|
MiR-33
miR-33 is a family of microRNA precursors, which are processed by the Dicer enzyme to give mature microRNAs. miR-33 is found in several animal species, including humans. In some species there is a single member of this family which gives the mature product mir-33. In humans there are two members of this family called mir-33a and mir-33b, which are located in intronic regions within two gene, protein-coding genes for Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBP-2 and SREBP-1) respectively. Function miR-33 plays a role in lipid metabolism; it downregulates a number of ABC transporters, including ABCA1 and ABCG1, which in turn regulate cholesterol and High-density lipoprotein, HDL generation. Further related roles of miR-33 have been proposed in fatty acid degradation and in macrophage response to low-density lipoprotein. It has been suggested that miR-33a and miR-33b regulates genes Involved in fatty acid metabolism and insulin signalling. Potential binding sites for mir-33 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Structure
Protein secondary structure is the three dimensional conformational isomerism, form of ''local segments'' of proteins. The two most common Protein structure#Secondary structure, secondary structural elements are alpha helix, alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein protein folding, folds into its three dimensional protein tertiary structure, tertiary structure. Secondary structure is formally defined by the pattern of hydrogen bonds between the Amine, amino hydrogen and carboxyl oxygen atoms in the peptide backbone chain, backbone. Secondary structure may alternatively be defined based on the regular pattern of backbone Dihedral angle#Dihedral angles of proteins, dihedral angles in a particular region of the Ramachandran plot regardless of whether it has the correct hydrogen bonds. The concept of secondary structure was first introduced by Kaj Ulrik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell membranes. When chemically isolated, it is a yellowish crystalline solid. Cholesterol also serves as a precursor for the biosynthesis of steroid hormones, bile acid and vitamin D. Cholesterol is the principal sterol synthesized by all animals. In vertebrates, hepatic cells typically produce the greatest amounts. It is absent among prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), although there are some exceptions, such as '' Mycoplasma'', which require cholesterol for growth. François Poulletier de la Salle first identified cholesterol in solid form in gallstones in 1769. However, it was not until 1815 that chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul named the compound "cholesterine". Etymology The word "cholesterol" comes from the Ancient Greek ''chole-'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MiR-122
miR-122 is a miRNA that is conserved among vertebrate species. miR-122 is not present in invertebrates, and no close paralogs of miR-122 have been detected. miR-122 is highly expressed in the liver, where it has been implicated as a regulator of fatty-acid metabolism in mouse studies. Reduced miR-122 levels are associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. miR-122 also plays an important positive role in the regulation of hepatitis C virus replication. Expression and regulation miR-122 was originally identified by cloning of tissue-specific microRNAs in mouse, where its expression is restricted to the liver. The liver-specific expression of miR-122 is conserved in zebrafish. miR-122 expression increases during embryogenesis until it constitutes 72% of total miRNA in adult human liver, making it one of the most highly expressed miRNAs in any tissue. In humans, miR-122 is encoded at a single genomic locus in chromosome 18. The primary miR-122 transcript (pri-miR-122) is a long non-co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematopoietic Stem Cell
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are the stem cells that give rise to other blood cells. This process is called haematopoiesis. In vertebrates, the very first definitive HSCs arise from the ventral endothelial wall of the embryonic aorta within the (midgestational) aorta-gonad-mesonephros region, through a process known as endothelial-to-hematopoietic transition. In adults, haematopoiesis occurs in the red bone marrow, in the core of most bones. The red bone marrow is derived from the layer of the embryo called the mesoderm. Haematopoiesis is the process by which all mature blood cells are produced. It must balance enormous production needs (the average person produces more than 500 billion blood cells every day) with the need to regulate the number of each blood cell type in the circulation. In vertebrates, the vast majority of hematopoiesis occurs in the bone marrow and is derived from a limited number of hematopoietic stem cells that are multipotent and capable of extensive se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses between 50 and 70 billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For an average human child between eight and fourteen years old, approximately twenty to thirty billion cells die per day. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the digits undergo apoptosis. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis produces cell fragments called apoptotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CDNA
In genetics, complementary DNA (cDNA) is DNA synthesized from a single-stranded RNA (e.g., messenger RNA (mRNA) or microRNA (miRNA)) template in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme reverse transcriptase. cDNA is often used to express a specific protein in a cell that does not normally express that protein (i.e., heterologous expression), or to sequence or quantify mRNA molecules using DNA based methods (qPCR, RNA-seq). cDNA that codes for a specific protein can be transferred to a recipient cell for expression, often bacterial or yeast expression systems. cDNA is also generated to analyze transcriptomic profiles in bulk tissue, single cells, or single nuclei in assays such as microarrays, qPCR, and RNA-seq. cDNA is also produced naturally by retroviruses (such as HIV-1, HIV-2, simian immunodeficiency virus, etc.) and then integrated into the host's genome, where it creates a provirus. The term ''cDNA'' is also used, typically in a bioinformatics context, to refer to an mR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-density Lipoprotein
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoprotein that transport all fat molecules around the body in extracellular water. These groups, from least dense to most dense, are chylomicrons (aka ULDL by the overall density naming convention), very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL), low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). LDL delivers fat molecules to cells. LDL is involved in atherosclerosis, a process in which it is oxidized within the walls of arteries. Overview Lipoproteins transfer lipids (fats) around the body in the extracellular fluid, making fats available to body cells for receptor-mediated endocytosis. Lipoproteins are complex particles composed of multiple proteins, typically 80–100 proteins per particle (organized by a single apolipoprotein B for LDL and the larger particles). A single LDL particle is about 220–275 angstroms in diameter, typically transporting 3,000 to 6,000 fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris, and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that are specific to healthy body cells on their surface. The process is called phagocytosis, which acts to defend the host against infection and injury. These large phagocytes are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They take various forms (with various names) throughout the body (e.g., histiocytes, Kupffer cells, alveolar macrophages, microglia, and others), but all are part of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Besides phagocytosis, they play a critical role in nonspecific defense (innate immunity) and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adaptive immunity) by recruiting other immune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
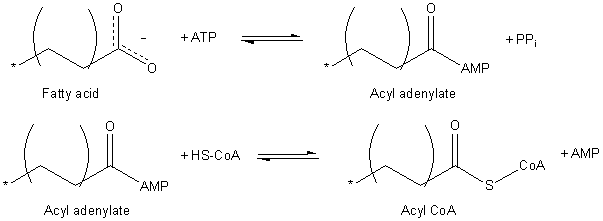
Fatty Acid Degradation
Fatty acid degradation is the process in which fatty acids are broken down into their metabolites, in the end generating acetyl-CoA, the entry molecule for the citric acid cycle, the main energy supply of living organisms, including bacteria and animals. It includes three major steps: * Lipolysis of and release from adipose tissue * Activation and transport into mitochondria * β-oxidation Lipolysis and release Initially in the process of degradation, fatty acids are stored in adipocytes. The breakdown of this fat is known as lipolysis. The products of lipolysis, free fatty acids, are released into the bloodstream and circulate throughout the body. During the breakdown of triacylglycerols into fatty acids, more than 75% of the fatty acids are converted back into triacylglycerol, a natural mechanism to conserve energy, even in cases of starvation and exercise. Activation and transport into mitochondria Fatty acids must be activated before they can be carried into the mitochondria, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-density Lipoprotein
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoproteins. Lipoproteins are complex particles composed of multiple proteins which transport all fat molecules (lipids) around the body within the water outside cells. They are typically composed of 80–100 proteins per particle (organized by one, two or three ApoA. HDL particles enlarge while circulating in the blood, aggregating more fat molecules) and transporting up to hundreds of fat molecules per particle. Overview Lipoproteins are divided into five subgroups, by density/size (an inverse relationship), which also correlates with function and incidence of cardiovascular events. Unlike the larger lipoprotein particles, which deliver fat molecules to cells, HDL particles remove fat molecules from cells. The lipids carried include cholesterol, phospholipids, and triglycerides, amounts of each are variable. Increasing concentrations of HDL particles are associated with decreasing accumulation of atherosclerosis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ABCG1
ATP-binding cassette sub-family G member 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ABCG1'' gene. It is a homolog of the well-known ''Drosophila'' gene ''white''. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the superfamily of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. ABC proteins transport various molecules across extra- and intra-cellular membranes. ABC genes are divided into seven distinct subfamilies (ABC1, MDR/TAP, MRP, ALD, OABP, GCN20, White). This protein is a member of the White subfamily ( subfamily G). It is involved in macrophage cholesterol and phospholipids transport, and may regulate cellular lipid homeostasis in other cell types. Several alternative splice variants have been identified. See also * ATP-binding cassette transporter The ATP-binding cassette transporters (ABC transporters) are a transport system superfamily that is one of the largest and possibly one of the oldest gene families. It is represented in all extant phyla, from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metazoa
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described—of which around 1 million are insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a bilaterally symmetric body plan. The Bilateria include the protostomes, containing animals such as nematodes, arthropods, flatworms, annelids and molluscs, and the deuterostomes, containing the echinoderms an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |