a cardiac transplant, is a surgical transplant procedure performed on patients with end-stage heart failure or severe coronary artery disease when other medical or surgical treatments have failed. , the most common procedure is to take a functioning heart, with or without both lungs, from a recently deceased organ donor (brain death is the standard) and implant it into the patient. The patient's own heart is either removed and replaced with the donor heart ( orthotopic procedure) or, much less commonly, the recipient's diseased heart is left in place to support the donor heart (heterotopic, or "piggyback", transplant procedure). Approximately 3,500 heart transplants are performed each year worldwide, more than half of which are in the US. Post-operative survival periods average 15 years. Heart transplantation is not considered to be a cure for heart disease; rather it is a life-saving treatment intended to improve the quality and duration of life for a reci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney Transplantation
Kidney transplant or renal transplant is the organ transplant of a kidney into a patient with end-stage kidney disease (ESRD). Kidney transplant is typically classified as deceased-donor (formerly known as cadaveric) or living-donor transplantation depending on the source of the donor organ. Living-donor kidney transplants are further characterized as genetically related (living-related) or non-related (living-unrelated) transplants, depending on whether a biological relationship exists between the donor and recipient. Before receiving a kidney transplant, a person with ESRD must undergo a thorough medical evaluation to make sure that they are healthy enough to undergo transplant surgery. If they are deemed a good candidate, they can be placed on a waiting list to receive a kidney from a deceased donor. Once they are placed on the waiting list, they can receive a new kidney very quickly, or they may have to wait many years; in the United States, the average waiting time is three t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |