|
Model-driven Architecture
Model-driven architecture (MDA) is a software design approach for the development of software systems. It provides a set of guidelines for the structuring of specifications, which are expressed as models. Model Driven Architecture is a kind of domain engineering, and supports model-driven engineering of software systems. It was launched by the Object Management Group (OMG) in 2001."OMG pursues new strategic direction to build on success of past efforts" Overview Model Driven Architecture® (MDA®) "provides an approach for deriving value from models and architecture in support of the full life cycle of physical, organizational and I.T. systems". A model is a (representation of) an abstraction of a system. MDA® provides value by producing models ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model-driven Engineering
Model-driven engineering (MDE) is a software development methodology that focuses on creating and exploiting domain models, which are conceptual model (computer science), conceptual models of all the topics related to a specific problem. Hence, it highlights and aims at representation (mathematics), abstract representations of the Knowledge representation and reasoning, knowledge and activities that govern a particular domain (software engineering), application domain, rather than the computing (i.e. algorithmic) concepts. MDE is a subfield of a software design approach referred as round-trip engineering. The scope of the MDE is much wider than that of the model-driven architecture, Model-Driven Architecture. Overview The MDE approach is meant to increase productivity by maximizing compatibility between systems (via reuse of standardized models), simplifying the process of design (via models of recurring design patterns in the application domain), and promoting communication betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eclipse Foundation
The Eclipse Foundation AISBL is an independent, Europe-based not-for-profit organization that acts as a steward of the Eclipse open source software development community, with legal jurisdiction in the European Union. It is an organization supported by over 350 members, and represents the world's largest sponsored collection of Open Source projects and developers. The Foundation focuses on key services such as intellectual property (IP) management, ecosystem development, and IT infrastructure. Projects The Eclipse Project was originally created by IBM in November 2001 and was supported by a consortium of software vendors. In 2004, the Eclipse Foundation was founded to lead and develop the Eclipse community. It was created to allow a vendor-neutral, open, and transparent community to be established around Eclipse. The Foundation utilizes a hierarchical project structure. Each project stems from a primary parent project and may have sub-projects. The uppermost projects, which do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATLAS Transformation Language
ATL (ATLAS Transformation Language) is a model transformation language and toolkit developed and maintained by OBEO and AtlanMod. It was initiated by the AtlanMod team (previously called ATLAS Group). In the field of Model-Driven Engineering (MDE), ATL provides ways to produce a set of target models from a set of source models. Released under the terms of the Eclipse Public License, ATL is an M2M (Eclipse) component, inside of the Eclipse Modeling Project (EMP). Overview ATL is a model transformation language (MTL) developed by OBEO and INRIA to answer the QVT Request For Proposal. QVT is an Object Management Group standard for performing model transformations. It can be used to do syntactic or semantic translation. ATL is built on top of a model transformation Virtual Machine. ATL is the ATLAS INRIA & LINA research group answer to the OMG MOF/QVT RFP. It is a model transformation language specified both as a metamodel and as a textual concrete syntax. It is a hybrid of decl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third-generation Programming Language
A third-generation programming language (3GL) is a high-level programming language, high-level computer programming language that tends to be more machine-independent and programmer-friendly than the machine code of the First-generation programming language, first-generation and assembly languages of the Second-generation programming language, second-generation, while having a less specific focus to the Fourth-generation programming language, fourth and Fifth-generation programming language, fifth generations. Examples of common and historical third-generation programming languages are ALGOL, BASIC, C (programming language), C, COBOL, Fortran, Java (programming language), Java, and Pascal (programming language), Pascal. Characteristics 3GLs are much more machine-independent and more programmer-friendly. This includes features like improved support for aggregate data types, and expressing concepts in a way that favors the programmer, not the computer. A third generation language imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Round-trip Engineering
Round-trip engineering (RTE) in the context of model-driven architecture is a functionality of software development tools that synchronizes two or more related software artifacts, such as, source code, models, configuration files, documentation, etc. between each other. The need for round-trip engineering arises when the same information is present in multiple artifacts and when an inconsistency may arise in case some artifacts are updated. For example, some piece of information was added to/changed in only one artifact (source code) and, as a result, it became missing in/inconsistent with the other artifacts (in models). Overview Round-trip engineering is closely related to traditional software engineering disciplines: forward engineering (creating software from specifications), reverse engineering (creating specifications from existing software), and reengineering (understanding existing software and modifying it). Round-trip engineering is often wrongly defined as simply supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forrester Research
Forrester Research, Inc. is a research and advisory firm. Forrester serves clients in North America, Europe, and Asia Pacific. The firm is headquartered in Cambridge, Massachusetts, Cambridge, MA with global offices in Amsterdam, London, New Delhi, New York City, New York, NY, Norwalk, Connecticut, Norwalk, CT, San Francisco, Singapore, Stockholm, and Sydney. History and Key Milestones * Forrester was founded in July 1983 by George Forrester Colony in Cambridge, Massachusetts, Cambridge, MA. * In January 2019, Forrester completed thacquisition of SiriusDecisions a business-to-business research and advisory firm, for $245 million in cash. This acquisition expanded Forrester’s capabilities in B2B marketing, sales, and product alignment, integrating SiriusDecisions’ methodologies, including the Demand Waterfall framework. Leadership * George F. Colony, chairman of the board and CEO. References External links * {{official website, http://www.forrester.com India to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hype Cycle
The Gartner hype cycle is a graphical presentation developed, used and branded by the American research and advisory firm Gartner to represent the maturity, adoption, and social application of specific technologies. The hype cycle framework was introduced in 1995 by Gartner analyst Jackie Fenn to provide a graphical and conceptual presentation of the maturity of emerging technologies through five phases. History Gartner's hype cycle framework was introduced in 1995 by analyst Jackie Fenn, who had joined the firm the year before. In her research reports, Fenn identified common patterns related to the maturity of emerging technologies. Fenn referred to this familiar progression as a "hype cycle" and created a graph depicting its ups and downs with each distinct stage given a title, starting with Technology trigger and ending with Plateau of productivity. The chart was included in a one-off research report, but it was popular with other Gartner analysts and clients and the "Hype Cyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gartner Group
Gartner, Inc. is an American research and advisory firm focusing on business and technology topics. Gartner provides its products and services through research reports, conferences, and consulting. Its clients include large corporations, government agencies, technology companies, and investment firms. Operations Gartner is a research and advisory firm with three business segments: research, conferences, and consulting. As of December 2024, Gartner has over 21,000 employees globally and operates in 90 countries and territories. It is headquartered in Stamford, Connecticut. Gene A. Hall is the chief executive officer. Gartner is a publicly traded company listed on the S&P 500. History 1980s Gideon Gartner and David Stein founded Gartner, Inc. in 1979 to provide IT industry research and analysis to businesses buying and selling computer hardware. Gideon Gartner had previously worked at IBM, and his new firm specialized in information about IBM and its products. Gartner's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
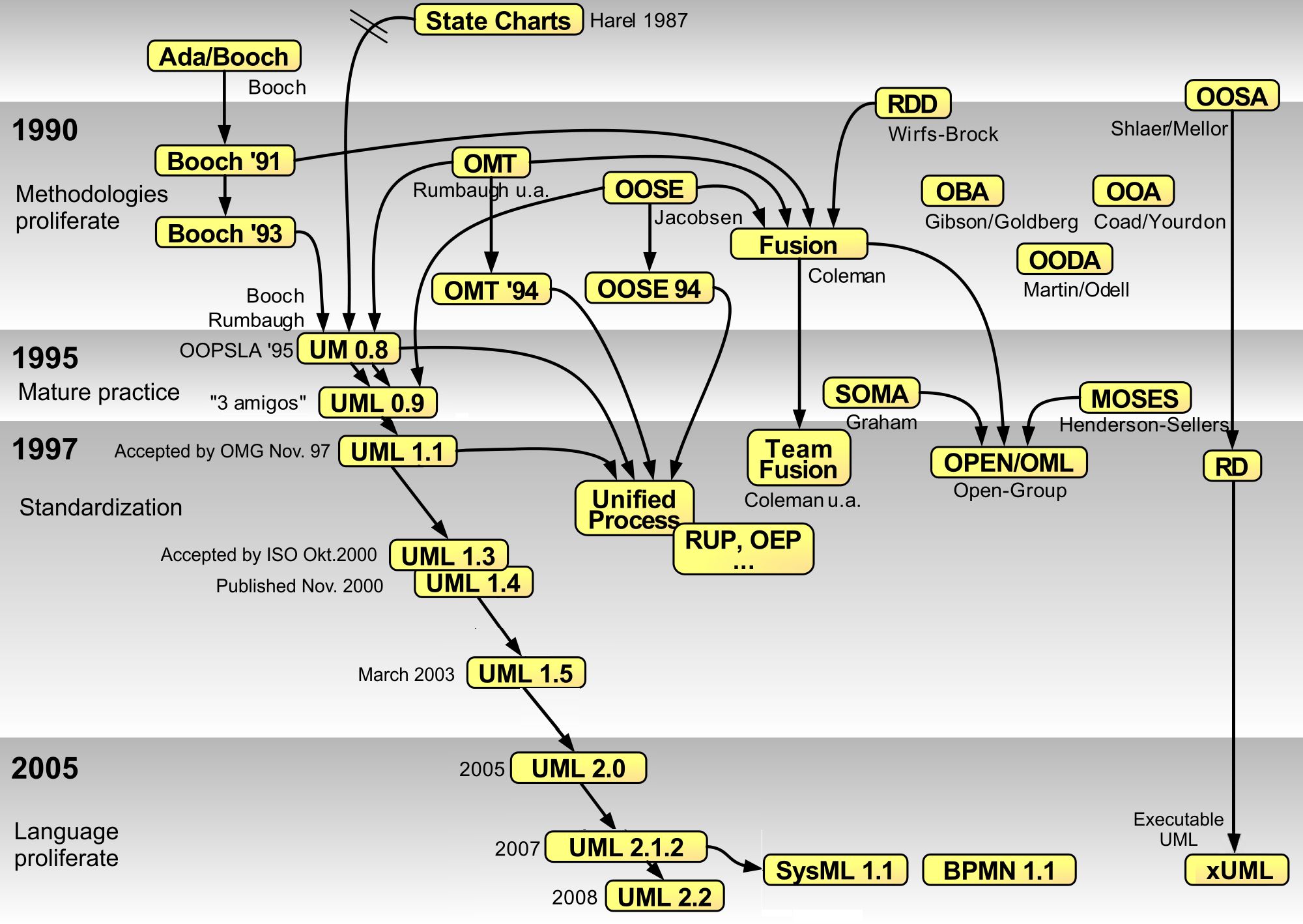
Shlaer–Mellor Method
The Shlaer–Mellor method, also known as object-oriented systems analysis (OOSA) or object-oriented analysis (OOA) is an object-oriented software development methodology introduced by Sally Shlaer and Stephen Mellor in 1988. The method makes the documented analysis so precise that it is possible to implement the analysis model directly by translation to the target architecture, rather than by elaborating model changes through a series of more platform-specific models. In the new millennium the Shlaer–Mellor method has migrated to the UML notation, becoming Executable UML. Overview The Shlaer–Mellor method is one of a number of software development methodologies which arrived in the late 1980s. Most familiar were object-oriented analysis and design (OOAD) by Grady Booch, object modeling technique (OMT) by James Rumbaugh, object-oriented software engineering by Ivar Jacobson and object-oriented analysis (OOA) by Shlaer and Mellor. These methods had adopted a new object-orie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The early 1980s and home computers, rise of personal computers through software like Windows, and the company has since expanded to Internet services, cloud computing, video gaming and other fields. Microsoft is the List of the largest software companies, largest software maker, one of the Trillion-dollar company, most valuable public U.S. companies, and one of the List of most valuable brands, most valuable brands globally. Microsoft was founded by Bill Gates and Paul Allen to develop and sell BASIC interpreters for the Altair 8800. It rose to dominate the personal computer operating system market with MS-DOS in the mid-1980s, followed by Windows. During the 41 years from 1980 to 2021 Microsoft released 9 versions of MS-DOS with a median frequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java EE
Jakarta EE, formerly Java Platform, Enterprise Edition (Java EE) and Java 2 Platform, Enterprise Edition (J2EE), is a set of specifications, extending Java SE with specifications for enterprise features such as distributed computing and web services. Jakarta EE applications are run on reference runtimes, which can be microservices or application servers, which handle transactions, security, scalability, concurrency and management of the components they are deploying. Jakarta EE is defined by its specification. The specification defines APIs (application programming interface) and their interactions. As with other Java Community Process specifications, providers must meet certain conformance requirements in order to declare their products as ''Jakarta EE compliant''. Examples of contexts in which Jakarta EE referencing runtimes are used are: e-commerce, accounting, banking information systems. History The platform created by Sun Microsystems was known as ''Java 2 Platform, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reference Architecture
A reference architecture in the field of software architecture or enterprise architecture provides a template solution for an architecture for a particular domain. It also provides a common vocabulary with which to discuss implementations, often with the aim to stress commonality. A software reference architecture is a software architecture where the structures and respective elements and relations provide templates for concrete architectures in a particular domain or in a family of software systems. An implementation of a reference architecture is called a framework or an application platform. A reference architecture often consists of a list of functions and some indication of their interfaces (or APIs) and interactions with each other and with functions located outside of the scope of the reference architecture. Reference architectures can be defined at different levels of abstraction. A highly abstract one might show different pieces of equipment on a communications network ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |