|
Multimoog
The Multimoog is a monophonic analog synthesizer manufactured by Moog Music from 1978 to 1981. Derived from the earlier Micromoog (internally, it consists of a stock Micromoog circuit board with the extra circuitry on a second board), the Multimoog was intended to be a less expensive alternative to the Minimoog. It nevertheless had some advanced features which the Minimoog did not—most notably, it was one of the earliest synthesizers to feature aftertouch capability. Key features include: * 44-note monophonic keyboard with aftertouch * ribbon-type pitch-bend controller * "glide" (portamento) * 2 voltage-controlled oscillators with waveform continuously adjustable from sawtooth, through square, to narrow pulse * oscillator sync * noise source * 24 dB/octave Moog transistor-ladder lowpass voltage-controlled filter * dedicated low-frequency oscillator with triangle, square, and random waveforms * extensive modulation routing options, including sample-and-hold, audio-frequency modu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moog Music
Moog Music Inc. () is an American synthesizer company based in Asheville, North Carolina. It was founded in 1953 as R. A. Moog Co. by Robert Moog and his father and was renamed Moog Music in 1972. Its early instruments included the Moog synthesizer (the first commercial synthesizer), followed by the Minimoog in 1970, two of the most influential electronic instruments of all time. In 1971, following a Recession of 1969–70, recession, Robert Moog sold Moog Music to Norlin Musical Instruments, where he remained employed as a designer until 1977. In 1978, he founded a new company, Big Briar. Moog Music filed for bankruptcy in 1987 and the Moog Music trademark was returned to Robert Moog in 2002, when Big Briar resumed operations under the name Moog Music. Moog Music also manages Moogfest, a pioneering electronic music and music technology festival in Durham, NC. History 1953–1967: R. A. Moog Co. Robert Moog founded R. A. Moog Co. with his father in 1953 at the age of 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Moog Synthesizer Players
This is a list of notable musicians who use Moog synthesizers. A *ABBA – a minimoog and polymoog played by Benny Andersson * Patrick Adams *Walter Afanasieff - Producer *Air *Don Airey *Damon Albarn - Blur *The Anniversary *Apoptygma Berzerk * Arandel *Arjen Lucassen *Army of Freshmen *Alesso B * Tony Banks – Genesis – Used a Polymoog mostly on ''And Then There Were Three'' (1978) information on the book from Armando Gallo – ''I Know What I Like'' (DIY) 1981 *Basilica and National Shrine of Our Lady of Consolation Many Synthesizers are used in the church's keyboard section *Les Baxter (See in 1968, ''Moog Rock'' Album) *Armin Van Buuren *Leroy Bach – Wilco *Zac Baird – Korn, Everlast, Fear and the Nervous System, Jonathan Davis and the SFA, Maimou *Peter Bardens – Camel * Battlecat – Hip hop producer (Snoop Dogg) *Peter Baumann – solo and with (Tangerine Dream) *Beastie Boys *The Beach Boys *The Beatles – one of the first mainstream albums to use a Moog wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micromoog
The Moog model 2090 Micromoog is a monophonic analog synthesizer produced by Moog Music from 1975 to 1979. During 1973 and 1974, Moog attempted to produce a synth system, possibly as a result of seeing Yamaha's massive GX-1. The bass and polyphonic components of the "Constellation" became the Taurus and Polymoog, respectively, and while the Lyra monophonic lead synth never went into production, the smaller MicroMoog emerged, using some of the ideas and technology. The monophonic Micromoog was designed by Moog Engineer Jim Scott in consultation with Tom Rhea, with electronic refinement input from David Luce, Robert Moog, as a scaled-down, cheaper alternative ($650–$800 market price) to the Minimoog. It was designed to tap into a market of musicians who wanted an introduction to synthesis, but who could not afford the $1,500 Minimoog. However, while the basic architecture was a simple VCO/VCF/VCA, inexpensive enhancements made it a more creative synth. Its single voltage-con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimoog
The Minimoog is an analog synthesizer first manufactured by Moog Music between 1970 and 1981. Designed as a more affordable, portable version of the modular Moog synthesizer, it was the first synthesizer sold in retail stores. It was first popular with progressive rock and jazz musicians and found wide use in disco, pop, rock and electronic music. Production of the Minimoog stopped in the early 1980s after the sale of Moog Music. In 2002, founder Robert Moog regained the rights to the Moog brand, bought the company, and released an updated version of the Minimoog, the Minimoog Voyager. In 2016 and in 2022, Moog Music released another new version of the original Minimoog. Development In the 1960s, RA Moog Co manufactured Moog synthesizers, which helped bring electronic sounds to music but remained inaccessible to ordinary people. These modular synthesizers were difficult to use and required users to connect components manually with patch cables to create sounds. They were a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage-controlled Filter
A voltage-controlled filter (VCF) is an electronic filter whose operating characteristics (primarily cutoff frequency) can be set by an input control voltage. Voltage controlled filters are widely used in synthesizers. A music synthesizer VCF allows its cutoff frequency, and sometimes its Q factor (resonance at the cutoff frequency), to be continuously varied. The filter outputs often include a lowpass response, and sometimes highpass, bandpass or notch responses. Some musical VCFs offer a variable ''slope'' which determines the rate of attenuation outside the bandpass, often at 6 dB/octave, 12 dB/octave, 18 dB/octave or 24 dB/octave (one-, two-, three- and four-pole filters, respectively). In modular analog synthesizers, VCFs receive signal input from signal sources, including oscillators and noise, or the output of other processors. By varying the cutoff frequency, the filter passes or attenuates partials of the input signal. In some popular electroni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Synthesizers
An analog (or analogue) synthesizer is a synthesizer that uses analog circuits and analog signals to generate sound electronically. The earliest analog synthesizers in the 1920s and 1930s, such as the Trautonium, were built with a variety of vacuum-tube (thermionic valve) and electro-mechanical technologies. After the 1960s, analog synthesizers were built using operational amplifier (op-amp) integrated circuits, and used potentiometers (pots, or variable resistors) to adjust the sound parameters. Analog synthesizers also use low-pass filters and high-pass filters to modify the sound. While 1960s-era analog synthesizers such as the Moog used a number of independent electronic modules connected by patch cables, later analog synthesizers such as the Minimoog integrated them into single units, eliminating patch cords in favour of integrated signal routing systems. History 1900–1920 The earliest mention of a "synthetic harmoniser" using electricity appears to be in 1906, cre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Moog
Robert Arthur Moog ( ; May 23, 1934 – August 21, 2005) was an American engineer and electronic music pioneer. He was the founder of the synthesizer manufacturer Moog Music and the inventor of the first commercial synthesizer, the Moog synthesizer, which debuted in 1964. In 1970, Moog released a more portable model, the Minimoog, described as the most famous and influential synthesizer in history. Among Moog's honors are a Technical Grammy Award, received in 2002, and an induction into the National Inventors Hall of Fame. By 1963, Moog had been designing and selling theremins for several years, while working towards a PhD in engineering physics at Cornell University. He developed his synthesizer in response to demand for more practical and affordable electronic music equipment, guided by suggestions and requests from composers. Moog's principal innovation was the voltage-controlled oscillator, which uses voltage to control pitch. He also introduced fundamental synthesizer conce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moog Synthesizer
The Moog synthesizer is a modular synthesizer developed by the American engineer Robert Moog. Moog debuted it in 1964, and Moog's company R. A. Moog Co. (later known as Moog Music) produced numerous models from 1965 to 1981, and again from 2014. It was the first commercial synthesizer, and is credited with creating the analog synthesizer as it is known today. The Moog synthesizer consists of separate modules which create and shape sounds, which are connected via patch cords. Modules include voltage-controlled oscillators, amplifiers, filters, envelope generators, noise generators, ring modulators, triggers, and mixers. The synthesizer can be played using controllers including keyboards, joysticks, pedals, and ribbon controllers, or controlled with sequencers. Its oscillators can produce waveforms of different timbres, which can be modulated and filtered to shape their sounds (subtractive synthesis). By 1963, Robert Moog had been designing and selling theremins for several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moog Modular Synthesizer
The Moog synthesizer is a modular synthesizer developed by the American engineer Robert Moog. Moog debuted it in 1964, and Moog's company R. A. Moog Co. (later known as Moog Music) produced numerous models from 1965 to 1981, and again from 2014. It was the first commercial synthesizer, and is credited with creating the analog synthesizer as it is known today. The Moog synthesizer consists of separate modules which create and shape sounds, which are connected via patch cords. Modules include voltage-controlled oscillators, amplifiers, filters, envelope generators, noise generators, ring modulators, triggers, and mixers. The synthesizer can be played using controllers including keyboards, joysticks, pedals, and ribbon controllers, or controlled with sequencers. Its oscillators can produce waveforms of different timbres, which can be modulated and filtered to shape their sounds (subtractive synthesis). By 1963, Robert Moog had been designing and selling theremins for several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memorymoog
The Memorymoog is a polyphonic electronic music synthesizer manufactured by Moog Music from 1982 to 1985, the last polyphonic synthesizer to be released by Moog Music before the company declared bankruptcy in 1987. While comparable to other polyphonic synthesizers of the time period, such as the Sequential Circuits Prophet-5 and Oberheim OB-Xa, the Memorymoog distinguished itself with 3 audio oscillators per voice and greater preset storage capacity. Overview While the earlier Polymoog synthesizer (1975) featured unlimited polyphony via divide-down technology, the 6-voice Memorymoog was the first polyphonic Moog to feature dedicated oscillators and filters for each voice. It is often described architecturally as six Minimoogs in one unit. Each of the six voices of the Memorymoog is made up of 3 voltage-controlled oscillators that can be set to any combination of pulse (variable width), saw, and triangle waveforms and freely switched over a 4–octave initial range. Each voice al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Envelope Generator
In sound and music, an envelope describes how a sound changes over time. It may relate to elements such as amplitude (volume), frequencies (with the use of filters) or pitch. For example, a piano key, when struck and held, creates a near-immediate initial sound which gradually decreases in volume to zero. Envelope generators, which allow users to control the different stages of a sound, are common features of synthesizers, samplers, and other electronic musical instruments. The most common form of envelope generator is controlled with four parameters: attack, decay, sustain and release (ADSR). Development The Hammond Novachord in 1938 used an early implementation of an ADSR envelope. A seven-position rotary knob selects preset ADS parameter for all 72 notes; a pedal controls the release. The envelope generator was created by the American engineer Robert Moog in the 1960s. While experimenting with the first Moog synthesizers, composer Herbert Deutsch suggested Moog find a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
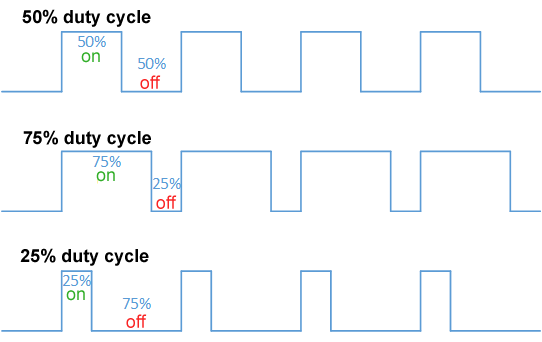
Pulse-width Modulation
Pulse-width modulation (PWM), or pulse-duration modulation (PDM), is a method of reducing the average power delivered by an electrical signal, by effectively chopping it up into discrete parts. The average value of voltage (and current) fed to the load is controlled by turning the switch between supply and load on and off at a fast rate. The longer the switch is on compared to the off periods, the higher the total power supplied to the load. Along with maximum power point tracking (MPPT), it is one of the primary methods of reducing the output of solar panels to that which can be utilized by a battery. PWM is particularly suited for running inertial loads such as motors, which are not as easily affected by this discrete switching, because their inertia causes them to react slowly. The PWM switching frequency has to be high enough not to affect the load, which is to say that the resultant waveform perceived by the load must be as smooth as possible. The rate (or frequency) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

%2C_MIM_PHX.jpg)