|
Muzzle Rise
Muzzle rise, muzzle flip or muzzle climb refers to the tendency of a firearm's or airgun's muzzle (front end of the barrel) to rise up after firing. It more specifically refers to the seemingly unpredictable "jump" of the firearm's muzzle, caused by combined recoil from multiple shots being fired in quick succession. It has an adverse effect on maintaining accuracy with using automatic weapons or rapid-firing semi-automatic firearms, as a moving muzzle can throw off the shooter's aim, causing subsequent shots to miss the intended target. Reason The primary reason for muzzle rise is that for nearly all guns, the bore axis (longitudinal centerline of the barrel) is above the gun's center of mass, while the contact points between the shooter and the gun (e.g. grips and stock) are often all below the center of mass. When the gun is fired, the bullet motion and the escaping propellant gases exert a reactional recoil directly backwards along the bore axis, while the countering f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rate Of Fire
Rate of fire is the frequency at which a specific weapon can fire or launch its projectiles. This can be influenced by several factors, including operator training level, mechanical limitations, ammunition availability, and weapon condition. In modern weaponry, it is usually measured in rounds per minute (RPM or round/min) or rounds per second (RPS or round/s). There are three different measurements for the rate of fire: cyclic, sustained, and rapid. Cyclic is the maximum rate of fire given only mechanical function, not taking into account degradation of function due to heat, wear, or ammunition constraints. Sustained is the maximum efficient rate of fire given the time taken to load the weapon and keep it cool enough to operate. Finally, rapid is the maximum reasonable rate of fire in an emergency when the rate of fire need not be upheld for long periods. Overview For manually operated weapons such as bolt-action rifles or artillery pieces, the rate of fire is governed primarily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
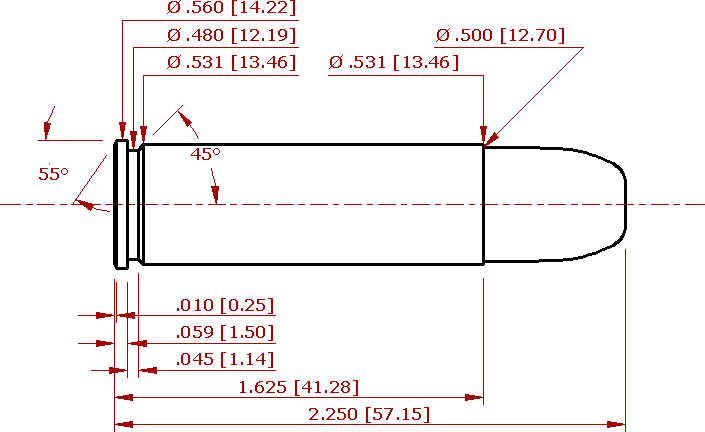
500 S&W Magnum
The .500 S&W Magnum or 12.7×41mmSR is a .50 caliber semi-rimmed revolver cartridge developed by Cor-Bon in partnership with the Smith & Wesson "X-Gun" engineering team for use in the Smith & Wesson Model 500 X-frame revolver and introduced in February 2003 at the SHOT Show. From its inception, it was intended to be the most powerful handgun cartridge to date, with the capacity to harvest all North American game species. While more powerful handgun cartridges, such as the .500 Bushwhacker, have emerged since, they are only available in custom firearms at this time, and the .500 S&W remains the most powerful production handgun cartridge. Cartridge history Smith & Wesson had been at the forefront of the development of powerful handgun cartridges such as the .357 S&W Magnum and the .44 Remington Magnum. However, since 1960, the company's .44 Magnum, which it had developed in partnership with Remington, was eclipsed by the .454 Casull. Since then, several other more powerful c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M1911 Pistol
The M1911 (Colt 1911 or Colt Government) is a single-action, recoil-operated, semi-automatic pistol chambered for the .45 ACP cartridge. The pistol's formal U.S. military designation as of 1940 was ''Automatic Pistol, Caliber .45, M1911'' for the original model adopted in March 1911, and ''Automatic Pistol, Caliber .45, M1911A1'' for the improved M1911A1 model which entered service in 1926. The designation changed to ''Pistol, Caliber .45, Automatic, M1911A1'' in the Vietnam War era. Designed by John Browning, the M1911 is the best-known of his designs to use the short recoil principle in its basic design. The pistol was widely copied, and this operating system rose to become the preeminent type of the 20th century and of nearly all modern centerfire pistols. It is popular with civilian shooters in competitive events such as the International Defensive Pistol Association and International Practical Shooting Confederation. The U.S. military procured around 2.7 million M1911 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudson H9
The Hudson H9 was a semi-automatic pistol made by the now defunct Hudson Mfg. Unveiled at the 2017 SHOT Show in Las Vegas, Nevada after three years of development, the H9 brought multiple patented and patent pending features together in a new pistol design. Proven design elements included: an M1911 straight-pull trigger, a short-recoil operated system, and the heritage S&W 5900 series magazine tube. The new design elements were: forward barrel cams in front of the trigger-guard, the sear design marrying the straight pull trigger with a striker-fired system while remaining drop safe, the placement of the recoil spring, and the pairing of an insert chassis with a steel frame. These elements lent to its most noticeable difference—its appearance. The striker-fired H9 was made first chambered in 9×19mm Parabellum at a weight of with a capacity of 15 rounds. The weight places the H9 within the same category as traditional aluminum frame handguns like the Beretta M9, Sig P226, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KRISS Vector
The KRISS Vector is a series of weapons based upon the parent submachine gun design developed by the American company KRISS USA, formerly Transformational Defense Industries (TDI). They use an unconventional delayed blowback system combined with in-line design to reduce perceived recoil and muzzle climb. History In the spring of 2007, TDI announced their development of a new submachine gun. It was an experimental weapon under advanced stages of development at that time. The name ''Kriss'' comes from a Southeast Asian dagger with a flame-shaped blade. The second generation prototype of the Vector, called the ''K10'', was announced at 2011 SHOT Show. It is a slightly more compact version of the Vector that is based on the same Super V system. The main difference is a redesign of the lower receiver intended for easy caliber interchangeability; utilizing just a single takedown pin, users can change between 9×19mm, .40 S&W and .45 ACP by mounting different lower receivers. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bore Axis
The bore axis of a firearm is the longitudinal axis through the geometric center of the gun barrel. In a rifled barrel, the projectile (bullet/ball, pellet or slug) will spin around the bore axis as it goes through the barrel. Boresighting is a process of placing one's line of sight down along the bore axis. Bore-to-sight distance The distance between the bore axis and the sight axis (the optical axis of a sighting device), also known as the ''sight height'', is an important factor to consider due to parallax principles. It is normally desirable to keep the sights of a firearm as close to the bore as possible, since a firearm with a large bore-to-sight distance will require more compensatory sight adjustment when shifting between shooting at different targets at close ranges (due to foreshortening). On the other hand, a firearm with a short bore-to-sight distance will need less sight adjustment when changing between targets at close ranges. At longer ranges the bore-to-sigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jatimatic
The Jatimatic is a Finnish 9×19mm Parabellum submachine gun developed in the late 1970s and early 1980s by Jali Timari. The submachine gun made its debut in 1983. The Jatimatic was manufactured in very limited numbers (approx. 400) initially by Tampereen Asepaja Oy of Tampere and later—Oy Golden Gun Ltd (as the GG-95 PDW, re-introduced unsuccessfully in 1995). The firearm was designed primarily for police, security forces and armored vehicle crews. It was never adopted into service by the Finnish Defence Forces, although the later GG-95 PDW version was tested by the FDF in the 1990s. Design details Operating mechanism The Jatimatic is an automatic, open bolt, blowback-operated firearm. A unique feature of this design is the angle of the bolt guide rails in relation to the bore axis. When fired, the telescopic bolt, which encloses the barrel for most of its length, recoils up an inclined plane at a 7° angle to the barrel, giving an element of braking to the bolt, and also re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moment Of Inertia
The moment of inertia, otherwise known as the mass moment of inertia, angular mass, second moment of mass, or most accurately, rotational inertia, of a rigid body is a quantity that determines the torque needed for a desired angular acceleration about a rotational axis, akin to how mass determines the force needed for a desired acceleration. It depends on the body's mass distribution and the axis chosen, with larger moments requiring more torque to change the body's rate of rotation. It is an extensive (additive) property: for a point mass the moment of inertia is simply the mass times the square of the perpendicular distance to the axis of rotation. The moment of inertia of a rigid composite system is the sum of the moments of inertia of its component subsystems (all taken about the same axis). Its simplest definition is the second moment of mass with respect to distance from an axis. For bodies constrained to rotate in a plane, only their moment of inertia about an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ported Barrel
A muzzle brake or recoil compensator is a device connected to, or a feature integral to the construction of, the muzzle or barrel of a firearm or cannon that is intended to redirect a portion of propellant gases to counter recoil and unwanted muzzle rise. Barrels with an integral muzzle brake are often said to be ported. The concept of a muzzle brake was first introduced for artillery. It was a common feature on many anti-tank guns, especially those mounted on tanks, in order to reduce the area needed to take up the strokes of recoil and kickback. They have been used in various forms for rifles and pistols to help control recoil and the rising of the barrel that normally occurs after firing. They are used on pistols for practical pistol competitions, and are usually called compensators in this context.STI article on Limcat Underg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silencer (firearms)
A silencer, also known as a sound suppressor, suppressor, or sound moderator, is a muzzle device that reduces the acoustic intensity of the muzzle report (sound of a gunshot) and muzzle rise when a gun (firearm or air gun) is discharged, by modulating the speed and pressure of the propellant gas from the muzzle and hence suppressing the muzzle blast. Like other muzzle devices, a silencer can be a detachable accessory mounted to the muzzle, or an integral part of the barrel. A typical silencer is a metallic (usually stainless steel or titanium) cylinder containing internal sound baffles, with a hollow bore to allow the projectile (bullet) to exit normally. During firing, the bullet flies through the bore with little hindrance, but most of the expanding gas ejecta behind it is retained through a longer and convoluted escape path created by the baffles, prolonging the release time. This slows down the gas and dissipates its kinetic energy into a larger surface area, reduci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


