|
Moving Object Detection
Moving object detection is a technique used in computer vision and image processing. Multiple consecutive frames from a video are compared by various methods to determine if any moving object is detected. Moving objects detection has been used for wide range of applications like video surveillance, activity recognition, road condition monitoring, airport safety, monitoring of protection along marine border, etc. Definition Moving object detection is to recognize the physical movement of an object in a given place or region. J. S. Kulchandani and K. J. Dangarwala, "Moving object detection: Review of recent research trends," 2015 International Conference on Pervasive Computing (ICPC), Pune, 2015, pp. 1-5. doi: 10.1109/PERVASIVE.2015.7087138. By acting [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Vision
Computer vision tasks include methods for image sensor, acquiring, Image processing, processing, Image analysis, analyzing, and understanding digital images, and extraction of high-dimensional data from the real world in order to produce numerical or symbolic information, e.g. in the form of decisions. "Understanding" in this context signifies the transformation of visual images (the input to the retina) into descriptions of the world that make sense to thought processes and can elicit appropriate action. This image understanding can be seen as the disentangling of symbolic information from image data using models constructed with the aid of geometry, physics, statistics, and learning theory. The scientific discipline of computer vision is concerned with the theory behind artificial systems that extract information from images. Image data can take many forms, such as video sequences, views from multiple cameras, multi-dimensional data from a 3D scanning, 3D scanner, 3D point clouds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activity Recognition
Activity recognition aims to recognize the actions and goals of one or more agents from a series of observations on the agents' actions and the environmental conditions. Since the 1980s, this research field has captured the attention of several computer science communities due to its strength in providing personalized support for many different applications and its connection to many different fields of study such as medicine, human-computer interaction, or sociology. Due to its multifaceted nature, different fields may refer to activity recognition as plan recognition, goal recognition, intent recognition, behavior recognition, location estimation and location-based services. Types Sensor-based, single-user activity recognition Sensor-based activity recognition integrates the emerging area of sensor networks with novel data mining and machine learning techniques to model a wide range of human activities. Mobile devices (e.g. smart phones) provide sufficient sensor data and calc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Segmentation
In digital image processing and computer vision, image segmentation is the process of partitioning a digital image into multiple image segments, also known as image regions or image objects (Set (mathematics), sets of pixels). The goal of segmentation is to simplify and/or change the representation of an image into something that is more meaningful and easier to analyze.Linda Shapiro, Linda G. Shapiro and George C. Stockman (2001): "Computer Vision", pp 279–325, New Jersey, Prentice-Hall, Image segmentation is typically used to locate objects and Boundary tracing, boundaries (lines, curves, etc.) in images. More precisely, image segmentation is the process of assigning a label to every pixel in an image such that pixels with the same label share certain characteristics. The result of image segmentation is a set of segments that collectively cover the entire image, or a set of Contour line, contours extracted from the image (see edge detection). Each of the pixels in a region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Tracking
Video tracking is the process of locating a moving object (or multiple objects) over time using a camera. It has a variety of uses, some of which are: human-computer interaction, security and surveillance, video communication and compression, augmented reality, traffic control, medical imaging and video editing. Video tracking can be a time-consuming process due to the amount of data that is contained in video. Adding further to the complexity is the possible need to use object recognition techniques for tracking, a challenging problem in its own right. Objective The objective of video tracking is to associate target objects in consecutive video frames. The association can be especially difficult when the objects are moving fast relative to the frame rate. Another situation that increases the complexity of the problem is when the tracked object changes orientation over time. For these situations video tracking systems usually employ a motion model which describes how the image ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Background Subtraction
Background may refer to: Performing arts and stagecraft * Background actor * Background artist * Background light * Background music * Background story * Background vocals * ''Background'' (play), a 1950 play by Warren Chetham-Strode Recorded works * ''Background'' (1953 film), a British drama * ''Background'' (1973 film), a documentary * ''Background'' (TV series), a Canadian journalistic television series * ''Background'' (Lifetime album), 1992 * ''Background'' (Bassi Maestro album), 2002 Science and engineering * Background extinction rate * Background independence, a condition in theoretical physics * Background noise * Background radiation, the natural radiation that is always present in a location ** Background (astronomy), small amounts of light coming from otherwise dark parts of the sky ** Cosmic background (other) ** Gravitational wave background ** X-ray background * Background process, software that is running but not being displayed * String ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Flow
Optical flow or optic flow is the pattern of apparent motion of objects, surfaces, and edges in a visual scene caused by the relative motion between an observer and a scene. Optical flow can also be defined as the distribution of apparent velocities of movement of brightness pattern in an image. The concept of optical flow was introduced by the American psychologist James J. Gibson in the 1940s to describe the visual stimulus provided to animals moving through the world. Gibson stressed the importance of optic flow for affordance perception, the ability to discern possibilities for action within the environment. Followers of Gibson and his ecological approach to psychology have further demonstrated the role of the optical flow stimulus for the perception of movement by the observer in the world; perception of the shape, distance and movement of objects in the world; and the control of locomotion. The term optical flow is also used by roboticists, encompassing related techniqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
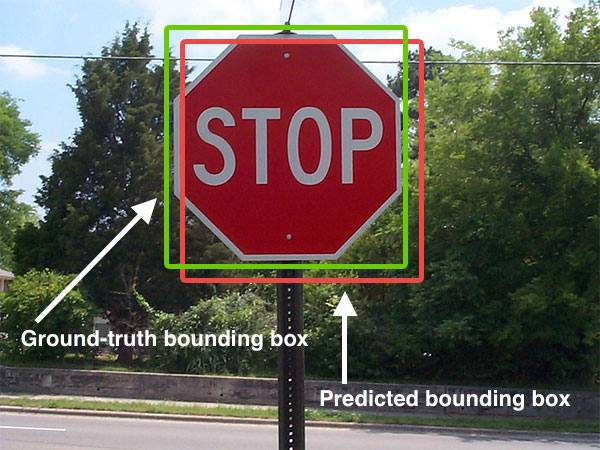
Object Detection
Object detection is a computer technology related to computer vision and image processing that deals with detecting instances of semantic objects of a certain class (such as humans, buildings, or cars) in digital images and videos. Well-researched domains of object detection include face detection and pedestrian detection. Object detection has applications in many areas of computer vision, including image retrieval and video surveillance. Uses It is widely used in computer vision tasks such as image annotation, vehicle counting, activity recognition, face detection, face recognition, video object co-segmentation. It is also used in tracking objects, for example tracking a ball during a football match, tracking movement of a cricket bat, or tracking a person in a video. Often, the test images are sampled from a different data distribution, making the object detection task significantly more difficult. To address the challenges caused by the domain gap between training and test ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
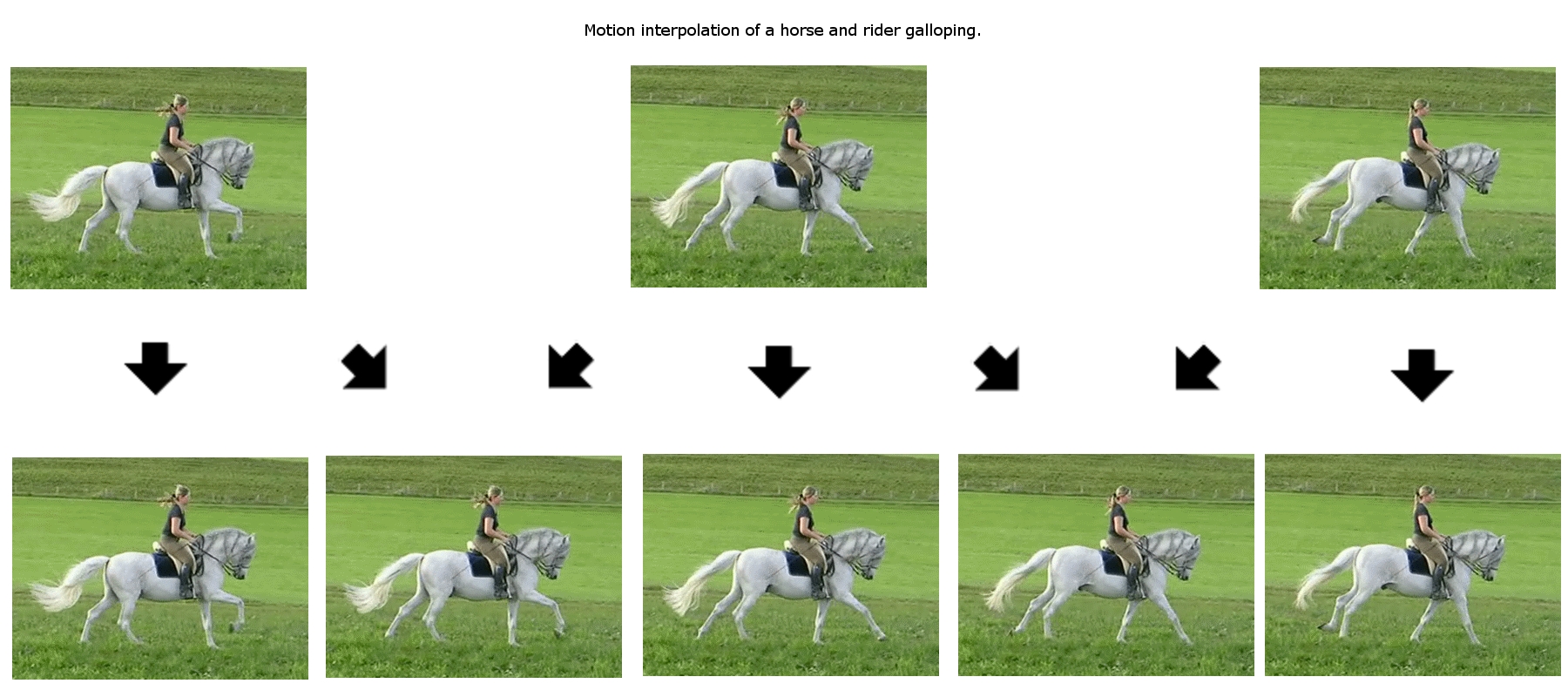
Motion Estimation
In computer vision and image processing, motion estimation is the process of determining ''motion vectors'' that describe the transformation from one 2D image to another; usually from adjacent video frame, frames in a video sequence. It is an well-posed problem, ill-posed problem as the motion happens in three dimensions (3D) but the images are a projection of the 3D scene onto a 2D plane. The motion vectors may relate to the whole image (''global motion estimation'') or specific parts, such as rectangular blocks, arbitrary shaped patches or even per pixel. The motion vectors may be represented by a translational model or many other models that can approximate the motion of a real video camera, such as rotation and translation in all three dimensions and zoom. Related terms More often than not, the term motion estimation and the term ''optical flow'' are used interchangeably. It is also related in concept to ''image registration'' and ''stereo correspondence''. In fact all of thes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Processing
An image or picture is a visual representation. An image can be two-dimensional, such as a drawing, painting, or photograph, or three-dimensional, such as a carving or sculpture. Images may be displayed through other media, including a projection on a surface, activation of electronic signals, or digital displays; they can also be reproduced through mechanical means, such as photography, printmaking, or photocopying. Images can also be animated through digital or physical processes. In the context of signal processing, an image is a distributed amplitude of color(s). In optics, the term ''image'' (or ''optical image'') refers specifically to the reproduction of an object formed by light waves coming from the object. A ''volatile image'' exists or is perceived only for a short period. This may be a reflection of an object by a mirror, a projection of a camera obscura, or a scene displayed on a cathode-ray tube. A ''fixed image'', also called a hard copy, is one that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |