|
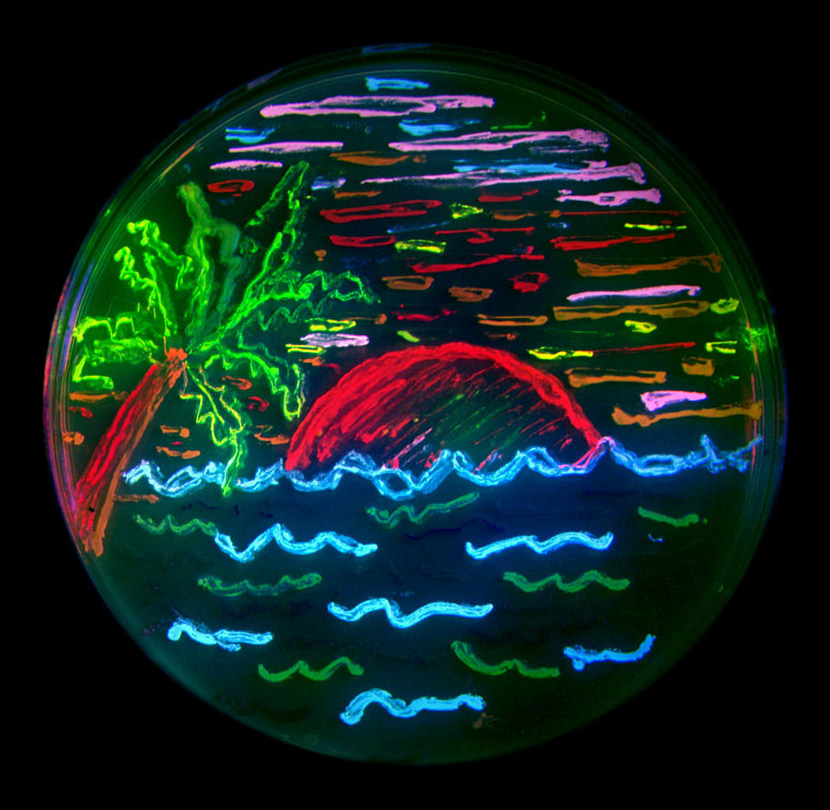
Microbial Art
Microbial art, agar art, or germ art is artwork created by culturing microorganisms in certain patterns. The microbes used can be bacteria, yeast fungi, or less commonly, protists. The microbes can be chosen for their natural colours, or can be engineered to express fluorescent proteins and viewed under ultraviolet light to make them fluoresce in colour. Methods Agar plates are used as a canvas, while pigmented or fluorescent bacteria and yeasts represent the paint. In order to preserve a piece of microbial art after a sufficient incubation, the microbe culture is sealed with epoxy. Microbe species can be chosen for their natural colours to form a palette for the artwork. Suitable species of bacteria (with their colours) include ''Bacillus subtilis'' (cream to brown), ''Chromobacterium violaceum'' (violet), ''Escherichia coli'' (colourless), '' Micrococcus luteus'' (yellow), ''Micrococcus roseus'' (pink), ''Proteus mirabilis'', ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' (brown), ''Pseudomonas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
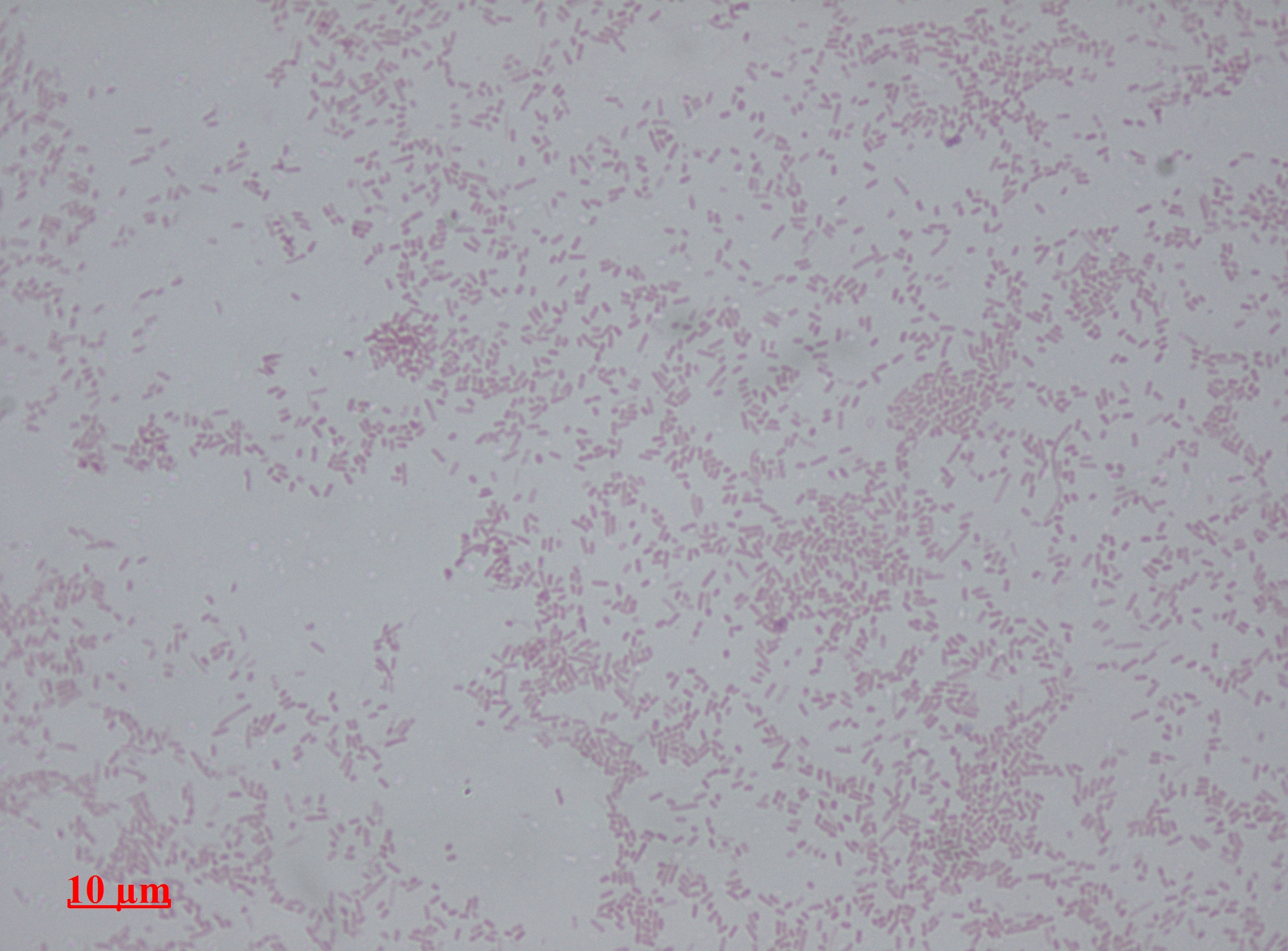
Proteus Mirabilis
''Proteus mirabilis'' is a Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium. It shows swarming motility and urease activity. ''P. mirabilis'' causes 90% of all ''Proteus'' infections in humans. It is widely distributed in soil and water. ''Proteus mirabilis'' can migrate across the surface of solid media or devices using a type of cooperative group motility called swarming. ''Proteus mirabilis'' is most frequently associated with infections of the urinary tract, especially in complicated or catheter-associated urinary tract infections. Diagnosis An alkaline urine sample is a possible sign of ''P. mirabilis''. It can be diagnosed in the lab due to characteristic swarming motility, and inability to metabolize lactose (on a MacConkey agar plate, for example). Also ''P. mirabilis'' produces a very distinct fishy odor. Disease This rod-shaped bacterium has the ability to produce high levels of urease, which hydrolyzes urea to ammonia (NH3), so makes the urine more al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspergillus Ochraceus
''Aspergillus ochraceus'' is a mold species in the genus '' Aspergillus'' known to produce the toxin ochratoxin A, one of the most abundant food-contaminating mycotoxins, and citrinin. It also produces the dihydroisocoumarin mellein. It is a filamentous fungus in nature and has characteristic biseriate conidiophores. Traditionally a soil fungus, has now began to adapt to varied ecological niches, like agricultural commodities, farmed animal and marine species. In humans and animals the consumption of this fungus produces chronic neurotoxic, immunosuppressive, genotoxic, carcinogenic and teratogenic effects. Its airborne spores are one of the potential causes of asthma in children and lung diseases in humans. The pig and chicken populations in the farms are the most affected by this fungus and its mycotoxins. Certain fungicides like mancozeb, copper oxychloride, and sulfur have inhibitory effects on the growth of this fungus and its mycotoxin producing capacities. History and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspergillus Flavus
''Aspergillus flavus'' is a saprotrophic and pathogenic fungus with a cosmopolitan distribution. It is best known for its colonization of cereal grains, legumes, and tree nuts. Postharvest rot typically develops during harvest, storage, and/or transit. Its specific name '' flavus'' derives from the Latin meaning yellow, a reference to the frequently observed colour of the spores. ''A. flavus'' infections can occur while hosts are still in the field (preharvest), but often show no symptoms (dormancy) until postharvest storage or transport. In addition to causing preharvest and postharvest infections, many strains produce significant quantities of toxic compounds known as mycotoxins, which, when consumed, are toxic to mammals. ''A. flavus'' is also an opportunistic human and animal pathogen, causing aspergillosis in immunocompromised individuals. Hosts ''Aspergillus flavus'' is found globally as a saprophyte in soils and causes disease on many important agriculture crops. Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saccharomyces Cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungus microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have been originally isolated from the skin of grapes. It is one of the most intensively studied eukaryotic model organisms in molecular and cell biology, much like ''Escherichia coli'' as the model bacterium. It is the microorganism behind the most common type of fermentation. ''S. cerevisiae'' cells are round to ovoid, 5–10 μm in diameter. It reproduces by budding. Many proteins important in human biology were first discovered by studying their homologs in yeast; these proteins include cell cycle proteins, signaling proteins, and protein-processing enzymes. ''S. cerevisiae'' is currently the only yeast cell known to have Berkeley bodies present, which are involved in particular secretory pathways. Antibodies against ''S. cerevis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus (plural, : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of Eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and Mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a Kingdom (biology), kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of motility, mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitute 1% of all described fungal species. Yeasts are unicellular organisms that evolved from multicellular ancestors, with some species having the ability to develop multicellular characteristics by forming strings of connected budding cells known as pseudohyphae or false hyphae. Yeast sizes vary greatly, depending on species and environment, typically measuring 3–4 µm in diameter, although some yeasts can grow to 40 µm in size. Most yeasts reproduce asexually by mitosis, and many do so by the asymmetric division process known as budding. With their single-celled growth habit, yeasts can be contrasted with molds, which grow hyphae. Fungal species that can take both forms (depending on temperature or other conditions) are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
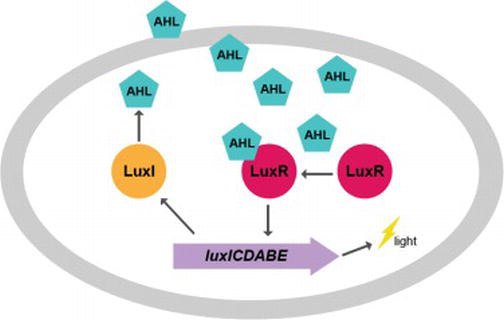
Bioluminescent
Bioluminescence is the production and emission of light by living organisms. It is a form of chemiluminescence. Bioluminescence occurs widely in marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some fungi, microorganisms including some bioluminescent bacteria, and terrestrial arthropods such as fireflies. In some animals, the light is bacteriogenic, produced by symbiotic bacteria such as those from the genus ''Vibrio''; in others, it is autogenic, produced by the animals themselves. In a general sense, the principal chemical reaction in bioluminescence involves a light-emitting molecule and an enzyme, generally called luciferin and luciferase, respectively. Because these are generic names, luciferins and luciferases are often distinguished by the species or group, e.g. firefly luciferin. In all characterized cases, the enzyme catalyzes the oxidation of the luciferin. In some species, the luciferase requires other cofactors, such as calcium or magnesium ions, and some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibrio Fischeri
''Aliivibrio fischeri'' (also called ''Vibrio fischeri'') is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium found globally in marine environments. This species has bioluminescent properties, and is found predominantly in symbiosis with various marine animals, such as the Hawaiian bobtail squid. It is heterotrophic, oxidase-positive, and motile by means of a single polar flagella. Free-living ''A. fischeri'' cells survive on decaying organic matter. The bacterium is a key research organism for examination of microbial bioluminescence, quorum sensing, and bacterial-animal symbiosis. It is named after Bernhard Fischer, a German microbiologist. Ribosomal RNA comparison led to the reclassification of this species from genus '' Vibrio'' to the newly created '' Aliivibrio'' in 2007. However, the name change is not generally accepted by most researchers, who still publish ''Vibrio fischeri'' (see Google Scholar for 2018-2019). Genome The genome for ''A. fischeri'' was completely sequence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
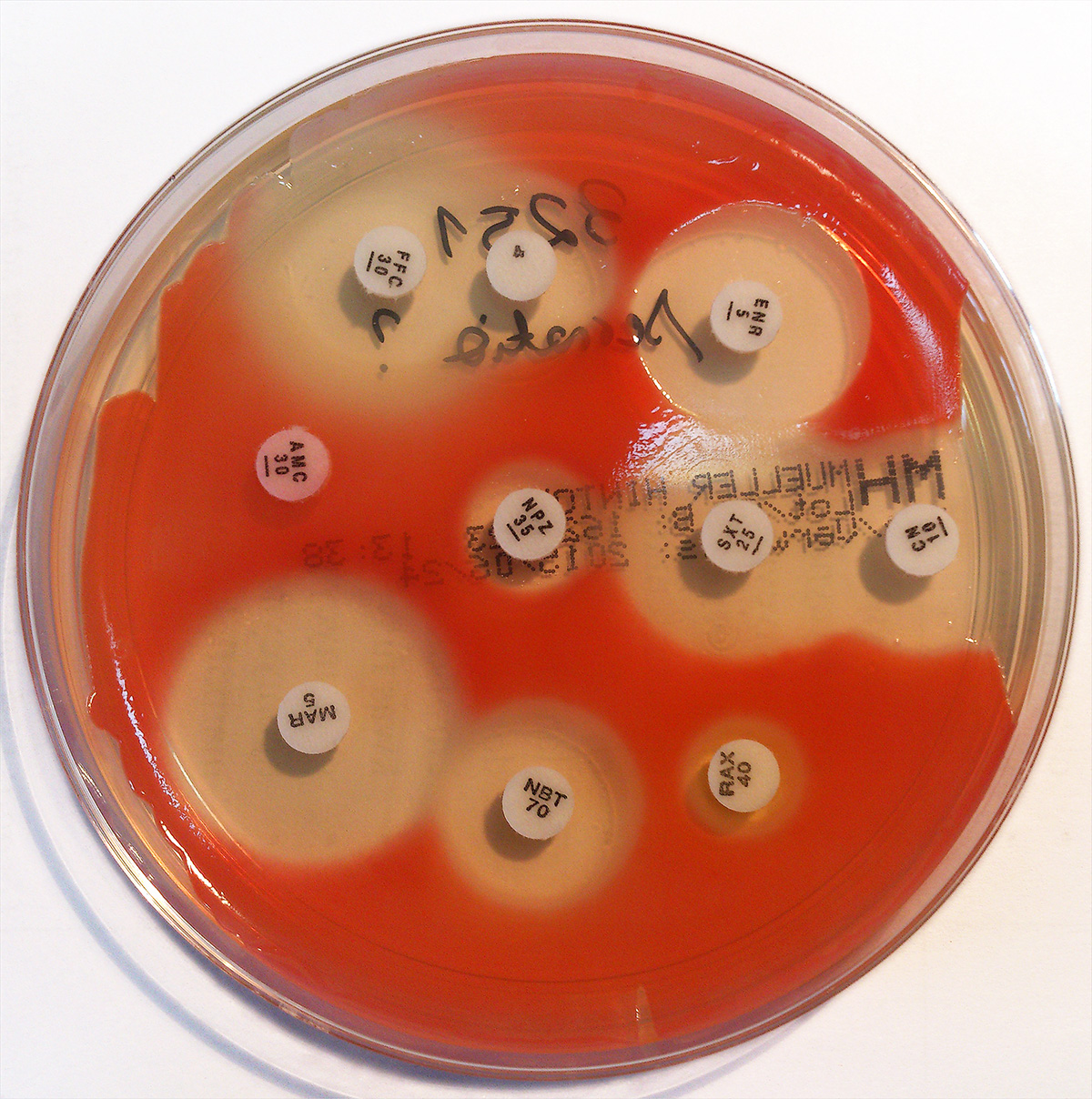
Staphylococcus Aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive for catalase and nitrate reduction and is a facultative anaerobe that can grow without the need for oxygen. Although ''S. aureus'' usually acts as a commensal of the human microbiota, it can also become an opportunistic pathogen, being a common cause of skin infections including abscesses, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, and food poisoning. Pathogenic strains often promote infections by producing virulence factors such as potent protein toxins, and the expression of a cell-surface protein that binds and inactivates antibodies. ''S. aureus'' is one of the leading pathogens for deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance and the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, such as methicillin-resistant ''S. aureu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serratia Marcescens
''Serratia marcescens'' () is a species of rod-shaped, Gram-negative bacteria in the family Yersiniaceae. It is a facultative anaerobe and an opportunistic pathogen in humans. It was discovered in 1819 by Bartolomeo Bizio in Padua, Italy.Serratia marcescens. (2011, April). Retrieved from https://microbewiki.kenyon.edu/index.php/Serratia_marcescens ''S. marcescens'' is commonly involved in hospital-acquired infections (HAIs), also called nosocomial infections, particularly catheter-associated bacteremia, urinary tract infections, and wound infections, and is responsible for 1.4% of HAI cases in the United States. It is commonly found in the respiratory and urinary tracts of hospitalized adults and in the gastrointestinal systems of children. Due to its abundant presence in the environment, and its preference for damp conditions, ''S. marcescens'' is commonly found growing in bathrooms (especially on tile grout, shower corners, toilet water lines, and basins), where it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyoverdine
Pyoverdines (alternatively, and less commonly, spelled as pyoverdins) are fluorescent siderophores produced by certain pseudomonads. Pyoverdines are important virulence factors, and are required for pathogenesis in many biological models of infection. Their contributions to bacterial pathogenesis include providing a crucial nutrient (i.e., iron), regulation of other virulence factors (including exotoxin A and the protease PrpL), supporting the formation of biofilms, and are increasingly recognized for having toxicity themselves. Pyoverdines have also been investigated as "Trojan Horse" molecules for the delivery of antimicrobials to otherwise resistant bacterial strains, as chelators that can be used for bioremediation of heavy metals, and as fluorescent reporters used to assay for the presence of iron and potentially other metals. Due to their bridging the gaps between pathogenicity, iron metabolism, and fluorescence, pyoverdines have piqued the curiosity of scientists around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |