|
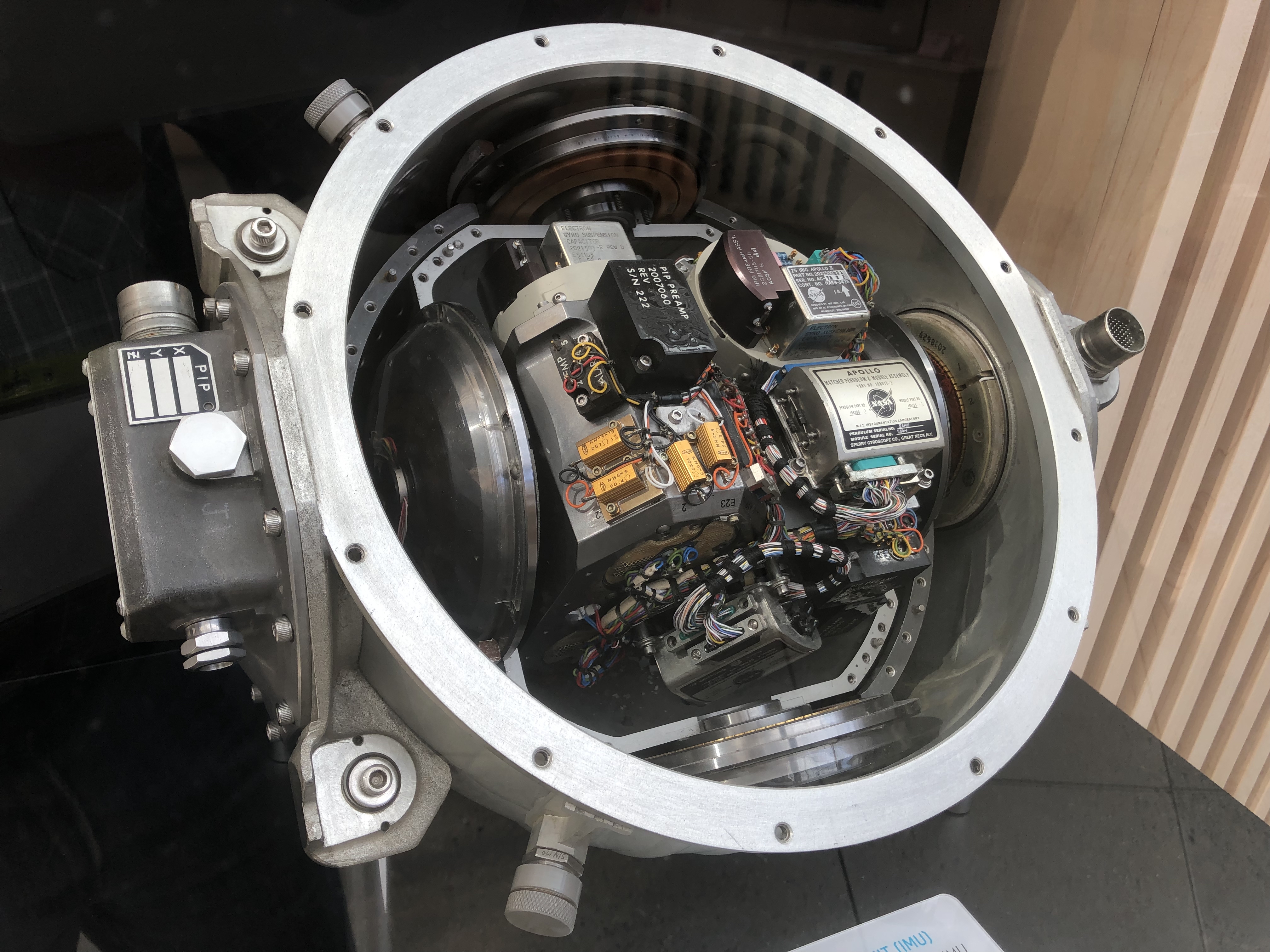
Miniature Inertial Measurement Unit
Miniature inertial measurement unit (MIMU) is an inertial measurement unit (IMU) developed and built by Honeywell International to control and stabilize spacecraft during mission operations. MIMUs can also be configured to perform as an inertial reference unit (IRU). MIMUs have been flown on GEO, Low Earth orbit (LEO), planetary missions and deep-space-probe applications. Missions Geostationary (GEO) missions *Spacebus Low-Earth orbiting (LEO) Missions *Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) Planetary missions *Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter – launched in 2005 on a mission to study the planet Mars *STEREO – launched in 2006 on a mission to study the Sun *Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter – launched in 2009 on a mission to study the Moon Deep-space-probe missions *New Horizons – launched in 2006 on a mission to study the planet Pluto Notes and references External links Images of Miniature Inertial Measurement Unit (MIMU) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inertial Measurement Unit
An inertial measurement unit (IMU) is an electronic device that measures and reports a body's specific force, angular rate, and sometimes the orientation of the body, using a combination of accelerometers, gyroscopes, and sometimes magnetometers. When the magnetometer is included, IMUs are referred to as IMMUs. IMUs are typically used to maneuver modern vehicles including motorcycles, missiles, aircraft (an attitude and heading reference system), including unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), among many others, and spacecraft, including satellites and landers. Recent developments allow for the production of IMU-enabled GPS devices. An IMU allows a GPS receiver to work when GPS-signals are unavailable, such as in tunnels, inside buildings, or when electronic interference is present. Operational principles An inertial measurement unit works by detecting linear acceleration using one or more accelerometers and rotational rate using one or more gyroscopes. Some also include a magnetom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honeywell International
Honeywell International Inc. is an American publicly traded, multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Charlotte, North Carolina. It primarily operates in four areas of business: aerospace, building technologies, performance materials and technologies (PMT), and safety and productivity solutions (SPS). Honeywell is a Fortune 100 company, ranked 94th in 2021. In 2021 the corporation had a global workforce of approximately 99,000 employees, down from 113,000 in 2019. The current chairman and chief executive officer (CEO) is Darius Adamczyk. The corporation's current name, Honeywell International Inc., is a product of the merger of Honeywell Inc. and AlliedSignal in 1999. The corporation headquarters were consolidated with AlliedSignal's headquarters in Morristown, New Jersey; however, the combined company chose the name "Honeywell" because of the considerable brand recognition. Honeywell was a component of the Dow Jones Industrial Average index from 1999 to 2008. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, planetary exploration, and transportation of humans and cargo. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle (carrier rocket). On a sub-orbital spaceflight, a space vehicle enters space and then returns to the surface without having gained sufficient energy or velocity to make a full Earth orbit. For orbital spaceflights, spacecraft enter closed orbits around the Earth or around other celestial bodies. Spacecraft used for human spaceflight carry people on board as crew or passengers from start or on orbit (space stations) only, whereas those used for robotic space missions operate either autonomously or telerobotically. Robotic spacecraft used to support scientific re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inertial Reference Unit
An inertial reference unit (IRU) is a type of inertial sensor which uses gyroscopes (electromechanical, ring laser gyro or MEMS) and accelerometers (electromechanical or MEMS) to determine a moving aircraft’s or spacecraft’s change in rotational attitude (angular orientation relative to some reference frame) and translational position (typically latitude, longitude and altitude) over a period of time. In other words, an IRU allows a device, whether airborne or submarine, to travel from one point to another without reference to external information. Another name often used interchangeably with IRU is Inertial Measurement Unit. The two basic classes of IRUs/IMUs are "gimballed" and "strapdown". The older, larger gimballed systems have become less prevalent over the years as the performance of newer, smaller strapdown systems has improved greatly via the use of solid-state sensors and advanced real-time computer algorithms. Gimballed systems are still used in some high-precision ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Earth Orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with a period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, with an altitude never more than about one-third of the radius of Earth. The term ''LEO region'' is also used for the area of space below an altitude of (about one-third of Earth's radius). Objects in orbits that pass through this zone, even if they have an apogee further out or are sub-orbital, are carefully tracked since they present a collision risk to the many LEO satellites. All crewed space stations to date have been within LEO. From 1968 to 1972, the Apollo program's lunar missions sent humans beyond LEO. Since the end of the Apollo program, no human spaceflights have been beyond LEO. Defining characteristics A wide variety of sources define LEO in terms of altitude. The altitude of an object in an elliptic orbit can vary significantly along the orbit. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacebus
Spacebus is a satellite bus produced at the Cannes Mandelieu Space Center in France by Thales Alenia Space. Spacebuses are typically used for geostationary communications satellites, and seventy-four have been launched since development started in the 1980s. Spacebus was originally produced by Aérospatiale and later passed to Alcatel Alenia Space. In 2006, it was sold to Thales Group as Thales Alenia Space. The first Spacebus satellite, Arabsat-1A, was launched in 1985. Since then, seventy-four have been launched, with one more completed, and six outstanding orders. The launch of the 50th Spacebus satellite, Star One C1, occurred in November 2007.Christian Lardier, « Ariane-5 : un tir de l'industrie européenne – le 50e Spacebus », dans ''Air & Cosmos'', N° 2100, du 16 novembre 2007 It was a Spacebus 3000B3, launched by an Ariane 5 rocket flying from the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana. Several variants have been built: the early Spacebus 100 and Spacebus 300; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defense Meteorological Satellite Program
The Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) monitors meteorological, oceanographic, and solar-terrestrial physics for the United States Department of Defense. The program is managed by the United States Space Force with on-orbit operations provided by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). The (originally classified) mission of the satellites was revealed in March 1973. They provide cloud cover imagery from polar orbits that are Sun-synchronous at nominal altitude of . History During the 1960s, one of the most important projects that the United States civil space program was involved in dealt with meteorology and weather forecasting. Unbeknownst to many, the U.S. military services were also starting up a weather satellite program. This program, the DMSP, would relay important weather and climate data to the military for more effective operations. From the onset of the DMSP program, knowledge of its existence was limited to "need-to-know" person ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' (MRO) is a spacecraft designed to study the geology and climate of Mars, provide reconnaissance of future landing sites, and relay data from surface missions back to Earth. It was launched on August 12, 2005, and reached Mars on March 10, 2006. In November 2006, after five months of aerobraking, it entered its final science orbit and began its primary science phase. The cost to develop and operate MRO through the end of its prime mission in 2010 was . The spacecraft continues to operate at Mars, far beyond its intended design life. Due to its critical role as a high-speed data-relay for ground missions, NASA intends to continue the mission as long as possible, at least through the late 2020s. Pre-launch After the twin failures of the ''Mars Climate Orbiter'' and the Mars Polar Lander missions in 1999, NASA reorganized and replanned its Mars Exploration Program. In October 2000, NASA announced its reformulated Mars plans, which reduced the numb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planet
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a young protostar orbited by a protoplanetary disk. Planets grow in this disk by the gradual accumulation of material driven by gravity, a process called accretion. The Solar System has at least eight planets: the terrestrial planets Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars, and the giant planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. These planets each rotate around an axis tilted with respect to its orbital pole. All of them possess an atmosphere, although that of Mercury is tenuous, and some share such features as ice caps, seasons, volcanism, hurricanes, tectonics, and even hydrology. Apart from Venus and Mars, the Solar System planets generate magnetic fields, and all except Venus and Mercury have natural satellites. The giant planets bear plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury (planet), Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Mars (mythology), Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin atmosphere (less than 1% that of Earth's), and has a crust primarily composed of elements similar to Earth's crust, as well as a core made of iron and nickel. Mars has surface features such as impact craters, valleys, dunes and polar ice caps. It has two small and irregularly shaped moons, Phobos (moon), Phobos and Deimos (moon), Deimos. Some of the most notable surface features on Mars include Olympus Mons, the largest volcano and List of tallest mountains in the Solar System, highest known mountain in the Solar System and Valles Marineris, one of the largest canyons in the Solar System. The North Polar Basin (Mars), Borealis basin in the Northern Hemisphere covers approximately 40% of the planet and may be a la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STEREO
Stereophonic sound, or more commonly stereo, is a method of sound reproduction that recreates a multi-directional, 3-dimensional audible perspective. This is usually achieved by using two independent audio channels through a configuration of two loudspeaker A loudspeaker (commonly referred to as a speaker or speaker driver) is an electroacoustic transducer that converts an electrical audio signal into a corresponding sound. A ''speaker system'', also often simply referred to as a "speaker" or " ...s (or stereo headphones) in such a way as to create the impression of sound heard from various directions, as in natural hearing. Because the multi-dimensional perspective is the crucial aspect, the term ''stereophonic'' also applies to systems with more than two channels or speakers such as quadraphonic and surround sound. Binaural recording, Binaural sound systems are also ''stereophonic''. Stereo sound has been in common use since the 1970s in entertainment media such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |