|
Methoxsalen
Methoxsalen, sold under the brand name Oxsoralen among others, is a medication used to treat psoriasis, eczema, vitiligo, and some cutaneous lymphomas in conjunction with exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UVA) light from lamps or sunlight. Methoxsalen modifies the way skin cells receive the UVA radiation, allegedly clearing up the disease. Levels of individual patient PUVA exposure were originally determined using the Fitzpatrick scale. The scale was developed after patients demonstrated symptoms of phototoxicity after oral ingestion of methoxsalen followed by PUVA therapy. Chemically, methoxsalen belongs to a class of organic natural molecules known as furanocoumarins. They consist of coumarin annulated with furan. It can also be injected and used topically. Natural sources In 1947, methoxsalen was isolated (under the name "ammoidin") from the plant ''Ammi majus'', bishop's weed. In 1970, Nielsen extracted 8-methoxypsoralen from four species of the genus '' Heracleum'' in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammi Majus
''Ammi majus'', commonly called bishop's flower, false bishop's weed, laceflower, bullwort, etc., is a member of the carrot family Apiaceae. The plant, which has white lace-like flower clusters, has a large distribution through Southern Europe, North Africa and West and Central Asia, though it is hypothesized to be native to the Nile River Valley. Nomenclature The plant is called by various common names: bishop's flower or bishop's weed (false bishop's weed); laceflower, lady's lace or false Queen Anne's lace; bullwort (large bullwort); white dill and greater ammi. It is known in Arabic as ''hirz al-shayateen'' () or ''khella/khilla shaitani'' (). The plant is also introduced into China, where it is called ''da a min qin'' ( zh, 大阿米芹) and cultivated in medicinal farms. Description ''Ammi majus'' is a herbaceous annual, or rather a biennial that behaves like an annual in cultivation. The lower leaves are 1-2-pinnate, upper leaves 2(-3)-pinnate with serrate lobes. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heracleum (plant)
''Heracleum'' is a genus of biennial and perennial herbs in the carrot family Apiaceae. They are found throughout the temperate northern hemisphere and in high mountains as far south as Ethiopia. Common names for the genus or its species include hogweed and cow parsnip. The genus name ''Heracleum'' was described by Carl Linnaeus in 1753. It derives from the Ancient Greek () "of Heracles", referring to the mythological hero. Species Many species of the genus ''Heracleum'' are similar in appearance. An outlier is ''H. mantegazzianum'', the large size of which is exceptional. Common species include: * ''Heracleum mantegazzianum'', giant hogweed, native to the western Caucasus region of Eurasia, a serious invasive species in many areas of Europe and North America * ''Heracleum sosnowskyi'', Sosnowsky's hogweed, native to the eastern Caucasus, a common weed throughout Europe and Asia * ''Heracleum persicum'', Persian hogweed, native to Iran, Iraq, and Turkey * ''Heracleum spho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Furanocoumarin
The furanocoumarins, or furocoumarins, are a class of organic chemical compounds produced by a variety of plants. Most of the plant species found to contain furanocoumarins belong to a handful of plant families. The families Apiaceae and Rutaceae include the largest numbers of plant species that contain furanocoumarins. The families Moraceae and Fabaceae include a few widely distributed plant species that contain furanocoumarins. Generally furanocoumarins are most abundant in plants that have flowered and in ripe seeds and fruits. (An exception is the common fig where furanocoumarins are found chiefly in the milky sap of the leaves and shoots but not the fruits. Cited in McGovern and Barkley 2000, section&nbsPhytophotodermatitis) During the early stages of plant growth, their presence is not easily detected. Structure The chemical structure of furanocoumarins consists of a furan ring fused with a coumarin. The furan ring may be fused in various ways producing several differen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Therapeutic Goods Administration
The Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) is the medicine and therapeutic regulatory agency of the Australian Government. As part of the Department of Health and Aged Care, the TGA regulates the quality, supply and advertising of medicines, pathology devices, medical devices, blood products and most other therapeutics. Any items that claim to have a therapeutic effect, are involved in the administration of medication, or are otherwise covered by the ''Therapeutic Goods Act 1989'', the ''Therapeutic Goods Regulations 1990'', or a ministerial order, must be approved by the TGA and registered in the Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods. Structure of the TGA and medical regulation in Australia In Australia, medical products are regulated by the TGA and, for controlled drugs such as cannabis, the Office of Drug Control (ODC). Together, the TGA and ODC form the Health Products Regulation Group within the Department of Health and Aged Care. The Health Products Regulation Group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heracleum Mantegazzianum
''Heracleum mantegazzianum'', commonly known as giant hogweed, is a monocarpic perennial herbaceous plant in the carrot family Apiaceae. ''H. mantegazzianum'' is also known as cartwheel-flower, giant cow parsley, giant cow parsnip, or hogsbane. In New Zealand, it is also sometimes called wild parsnip (not to be confused with ''Pastinaca sativa'') or wild rhubarb. Giant hogweed is native to the western Caucasus region of Eurasia. It was introduced to Britain as an ornamental plant in the 19th century, and has also spread to other areas in Western Europe, the United States, and Canada. Its close relatives, Sosnowsky's hogweed and Persian hogweed, have similarly spread to other parts of Europe. The sap of giant hogweed is phototoxic and causes phytophotodermatitis in humans, resulting in blisters and scars. These serious reactions are due to the furanocoumarin derivatives in the leaves, roots, stems, flowers, and seeds of the plant. Consequently, it is considered to be a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heracleum Sphondylium
''Heracleum sphondylium'', commonly known as hogweed, common hogweed or cow parsnip, is a herbaceous perennial or biennial plant, in the umbelliferous family Apiaceae that includes fennel, cow parsley, ground elder and giant hogweed. It is native to Europe and Asia. The common name eltrot may also be applied, but is not specific to this species. Umbelliferous plants are so named because of the umbrella-like arrangement of flowers they produce. The North American species '' Heracleum maximum'' (also called "cow parsnip") is sometimes included as a subspecies of ''H. sphondylium''. The plant provides a great deal of nectar for pollinators. It was rated in the top 10 for most nectar production (nectar per unit cover per year) in a UK plants survey conducted by the AgriLand project which is supported by the UK Insect Pollinators Initiative. Etymology The species name ''sphondylium'', meaning "vertebrate", refers to the shape of the segmented stem. It was described by Carl Linnae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bergapten
Bergapten (5-methoxypsoralen) is a naturally-occurring organic chemical compound produced by numerous plant species, especially from the carrot family Apiaceae and the citrus family Rutaceae. For example, bergapten has been extracted from 24 species of the genus '' Heracleum'' in the family Apiaceae. Cited by Mitchell and Rook (1979). In the family Rutaceae, various ''Citrus'' species contain significant amounts of bergapten, especially the bergamot orange, the micrantha, and certain varieties of lime and bitter orange. Bergapten belongs to a class of chemical compounds known as the furanocoumarins. In 1834, Kalbrunner isolated 5-methoxypsoralen from bergamot essential oil, hence the common name "bergapten". It was the first furanocoumarin to be isolated and identified. Toxicity Bergapten is a derivative of psoralen, the parent compound of a family of naturally-occurring organic compounds known as the linear furanocoumarins (so called since they exhibit a linear chemical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shikimate
Shikimic acid, more commonly known as its anionic form shikimate, is a cyclohexene, a cyclitol and a cyclohexanecarboxylic acid. It is an important biochemical metabolite in plants and microorganisms. Its name comes from the Japanese flower ''shikimi'' (, the Japanese star anise, ''Illicium anisatum''), from which it was first isolated in 1885 by Johan Fredrik Eykman. The elucidation of its structure was made nearly 50 years later. Biosynthesis Phosphoenolpyruvate and erythrose-4-phosphate condense to form 3-deoxy-D-arabinoheptulosonate-7-phosphate (DAHP), in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme DAHP synthase. DAHP is then transformed to 3-dehydroquinate (DHQ), in a reaction catalyzed by DHQ synthase. Although this reaction requires nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) as a cofactor, the enzymic mechanism regenerates it, resulting in the net use of no NAD. : DHQ is dehydrated to 3-dehydroshikimic acid by the enzyme 3-dehydroquinate dehydratase, which is reduced to shi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
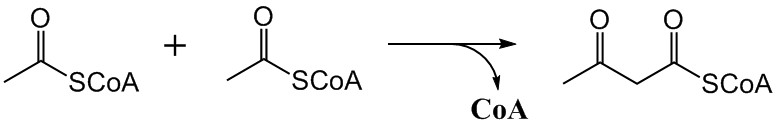
Mevalonate Pathway
The mevalonate pathway, also known as the isoprenoid pathway or HMG-CoA reductase pathway is an essential metabolic pathway present in eukaryotes, archaea, and some bacteria. The pathway produces two five-carbon building blocks called isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP), which are used to make isoprenoids, a diverse class of over 30,000 biomolecules such as cholesterol, vitamin K, coenzyme Q10, and all steroid hormones. The mevalonate pathway begins with acetyl-CoA and ends with the production of IPP and DMAPP. It is best known as the target of statins, a class of cholesterol lowering drugs. Statins inhibit HMG-CoA reductase within the mevalonate pathway. Upper mevalonate pathway The mevalonate pathway of eukaryotes, archaea, and eubacteria all begin the same way. The sole carbon feed stock of the pathway is acetyl-CoA. The first step condenses two acetyl-CoA molecules to yield acetoacetyl-CoA. This is followed by a second condensation to for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umbelliferone
Umbelliferone, also known as 7-hydroxycoumarin, hydrangine, skimmetine, and ''beta''-umbelliferone, is a natural product of the coumarin family. It absorbs ultraviolet light strongly at several wavelengths. There are some indications that this chemical is antimutagenic, it is used in sunscreens. Umbelliferone has been reported to have antioxidant properties. It is a yellowish-white crystalline solid that has a slight solubility in hot water, but high solubility in ethanol. Natural occurrences and name Umbelliferone's name is from the umbelliferae family of plants, and the plant family in turn was named for their umbrella-shaped inflorescences, each called an umbel. Umbelliferone occurs in many familiar plants from the Apiaceae (Umbelliferae) family such as carrot, coriander and garden angelica, as well as in plants from other families, such as the mouse-ear hawkweed (''Hieracium pilosella'', Asteraceae) or the bigleaf hydrangea (''Hydrangea macrophylla'', Hydrangeaceae, under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umbelliferone
Umbelliferone, also known as 7-hydroxycoumarin, hydrangine, skimmetine, and ''beta''-umbelliferone, is a natural product of the coumarin family. It absorbs ultraviolet light strongly at several wavelengths. There are some indications that this chemical is antimutagenic, it is used in sunscreens. Umbelliferone has been reported to have antioxidant properties. It is a yellowish-white crystalline solid that has a slight solubility in hot water, but high solubility in ethanol. Natural occurrences and name Umbelliferone's name is from the umbelliferae family of plants, and the plant family in turn was named for their umbrella-shaped inflorescences, each called an umbel. Umbelliferone occurs in many familiar plants from the Apiaceae (Umbelliferae) family such as carrot, coriander and garden angelica, as well as in plants from other families, such as the mouse-ear hawkweed (''Hieracium pilosella'', Asteraceae) or the bigleaf hydrangea (''Hydrangea macrophylla'', Hydrangeaceae, under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenylpropanoid
The phenylpropanoids are a diverse family of organic compounds that are synthesized by plants from the amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine. Their name is derived from the six-carbon, aromatic phenyl group and the three-carbon propene tail of coumaric acid, which is the central intermediate in phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. From 4-coumaroyl-CoA emanates the biosynthesis of myriad natural products including lignols (precursors to lignin and lignocellulose), flavonoids, isoflavonoids, coumarins, aurones, stilbenes, catechin, and phenylpropanoids. The coumaroyl component is produced from cinnamic acid. Phenylpropanoids are found throughout the plant kingdom, where they serve as essential components of a number of structural polymers, provide protection from ultraviolet light, defend against herbivores and pathogens, and also mediate plant-pollinator interactions as floral pigments and scent compounds. Hydroxycinnamic acids Phenylalanine is first converted to cinnamic aci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_I_(cropped).jpg)